标签:style blog http color java 使用 os strong
AOP介绍
在AOP联盟的官方网站里(http://aopalliance.sourceforge.net/)
AOP是一种能够增强多种已存在的中间件环境(such as J2EE)或者开发环境(e.g. Eclipse)功能的编程技术。
AOP 实现方式与相关项目
关于AOP在很多项目中都有实现,实现的方式也有不同,目前主要有三种处理方式:Proxy(代理), Interceptor(拦截器), bytecode translator(字节码翻译)。
AOP相关的项目有:
- ASM: a lightweight bytecode translator.
- AspectJ: an AO source-level weaver. New Language.
- AspectWerkz: an AO framework (bytecode-level dynamic weaver+configuration).
- BCEL: a bytecode translator.
- CGLIB: high-level API for class artifact manipulation and method interception.
- JAC: an AO middleware (bytecode-level dynamic weaver+configuration+aspects). Framework.
- Javassist: a bytecode translator with a high-level API.
- JBoss-AOP: interception and metadata-based AO framework.
- JMangler: a bytecode translator with a composition framework for translations.
- Nanning: an AO weaver (framework).
- Prose: an AO bytecode-level dynamic weaver (framework).
- ... and many others (email me to add a new one)
而在.Net平台下, PostSharp也是一个有名的AOP框架,它采用的方式与AspectJ类似,AspectJ是通过字节码织入方式,PostSharp是通过修改编译后的文件方式。
AOP分层架构
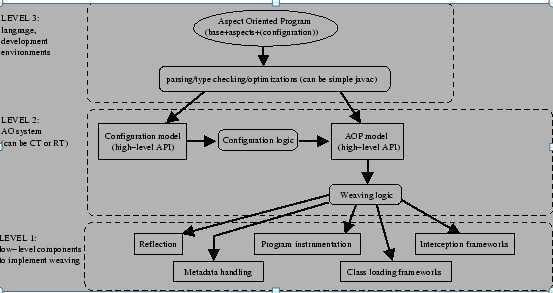
AOP分层架构中,从概念到实现,分为3个层次:
level 1: 是一种AOP框架的底层处理,是处理Aspect与Target的织入过程,处理方式有:反射、元数据处理、拦截器、代理等等。也就是说,上面提到的几种方式都可以用于
aspect织入到Target上。
level 2: 是AO(面向切面)系统的实现过程。可以在编译期,也可以在运行期。
level 3: 是最高层,这一层中,把面向切面的编程看作是:base + aspect + config。这一层是开发人员直接使用的。
base: 就是target,就是待增加的目标对象。
AOP要用到的技术说明
AOP并不是一门新的技术,而是在已有技术上实现的新功能。
在Level1层:
·反射:没有反射就没有各种框架,现在的AOP框架已有很多,上面已列出常用的。这些框架的底层,都使用到了反射技术。
·拦截器框架:拦截器框架也已有很多,Struts2中有,不是采用动态代理实现的。Java提供了一种标准的拦截器框架,是使用动态代理技术实现的。
·元数据处理:一般来说会和拦截器一起使用,允许扩展类(例如实现新接口)。
·类加载框架:或者通过拦截器框架织入、或者通过字节码织入,都是需要类加载框架的支持。
AOP标准接口
尽管各个AOP框架的实现有所不同,但又一些通用的东西。AOP联盟就把这些通用的东西制定成为AOP标准接口,在aopalliance.1.0.jar里。
这个jar包中的制定的接口很少,但却很重要:
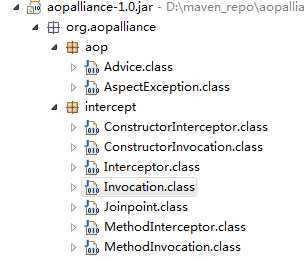
从之前的level 1的组件说明(技术说明)中,了解到:AOP在多处运用到了拦截器,因此AOP联盟也将拦截器封装进这个jar中。
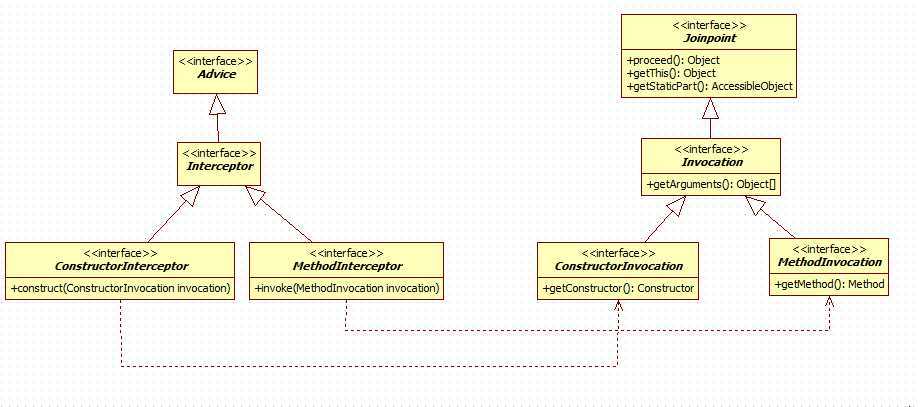
AOP的要义:在JoinPoint加入Advice。
Spring AOP:
AOP 面向切面编程。AOP是Spring的两大核心之一,在Spring中,AOP的典型应用是事务管理。
AOP中有很多概念需要了解:
看官方参考文档中的说明:
- Aspect: a modularization of a concern that cuts across multiple classes. Transaction management is a good example of a crosscutting concern in enterprise Java applications. In Spring AOP, aspects are implemented using regular classes (the schema-based approach) or regular classes annotated with the
@Aspect annotation (the @AspectJ style).
Aspect:切面,是AOP模块的核心,在Spring中,AOP以有规则的类或者注解完成。
Join point: a point during the execution of a program, such as the execution of a method or the handling of an exception. In Spring AOP, a join point always represents a method execution.
连接点,就是sayFoo,sayHello等实际要执行的方法。
- Advice: action taken by an aspect at a particular join point. Different types of advice include "around," "before" and "after" advice. (Advice types are discussed below.) Many AOP frameworks, including Spring, model an advice as an interceptor, maintaining a chain of interceptors around the join point.
建议就是在sayFoo前后执行的方法,例如之前的befor(),after();
- Pointcut: a predicate that matches join points. Advice is associated with a pointcut expression and runs at any join point matched by the pointcut (for example, the execution of a method with a certain name). The concept of join points as matched by pointcut expressions is central to AOP, and Spring uses the AspectJ pointcut expression language by default.
切点:就是指定在那些地方切入。切点是一个表达式,与这个表达式匹配的方法就是join point。例如表达式为:**.*.say*就是任意packget下任意class的sayXxx方法。方法名以say开头。这个表达式就是pointCut,匹配到的sayHello, sayFoo就是join Point。
- Introduction: declaring additional methods or fields on behalf of a type. Spring AOP allows you to introduce new interfaces (and a corresponding implementation) to any advised object. For example, you could use an introduction to make a bean implement an
IsModified interface, to simplify caching. (An introduction is known as an inter-type declaration in the AspectJ community.)
说明,就可以让一个被advised对象(target)实现某个接口。添加额外功能。
- Target object: object being advised by one or more aspects. Also referred to as the advised object. Since Spring AOP is implemented using runtime proxies, this object will always be a proxied object.
target,就是要被advised的对象(),也就是说他是被代理的对象。它就相当于上面例子中的FooImpl,HelloImpl对象。
- AOP proxy: an object created by the AOP framework in order to implement the aspect contracts (advise method executions and so on). In the Spring Framework, an AOP proxy will be a JDK dynamic proxy or a CGLIB proxy.
他是根据AOP代理有两种:一种是Java的动态代理,一种是CgLib代理。
- Weaving: linking aspects with other application types or objects to create an advised object. This can be done at compile time (using the AspectJ compiler, for example), load time, or at runtime. Spring AOP, like other pure Java AOP frameworks, performs weaving at runtime.
织入:这是一个动词,在target(FooImpl)中与point cut (切点表达式, xxx.x.say**)匹配的join point(sayFoo) 的前后加入advice(before(), after(),并且可以另外附加实现Introduction(新的接口),最终形成AOP Proxy(Dynamic Proxy, CGLIB Proxy)的过程,称为weaving(织入)。
标准AOP与Spring AOP,布布扣,bubuko.com
标准AOP与Spring AOP
标签:style blog http color java 使用 os strong
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/f1194361820/p/3878855.html


