标签:
| 1、Set基本数据类型 |
a、set集合,是一个无序且不重复的元素集合

class set(object): """ set() -> new empty set object set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements. """ def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Add an element to a set,添加元素 This has no effect if the element is already present. """ pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements from this set. 清楚内容""" pass def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a shallow copy of a set. 浅拷贝 """ pass def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. A中存在,B中不存在 (i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.) """ pass def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements of another set from this set. 从当前集合中删除和B中相同的元素""" pass def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing. 移除指定元素,不存在不保错 """ pass def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the intersection of two sets as a new set. 交集 (i.e. all elements that are in both sets.) """ pass def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. 取交集并更更新到A中 """ pass def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return True if two sets have a null intersection. 如果没有交集,返回True,否则返回False""" pass def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Report whether another set contains this set. 是否是子序列""" pass def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Report whether this set contains another set. 是否是父序列""" pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove and return an arbitrary set element. Raises KeyError if the set is empty. 移除元素 """ pass def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. 移除指定元素,不存在保错 """ pass def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. 对称交集 (i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.) """ pass def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. 对称交集,并更新到a中 """ pass def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the union of sets as a new set. 并集 (i.e. all elements that are in either set.) """ pass def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the union of itself and others. 更新 """ pass
b、数据类型模块举例
se = {11,22,33,44,55}
be = {44,55,66,77,88}
# se.add(66)
# print(se) #添加元素,不能直接打印!
#
#
#
# se.clear()
# print(se) #清除se集合里面所有的值,不能清除单个
#
#
#
# ce=be.difference(se) #se中存在,be中不存在的值,必须赋值给一个新的变量
# print(ce)
#
#
# se.difference_update(be)
# print(se) #在se中删除和be相同的值,不能赋值给一个新的变量,先输入转换,然后打印,也不能直接打印!
# se.discard(11)
# print(se) #移除指定元素,移除不存在的时候,不会报错
# se.remove(11)
# print(se) #移除指定的元素,移除不存在的会报错
# se.pop()
# print(se) #移除随机的元素
#
#
# ret=se.pop()
# print(ret) #移除元素,并且可以把移除的元素赋值给另一个变量
# ce = se.intersection(be)
# print(ce) #取出两个集合的交集(相同的元素)
# se.intersection_update(be)
# print(se) #取出两个集合的交集,并更新到se集合中
# ret = se.isdisjoint(be)
# print(ret) #判断两个集合之间又没有交集,如果有交集返回False,没有返回True
# ret=se.issubset(be)
# print(ret) #判断se是否是be集合的子序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase
# ret = se.issuperset(be)
# print(ret) #判断se是不是be集合的父序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase
# ret=se.symmetric_difference(be)
# print(ret) #对称交集,取出除了不相同的元素
# se.symmetric_difference_update(be)
# print(se) #对称交集,取出不相同的元素并更新到se集合中
# ret = se.union(be)
# print(ret) #并集,把两个元素集合并在一个新的变量中
| 2、深浅拷贝 |
a、数字和字符串
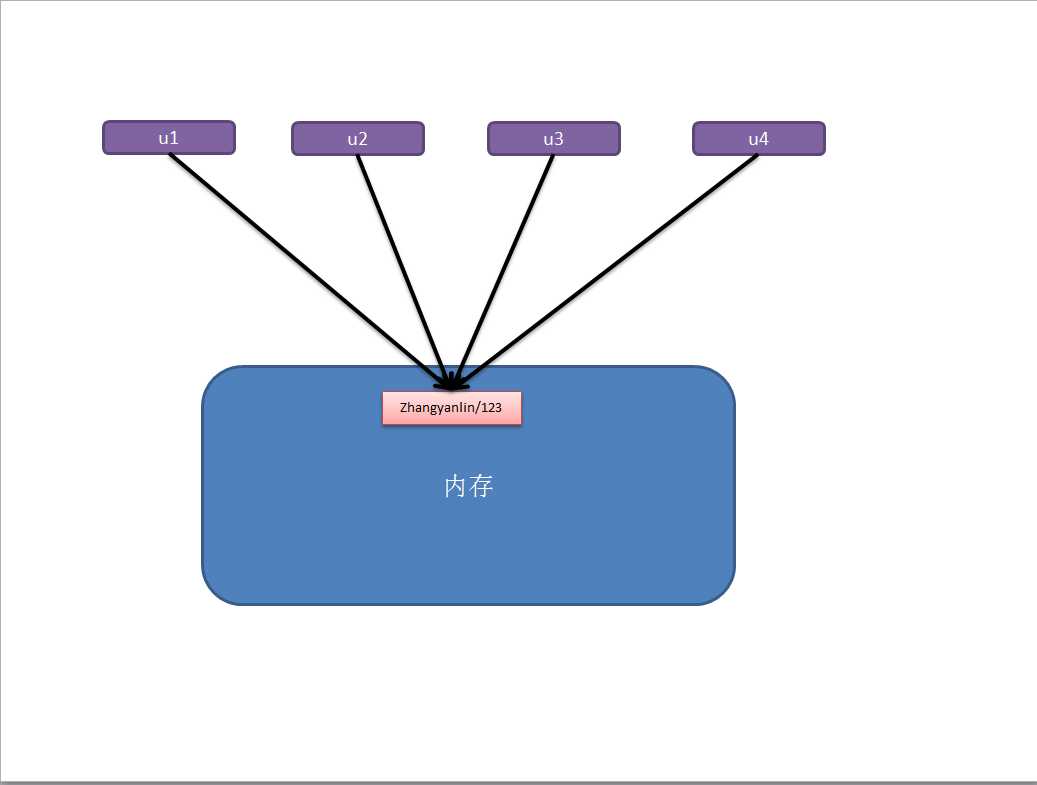
对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址。
import copy # ######### 数字、字符串 ######### n1 = 123 # n1 = "i am alex age 10" print(id(n1)) # ## 赋值 ## n2 = n1 print(id(n2)) # ## 浅拷贝 ## n2 = copy.copy(n1) print(id(n2)) # ## 深拷贝 ## n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1) print(id(n3))
b、其他基本数据类型
对于字典、元祖、列表 而言,进行赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝时,其内存地址的变化是不同的。
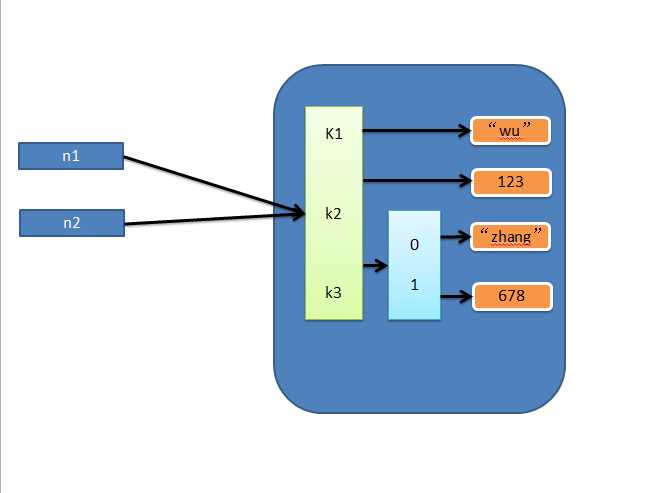
1、赋值
赋值,只是创建一个变量,该变量指向原来内存地址,如:
n1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["Aylin", 456]}
n2 = n1
2、浅拷贝
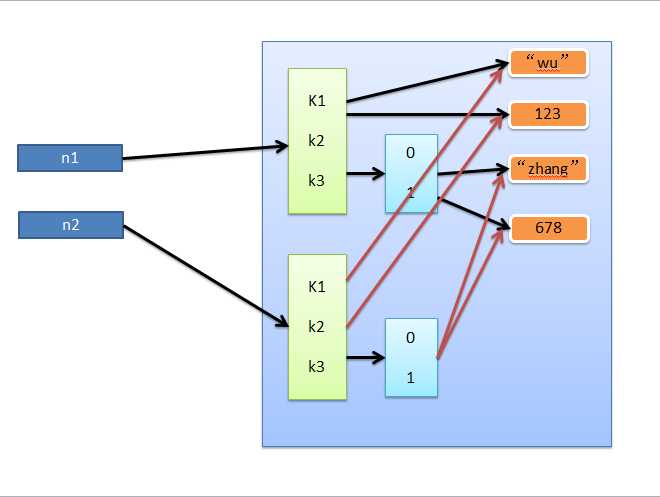
浅拷贝,在内存中只额外创建第一层数据
import copy
n1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["aylin", 456]}
n3 = copy.copy(n1)
3、深拷贝
深拷贝,在内存中将所有的数据重新创建一份(排除最后一层,即:python内部对字符串和数字的优化)
| 3、函数 |
.函数的定义主要有如下要点:
1、返回值
函数是一个功能块,该功能到底执行成功与否,需要通过返回值来告知调用者。
以上要点中,比较重要有参数和返回值:
def 发送短信():
发送短信的代码...
if 发送成功:
return True
else:
return False
while True:
# 每次执行发送短信函数,都会将返回值自动赋值给result
# 之后,可以根据result来写日志,或重发等操作
result = 发送短信()
if result == False:
短信发送失败...
函数的有三中不同的参数:
# ######### 定义函数 #########
# name 叫做函数func的形式参数,简称:形参
def func(name):
print name
# ######### 执行函数 #########
# ‘zhangyanlin‘ 叫做函数func的实际参数,简称:实参
func(‘zhangyanlin‘)
def func(name, age = 18):
print "%s:%s" %(name,age)
# 指定参数
func(‘zhangyanlin‘, 19)
# 使用默认参数
func(‘nick‘)
注:默认参数需要放在参数列表最后
def func(*args):
print args
# 执行方式一
func(11,33,4,4454,5)
# 执行方式二
li = [11,2,2,3,3,4,54]
func(*li)
def func(**kwargs):
print args
# 执行方式一
func(name=‘wupeiqi‘,age=18)
# 执行方式二
li = {‘name‘:‘wupeiqi‘, age:18, ‘gender‘:‘male‘}
func(**li)
def func(*args, **kwargs):
print args
print kwargs
邮件实例:
def email(p,j,k):
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.utils import formataddr
set = True
try:
msg = MIMEText(‘j‘, ‘plain‘, ‘utf-8‘) #j 邮件内容
msg[‘From‘] = formataddr(["武沛齐",‘wptawy@126.com‘])
msg[‘To‘] = formataddr(["走人",‘424662508@qq.com‘])
msg[‘Subject‘] = "k" #k主题
server = smtplib.SMTP("smtp.126.com", 25)
server.login("wptawy@126.com", "WW.3945.59")
server.sendmail(‘wptawy@126.com‘, [p], msg.as_string())
server.quit()
except:
set = False
return True
formmail = input("请你输入收件人邮箱:")
zhuti = input("请您输入邮件主题:")
neirong = input("请您输入邮件内容:")
aa=email(formmail,neirong,zhuti)
if aa:
print("邮件发送成功!")
else:
print("邮件发送失败!")
Python Set集合,函数,深入拷贝,浅入拷贝--小白基础
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/aylin/p/5467506.html