标签:
最近要做客户端和服务器端的双向认证,在客户端向服务器端发送带证书的请求这里有一点问题,网上的例子大多都不太好使,于是找了github上httpclient源代码中的例子改造了一下,终于弄明白了
github上我参考的例子在:https://github.com/apache/httpclient/blob/4.5.x/httpclient/src/examples/org/apache/http/examples/client/ClientCustomSSL.java
下面先贴上我自己的代码(需要导入HttpClient等相关jar包),然后再说明
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.http.HttpEntity; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet; import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory; import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.TrustStrategy; import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; import org.apache.http.ssl.SSLContexts; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.security.KeyStore; import java.security.cert.CertificateException; import java.security.cert.X509Certificate; /* * Created with Intellij IDEA * USER: 焦一平 * Date: 2016/5/8 * Time: 1:10 * To change this template use File | Settings | File Template */ public class SSLDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("PKCS12"); keyStore.load(new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\client.pfx")), "123456".toCharArray()); SSLContext sslcontext = SSLContexts.custom() //忽略掉对服务器端证书的校验 .loadTrustMaterial(new TrustStrategy() { @Override public boolean isTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException { return chain.length == 1; } }) .loadKeyMaterial(keyStore, "123456".toCharArray()) .build(); SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslConnectionSocketFactory = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory( sslcontext, new String[]{"TLSv1"}, null, SSLConnectionSocketFactory.getDefaultHostnameVerifier()); CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.custom() .setSSLSocketFactory(sslConnectionSocketFactory) .build(); try { HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("https://192.168.62.130/status.jsp"); System.out.println("Executing request " + httpget.getRequestLine()); CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget); try { HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity(); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine()); System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(entity.getContent())); EntityUtils.consume(entity); } finally { response.close(); } } finally { httpclient.close(); } } }
SSLContexts.custom() 方法返回一个 SSLContextBuilder实例,来构建SSLContext,下面是SSLContextBuilder的方法列表:
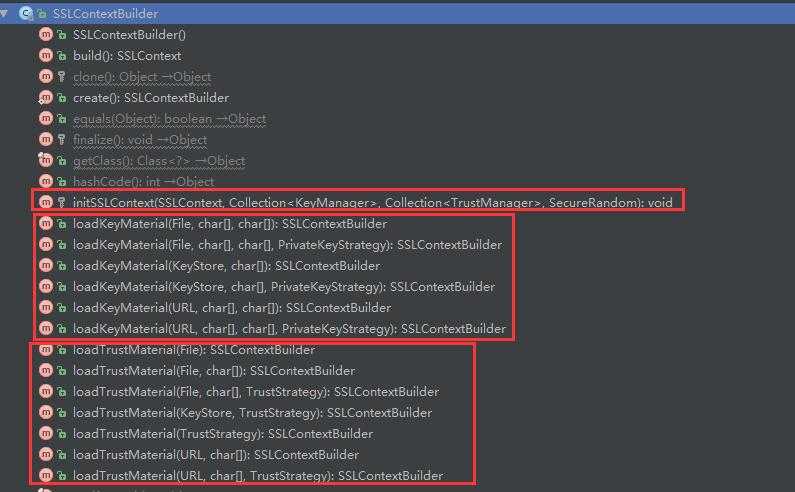
其中:
loadKeyMaterial()重载方法是加载客户端证书用的
loadTrustMaterial()重载方法是加载服务器端相关信息用的(我们就是使用 loadTrustMaterial(TrustStrategy trustStrategy) 方法自己实现了一个信任策略,不对服务器端的证书进行校验),
在生成HttpClient的时候,指定相应的 SSLSocketFactory,之后,使用这个HttpClient发送的GET请求和POST请求就自动地附加上了证书信息
如果我们只需要忽略掉对服务器端证书的验证,而不需要发送客户端证书信息,在构建SSLContext的时候,只需要 loadTrustMaterial() 不需要 loadKeyMaterial()
客户端如何只信任某个服务器端的证书信息 会在之后的文章中写
如何使用HttpClient来发送带客户端证书的请求,以及如何忽略掉对服务器端证书的校验
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jiaoyiping/p/5469660.html