标签:
在Android开发中,我们或许会碰到这么一种业务需求,一项任务分成几个子任务,子任务按顺序先后执行,子任务全部执行完后,这项任务才算成功。那么,利用几个子线程顺序执行是可以达到这个目的的,但是每个线程必须去手动控制,而且得在一个子线程执行完后,再开启另一个子线程。或者,全部放到一个线程中让其顺序执行。这样都可以做到,但是,如果这是一个后台任务,就得放到Service里面,由于Service和Activity是同级的,所以,要执行耗时任务,就得在Service里面开子线程来执行。那么,有没有一种简单的方法来处理这个过程呢,答案就是IntentService。
IntentService是继承于Service并处理异步请求的一个类,在IntentService内有一个工作线程来处理耗时操作,启动IntentService的方式和启动传统Service一样,同时,当任务执行完后,IntentService会自动停止,而不需要我们去手动控制。另外,可以启动IntentService多次,而每一个耗时操作会以工作队列的方式在IntentService的onHandleIntent回调方法中执行,并且,每次只会执行一个工作线程,执行完第一个再执行第二个,以此类推。
所有请求都在一个单线程中,不会阻塞应用程序的主线程(UI Thread),同一时间只处理一个请求。
那么,用IntentService有什么好处呢?首先,我们省去了在Service中手动开线程的麻烦,第二,当操作完成时,我们不用手动停止Service,第三,it‘s so easy to use!
下面我们来看个例子:
在main.xml文件中:
1 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 6 android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 7 android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 8 android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 9 tools:context=".MainActivity" > 10 11 <Button 12 android:id="@+id/button1" 13 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 14 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 15 android:text="下载图片" /> 16 17 </RelativeLayout>
在MainActivity.java文件中:
1 public class MainActivity extends Activity { 2 3 private Button button; 4 5 @Override 6 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 7 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 8 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 9 button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); 10 button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { 11 12 public void onClick(View v) { 13 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 14 Intent service = new Intent(MainActivity.this, IntentSer.class); 15 startService(service); 16 } 17 }); 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { 22 // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. 23 getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); 24 return true; 25 } 26 27 }
在IntentSer.java文件中:
1 public class IntentSer extends IntentService { 2 3 private String path_url = "http://t1.ituba.cc/uploads/allimg/c101201/12911X4Fb460-2E024.jpg"; 4 5 6 public IntentSer() { 7 super("IntentSer"); 8 // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) { 13 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 14 15 File file = new File(this.getFilesDir(),"service.png"); 16 try { 17 FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); 18 19 InputStream inputStream = new URL(path_url).openStream(); 20 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; 21 int len = -1; 22 while((len = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1){ 23 outputStream.write(buffer, 0, len); 24 } 25 outputStream.close(); 26 inputStream.close(); 27 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 28 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } catch (MalformedURLException e) { 31 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 38 } 39 40 41 }
在AndroidManifest.xml文件中记得加网络权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
由于IntentService继承于Service,所以要配置环境:
<service android:name=".IntentSer"></service>
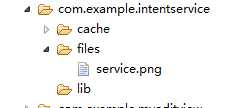
运行结果:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/SoulCode/p/5468049.html