标签:
新建项目:
安装DotNetOpenAuth:
新增OAuthController:
代码如下:

public class OAuthController : Controller { private readonly AuthorizationServer authorizationServer = new AuthorizationServer(new OAuth2AuthorizationServer()); public async Task<ActionResult> Token() { var request = await this.authorizationServer.HandleTokenRequestAsync(this.Request, this.Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); Response.ContentType = request.Content.Headers.ContentType.ToString(); return request.AsActionResult(); } public async Task<ActionResult> Authorize() { var pendingRequest = await this.authorizationServer.ReadAuthorizationRequestAsync(Request, Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); if (pendingRequest == null) { throw new HttpException((int)HttpStatusCode.BadRequest, "Missing authorization request."); } var requestingClient = MvcApplication.DataContext.Clients.First(c => c.ClientIdentifier == pendingRequest.ClientIdentifier); // Consider auto-approving if safe to do so. if (((OAuth2AuthorizationServer)this.authorizationServer.AuthorizationServerServices).CanBeAutoApproved(pendingRequest)) { var approval = this.authorizationServer.PrepareApproveAuthorizationRequest(pendingRequest, HttpContext.User.Identity.Name); var response = await this.authorizationServer.Channel.PrepareResponseAsync(approval, Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); Response.ContentType = response.Content.Headers.ContentType.ToString(); return response.AsActionResult(); } var model = new AccountAuthorizeModel { ClientApp = requestingClient.Name, Scope = pendingRequest.Scope, AuthorizationRequest = pendingRequest, }; return View(model); } public async Task<ActionResult> AuthorizeResponse(bool isApproved) { var pendingRequest = await this.authorizationServer.ReadAuthorizationRequestAsync(Request, Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); if (pendingRequest == null) { throw new HttpException((int)HttpStatusCode.BadRequest, "Missing authorization request."); } IDirectedProtocolMessage response; if (isApproved) { // The authorization we file in our database lasts until the user explicitly revokes it. // You can cause the authorization to expire by setting the ExpirationDateUTC // property in the below created ClientAuthorization. var client = MvcApplication.DataContext.Clients.First(c => c.ClientIdentifier == pendingRequest.ClientIdentifier); client.ClientAuthorizations.Add( new ClientAuthorization { Scope = OAuthUtilities.JoinScopes(pendingRequest.Scope), User = MvcApplication.LoggedInUser, CreatedOnUtc = DateTime.UtcNow, }); MvcApplication.DataContext.SaveChanges(); // submit now so that this new row can be retrieved later in this same HTTP request // In this simple sample, the user either agrees to the entire scope requested by the client or none of it. // But in a real app, you could grant a reduced scope of access to the client by passing a scope parameter to this method. response = this.authorizationServer.PrepareApproveAuthorizationRequest(pendingRequest, User.Identity.Name); } else { response = this.authorizationServer.PrepareRejectAuthorizationRequest(pendingRequest); } var preparedResponse = await this.authorizationServer.Channel.PrepareResponseAsync(response, Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); Response.ContentType = preparedResponse.Content.Headers.ContentType.ToString(); return preparedResponse.AsActionResult(); } }
添加Code目录,写入这些类:
Client:需实现IClientDescription接口

public class Client:IClientDescription { public int ClientId { get; set; } [Required] [MaxLength(50)] public string ClientIdentifier { get; set; } [MaxLength(50)] public string ClientSecret { get; set; } public string Callback { get; set; } [Required] public string Name { get; set; } public int ClientType { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<ClientAuthorization> ClientAuthorizations { get; set; } public Uri DefaultCallback { get { return string.IsNullOrEmpty(this.Callback) ? null : new Uri(this.Callback); } } ClientType IClientDescription.ClientType { get { return (ClientType)this.ClientType; } } public bool HasNonEmptySecret { get { return !string.IsNullOrEmpty(this.ClientSecret); } } public bool IsCallbackAllowed(Uri callback) { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(this.Callback)) { return true; } // In this sample, it‘s enough of a callback URL match if the scheme and host match. // In a production app, it is advisable to require a match on the path as well. Uri acceptableCallbackPattern = new Uri(this.Callback); if (string.Equals(acceptableCallbackPattern.GetLeftPart(UriPartial.Authority), callback.GetLeftPart(UriPartial.Authority), StringComparison.Ordinal)) { return true; } return false; } public bool IsValidClientSecret(string secret) { return MessagingUtilities.EqualsConstantTime(secret, this.ClientSecret); } }
User:

public class User { public int UserId { get; set; } [Required] [MaxLength(150)] public string OpenIDClaimedIdentifier { get; set; } [MaxLength(150)] public string OpenIDFriendlyIdentifier { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<ClientAuthorization> ClientAuthorizations { get; set; } }
ClientAuthorization:

public class ClientAuthorization { [Key] public int AuthorizationId { get; set; } [Required] public DateTime CreatedOnUtc { get; set; } [Required] public int ClientId { get; set; } public int UserId { get; set; } [Required] public string Scope { get; set; } public DateTime? ExpirationDateUtc { get; set; } public virtual Client Client { get; set; } public virtual User User { get; set; } }
Nonce:

public class Nonce { [Key] [Column(Order = 1)] public string Context { get; set; } [Key] [Column(Order = 2)] public string Code { get; set; } [Key] [Column(Order = 3)] public DateTime Timestamp { get; set; } }
SymmetricCryptoKey:

public class SymmetricCryptoKey { [Key] [Column(Order = 1)] public string Bucket { get; set; } [Key] [Column(Order = 2)] public string Handle { get; set; } public DateTime ExpiresUtc { get; set; } [Required] public byte[] Secret { get; set; } }
上面这5个类有数据库里的实际对应表。
DatabaseKeyNonceStore:
 View Code
View Code这里需要添加System.Data.Linq的引用,这个类需要实现INonceStore, ICryptoKeyStore
Utilities:

internal static class Utilities { internal static DateTime AsUtc(this DateTime value) { if (value.Kind == DateTimeKind.Unspecified) { return new DateTime(value.Ticks, DateTimeKind.Utc); } return value.ToUniversalTime(); } }
DataContext:

public class DataContext:DbContext { public DataContext(): base("name=DefaultConnection") { } public DbSet<ClientAuthorization> ClientAuthorizations { get; set; } public DbSet<Client> Clients { get; set; } public DbSet<User> Users { get; set; } public DbSet<Nonce> Nonces { get; set; } public DbSet<SymmetricCryptoKey> SymmetricCryptoKeys { get; set; } }
OAuth2AuthorizationServer:

public class OAuth2AuthorizationServer : IAuthorizationServerHost { public ICryptoKeyStore CryptoKeyStore { get { return MvcApplication.KeyNonceStore; } } public INonceStore NonceStore { get { return MvcApplication.KeyNonceStore; } } public AutomatedAuthorizationCheckResponse CheckAuthorizeClientCredentialsGrant(IAccessTokenRequest accessRequest) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public AutomatedUserAuthorizationCheckResponse CheckAuthorizeResourceOwnerCredentialGrant(string userName, string password, IAccessTokenRequest accessRequest) { //用户名、密码验证 throw new NotImplementedException(); } public AccessTokenResult CreateAccessToken(IAccessTokenRequest accessTokenRequestMessage) { var accessToken = new AuthorizationServerAccessToken(); accessToken.Lifetime = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(2); // Also take into account the remaining life of the authorization and artificially shorten the access token‘s lifetime // to account for that if necessary. //// TODO: code here accessToken.ResourceServerEncryptionKey = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(); accessToken.ResourceServerEncryptionKey.ImportParameters(ResourceServerEncryptionPublicKey); accessToken.AccessTokenSigningKey = CreateRSA(); var result = new AccessTokenResult(accessToken); return result; } private static RSACryptoServiceProvider CreateRSA() { var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(); rsa.ImportParameters(CreateAuthorizationServerSigningKey()); return rsa; } #if DEBUG /// <summary> /// This is the FOR SAMPLE ONLY hard-coded public key of the complementary OAuthResourceServer sample. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// In a real app, the authorization server would need to determine which resource server the access token needs to be encoded for /// based on the authorization request. It would then need to look up the public key for that resource server and use that in /// preparing the access token for the client to use against that resource server. /// </remarks> private static readonly RSAParameters ResourceServerEncryptionPublicKey = new RSAParameters { Exponent = new byte[] { 1, 0, 1 }, Modulus = new byte[] { 166, 175, 117, 169, 211, 251, 45, 215, 55, 53, 202, 65, 153, 155, 92, 219, 235, 243, 61, 170, 101, 250, 221, 214, 239, 175, 238, 175, 239, 20, 144, 72, 227, 221, 4, 219, 32, 225, 101, 96, 18, 33, 117, 176, 110, 123, 109, 23, 29, 85, 93, 50, 129, 163, 113, 57, 122, 212, 141, 145, 17, 31, 67, 165, 181, 91, 117, 23, 138, 251, 198, 132, 188, 213, 10, 157, 116, 229, 48, 168, 8, 127, 28, 156, 239, 124, 117, 36, 232, 100, 222, 23, 52, 186, 239, 5, 63, 207, 185, 16, 137, 73, 137, 147, 252, 71, 9, 239, 113, 27, 88, 255, 91, 56, 192, 142, 210, 21, 34, 81, 204, 239, 57, 60, 140, 249, 15, 101 }, }; #else [Obsolete("You must use a real key for a real app.", true)] private static readonly RSAParameters ResourceServerEncryptionPublicKey; #endif private static RSAParameters CreateAuthorizationServerSigningKey() { #if DEBUG // Since the sample authorization server and the sample resource server must work together, // we hard-code a FOR SAMPLE USE ONLY key pair. The matching public key information is hard-coded into the OAuthResourceServer sample. // In a real app, the RSA parameters would typically come from a certificate that may already exist. It may simply be the HTTPS certificate for the auth server. return new RSAParameters { Exponent = new byte[] { 1, 0, 1 }, Modulus = new byte[] { 210, 95, 53, 12, 203, 114, 150, 23, 23, 88, 4, 200, 47, 219, 73, 54, 146, 253, 126, 121, 105, 91, 118, 217, 182, 167, 140, 6, 67, 112, 97, 183, 66, 112, 245, 103, 136, 222, 205, 28, 196, 45, 6, 223, 192, 76, 56, 180, 90, 120, 144, 19, 31, 193, 37, 129, 186, 214, 36, 53, 204, 53, 108, 133, 112, 17, 133, 244, 3, 12, 230, 29, 243, 51, 79, 253, 10, 111, 185, 23, 74, 230, 99, 94, 78, 49, 209, 39, 95, 213, 248, 212, 22, 4, 222, 145, 77, 190, 136, 230, 134, 70, 228, 241, 194, 216, 163, 234, 52, 1, 64, 181, 139, 128, 90, 255, 214, 60, 168, 233, 254, 110, 31, 102, 58, 67, 201, 33 }, P = new byte[] { 237, 238, 79, 75, 29, 57, 145, 201, 57, 177, 215, 108, 40, 77, 232, 237, 113, 38, 157, 195, 174, 134, 188, 175, 121, 28, 11, 236, 80, 146, 12, 38, 8, 12, 104, 46, 6, 247, 14, 149, 196, 23, 130, 116, 141, 137, 225, 74, 84, 111, 44, 163, 55, 10, 246, 154, 195, 158, 186, 241, 162, 11, 217, 77 }, Q = new byte[] { 226, 89, 29, 67, 178, 205, 30, 152, 184, 165, 15, 152, 131, 245, 141, 80, 150, 3, 224, 136, 188, 248, 149, 36, 200, 250, 207, 156, 224, 79, 150, 191, 84, 214, 233, 173, 95, 192, 55, 123, 124, 255, 53, 85, 11, 233, 156, 66, 14, 27, 27, 163, 108, 199, 90, 37, 118, 38, 78, 171, 80, 26, 101, 37 }, DP = new byte[] { 108, 176, 122, 132, 131, 187, 50, 191, 203, 157, 84, 29, 82, 100, 20, 205, 178, 236, 195, 17, 10, 254, 253, 222, 226, 226, 79, 8, 10, 222, 76, 178, 106, 230, 208, 8, 134, 162, 1, 133, 164, 232, 96, 109, 193, 226, 132, 138, 33, 252, 15, 86, 23, 228, 232, 54, 86, 186, 130, 7, 179, 208, 217, 217 }, DQ = new byte[] { 175, 63, 252, 46, 140, 99, 208, 138, 194, 123, 218, 101, 101, 214, 91, 65, 199, 196, 220, 182, 66, 73, 221, 128, 11, 180, 85, 198, 202, 206, 20, 147, 179, 102, 106, 170, 247, 245, 229, 127, 81, 58, 111, 218, 151, 76, 154, 213, 114, 2, 127, 21, 187, 133, 102, 64, 151, 7, 245, 229, 34, 50, 45, 153 }, InverseQ = new byte[] { 137, 156, 11, 248, 118, 201, 135, 145, 134, 121, 14, 162, 149, 14, 98, 84, 108, 160, 27, 91, 230, 116, 216, 181, 200, 49, 34, 254, 119, 153, 179, 52, 231, 234, 36, 148, 71, 161, 182, 171, 35, 182, 46, 164, 179, 100, 226, 71, 119, 23, 0, 16, 240, 4, 30, 57, 76, 109, 89, 131, 56, 219, 71, 206 }, D = new byte[] { 108, 15, 123, 176, 150, 208, 197, 72, 23, 53, 159, 63, 53, 85, 238, 197, 153, 187, 156, 187, 192, 226, 186, 170, 26, 168, 245, 196, 65, 223, 248, 81, 170, 79, 91, 191, 83, 15, 31, 77, 39, 119, 249, 143, 245, 183, 49, 105, 115, 15, 122, 242, 87, 221, 94, 230, 196, 146, 59, 7, 103, 94, 9, 223, 146, 180, 189, 86, 190, 94, 242, 59, 32, 54, 23, 181, 124, 170, 63, 172, 90, 158, 169, 140, 6, 102, 170, 0, 135, 199, 35, 196, 212, 238, 196, 56, 14, 0, 140, 197, 169, 240, 156, 43, 182, 123, 102, 79, 89, 20, 120, 171, 43, 223, 58, 190, 230, 166, 185, 162, 186, 226, 31, 206, 196, 188, 104, 1 }, }; #else // This is how you could generate your own public/private key pair. // As we generate a new random key, we need to set the UseMachineKeyStore flag so that this doesn‘t // crash on IIS. For more information: // http://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/clr/thread/7ea48fd0-8d6b-43ed-b272-1a0249ae490f?prof=required var cspParameters = new CspParameters(); cspParameters.Flags = CspProviderFlags.UseArchivableKey | CspProviderFlags.UseMachineKeyStore; var keyPair = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(cspParameters); // After exporting the private/public key information, read the information out and store it somewhere var privateKey = keyPair.ExportParameters(true); var publicKey = keyPair.ExportParameters(false); // Ultimately the private key information must be what is returned through the AccessTokenSigningPrivateKey property. return privateKey; #endif } public IClientDescription GetClient(string clientIdentifier) { var consumerRow = MvcApplication.DataContext.Clients.SingleOrDefault( consumerCandidate => consumerCandidate.ClientIdentifier == clientIdentifier); if (consumerRow == null) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("clientIdentifier"); } return consumerRow; } public bool IsAuthorizationValid(IAuthorizationDescription authorization) { return this.IsAuthorizationValid(authorization.Scope, authorization.ClientIdentifier, authorization.UtcIssued, authorization.User); } private bool IsAuthorizationValid(HashSet<string> requestedScopes, string clientIdentifier, DateTime issuedUtc, string username) { issuedUtc += TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1); var grantedScopeStrings = from auth in MvcApplication.DataContext.ClientAuthorizations where auth.Client.ClientIdentifier == clientIdentifier && auth.CreatedOnUtc <= issuedUtc && (!auth.ExpirationDateUtc.HasValue || auth.ExpirationDateUtc.Value >= DateTime.UtcNow) && auth.User.OpenIDClaimedIdentifier == username select auth.Scope; if (!grantedScopeStrings.Any()) { return false; } var grantedScopes = new HashSet<string>(OAuthUtilities.ScopeStringComparer); foreach (string scope in grantedScopeStrings) { grantedScopes.UnionWith(OAuthUtilities.SplitScopes(scope)); } return requestedScopes.IsSubsetOf(grantedScopes); } public bool CanBeAutoApproved(EndUserAuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest) { if (authorizationRequest == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("authorizationRequest"); } // NEVER issue an auto-approval to a client that would end up getting an access token immediately // (without a client secret), as that would allow arbitrary clients to masquarade as an approved client // and obtain unauthorized access to user data. if (authorizationRequest.ResponseType == EndUserAuthorizationResponseType.AuthorizationCode) { // Never issue auto-approval if the client secret is blank, since that too makes it easy to spoof // a client‘s identity and obtain unauthorized access. var requestingClient = MvcApplication.DataContext.Clients.First(c => c.ClientIdentifier == authorizationRequest.ClientIdentifier); if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestingClient.ClientSecret)) { return this.IsAuthorizationValid( authorizationRequest.Scope, authorizationRequest.ClientIdentifier, DateTime.UtcNow, HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name); } } // Default to not auto-approving. return false; } }
在Models目录中添加AccountAuthorizeModel:

public class AccountAuthorizeModel { public string ClientApp { get; set; } public HashSet<string> Scope { get; set; } public EndUserAuthorizationRequest AuthorizationRequest { get; set; } }
在Global.asax中加入:

public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication { protected void Application_Start() { AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas(); FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters); RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes); BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles); KeyNonceStore = new DatabaseKeyNonceStore(); } /// <summary> /// 连接数据库. /// </summary> public static DataContext DataContext { get { DataContext dataContext = DataContextSimple; if (dataContext == null) { dataContext = new DataContext(); DataContextSimple = dataContext; } return dataContext; } } public static User LoggedInUser { get { return DataContext.Users.SingleOrDefault(user => user.OpenIDClaimedIdentifier == HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name); } } public static DatabaseKeyNonceStore KeyNonceStore { get; set; } protected void Application_EndRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { CommitAndCloseDatabaseIfNecessary(); } private static DataContext DataContextSimple { get { if (HttpContext.Current != null) { return HttpContext.Current.Items["DataContext"] as DataContext; } else { throw new InvalidOperationException(); } } set { if (HttpContext.Current != null) { HttpContext.Current.Items["DataContext"] = value; } else { throw new InvalidOperationException(); } } } private static void CommitAndCloseDatabaseIfNecessary() { var dataContext = DataContextSimple; if (dataContext != null) { dataContext.SaveChanges(); } } }
在HomeController中添加方法:

[HttpPost] public ActionResult CreateDatabase() { MvcApplication.DataContext.Clients.Add(new Client { ClientIdentifier = "sampleconsumer", ClientSecret = "samplesecret", Name = "Some sample client", }); MvcApplication.DataContext.Clients.Add(new Client { ClientIdentifier = "sampleImplicitConsumer", Name = "Some sample client used for implicit grants (no secret)", Callback = "http://localhost:59722/", }); try { MvcApplication.DataContext.SaveChanges(); ViewBag.Success = true; } catch (Exception ex) { ViewBag.Error = ex.Message; } return View(); }
修改Home/Index页面添加一个按钮:

<div class="jumbotron"> <h1>ASP.NET</h1> <p class="lead">ASP.NET is a free web framework for building great Web sites and Web applications using HTML, CSS and JavaScript.</p> <p><a href="http://asp.net" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg">Learn more »</a></p> @using (Html.BeginForm("CreateDatabase", "home")) { <input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg" value="创建数据库" /> } </div>
添加CreateDatabase页面:

@{ ViewBag.Title = "CreateDatabase"; } <h2>CreateDatabase</h2> <div class="jumbotron"> @if (ViewBag.Success) { <p>数据库创建成功。</p> } else { <p>数据库创建失败:@ViewBag.Error</p> } </div>
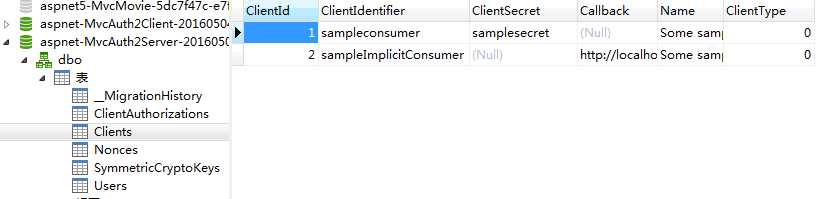
运行项目,点击创建数据库,可以看到新增的表和数据:

接下来就可以用上一篇的客户端来进行测试了:
首先修改下客户端的代码:

private static AuthorizationServerDescription authServerDescription = new AuthorizationServerDescription { TokenEndpoint = new Uri("http://localhost:26259/OAuth/Token"), AuthorizationEndpoint = new Uri("http://localhost:26259/OAuth/Authorize"), };
然后启动服务端和客户端,访问客户端:http://localhost:18180/Authorize,发现报错了:
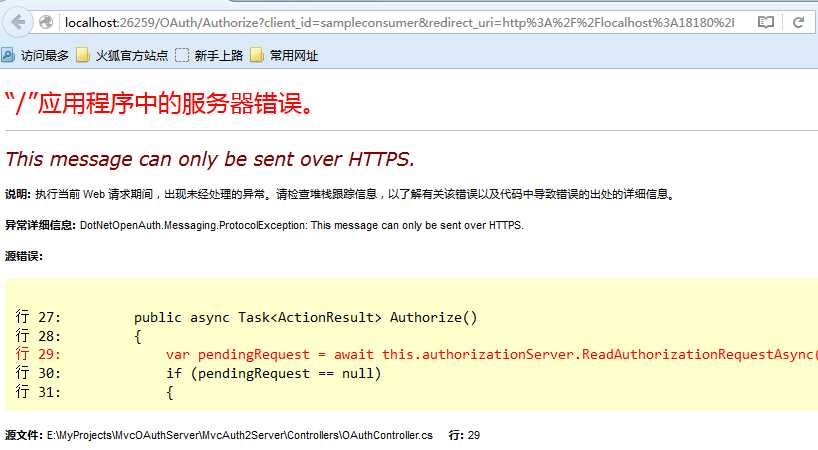
这个错误很熟悉了吧,修改服务端的配置:

<messaging relaxSslRequirements="true"> <untrustedWebRequest> <whitelistHosts> <!-- Uncomment to enable communication with localhost (should generally not activate in production!) --> <!--<add name="localhost" />--> </whitelistHosts> </untrustedWebRequest> </messaging>
再次启动,发现找不到页面:
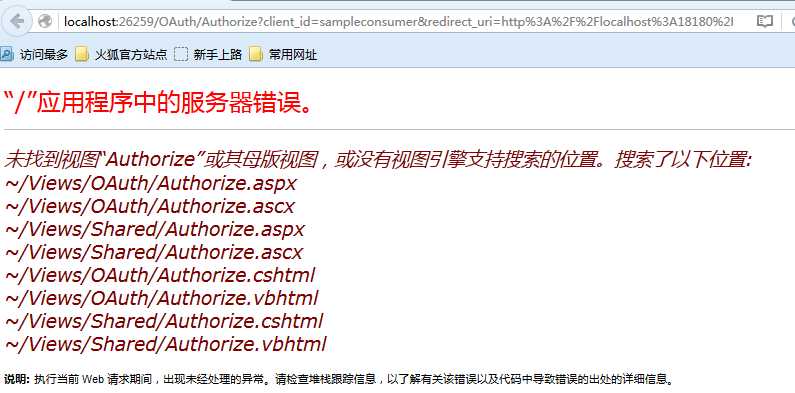
因为此时我们还没有添加这个页面,接下来添加这个页面:

@using MvcAuth2Server.Models @using DotNetOpenAuth.OAuth2 @model AccountAuthorizeModel @{ ViewBag.Title = "Authorize"; } <h2>Authorize</h2> <div style="background-color: Yellow"> <b>Warning</b>: Never give your login credentials to another web site or application. </div> <p> The @Html.Encode(Model.ClientApp) application is requesting to access the private data in your account here. Is that alright with you? </p> <p> <b>Requested access: </b> @Html.Encode(String.Join(" ", Model.Scope.ToArray())) </p> <p> If you grant access now, you can revoke it at any time by returning to @Html.ActionLink("your account page", "Edit") </p> @using (Html.BeginForm("AuthorizeResponse", "OAuth")) { @Html.AntiForgeryToken() @Html.Hidden("IsApproved") @Html.Hidden("client_id", Model.AuthorizationRequest.ClientIdentifier) @Html.Hidden("redirect_uri", Model.AuthorizationRequest.Callback) @Html.Hidden("state", Model.AuthorizationRequest.ClientState) @Html.Hidden("scope", OAuthUtilities.JoinScopes(Model.AuthorizationRequest.Scope)) @Html.Hidden("response_type", Model.AuthorizationRequest.ResponseType == DotNetOpenAuth.OAuth2.Messages.EndUserAuthorizationResponseType.AccessToken ? "token" : "code") <div style="display: none" id="responseButtonsDiv"> <input type="submit" value="Yes" onclick="document.getElementsByName(‘IsApproved‘)[0].value = true; return true;" /> <input type="submit" value="No" onclick="document.getElementsByName(‘IsApproved‘)[0].value = false; return true;" /> </div> <div id="javascriptDisabled"> <b>Javascript appears to be disabled in your browser. </b>This page requires Javascript to be enabled to better protect your security. </div> <script language="javascript" type="text/javascript"> //<![CDATA[ // we use HTML to hide the action buttons and Javascript to show them // to protect against click-jacking in an iframe whose javascript is disabled. document.getElementById(‘responseButtonsDiv‘).style.display = ‘block‘; document.getElementById(‘javascriptDisabled‘).style.display = ‘none‘; // Frame busting code (to protect us from being hosted in an iframe). // This protects us from click-jacking. if (document.location !== window.top.location) { window.top.location = document.location; } //]]> </script> }
再次运行,就看到下面的页面了:
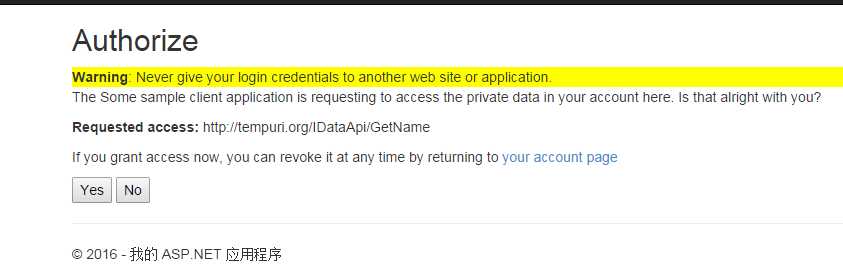
这里就有问题了,还没授权登录呢,怎么就过了呢,原因在这里:

[Authorize, AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Get | HttpVerbs.Post)] public async Task<ActionResult> Authorize()
更新OAuth里的两个方法:

[Authorize, AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Get | HttpVerbs.Post)] [HttpHeader("x-frame-options", "SAMEORIGIN")] // mitigates clickjacking public async Task<ActionResult> Authorize()

[Authorize, HttpPost, ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public async Task<ActionResult> AuthorizeResponse(bool isApproved)
这里有个HttpHeader,在Code目录下添加此类:

public class HttpHeaderAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute { /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="HttpHeaderAttribute"/> class. /// </summary> /// <param name="name">The HTTP header name.</param> /// <param name="value">The HTTP header value.</param> public HttpHeaderAttribute(string name, string value) { this.Name = name; this.Value = value; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the name of the HTTP Header. /// </summary> public string Name { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the value of the HTTP Header. /// </summary> public string Value { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Called by the MVC framework after the action result executes. /// </summary> /// <param name="filterContext">The filter context.</param> public override void OnResultExecuted(ResultExecutedContext filterContext) { filterContext.HttpContext.Response.AppendHeader(this.Name, this.Value); base.OnResultExecuted(filterContext); } }
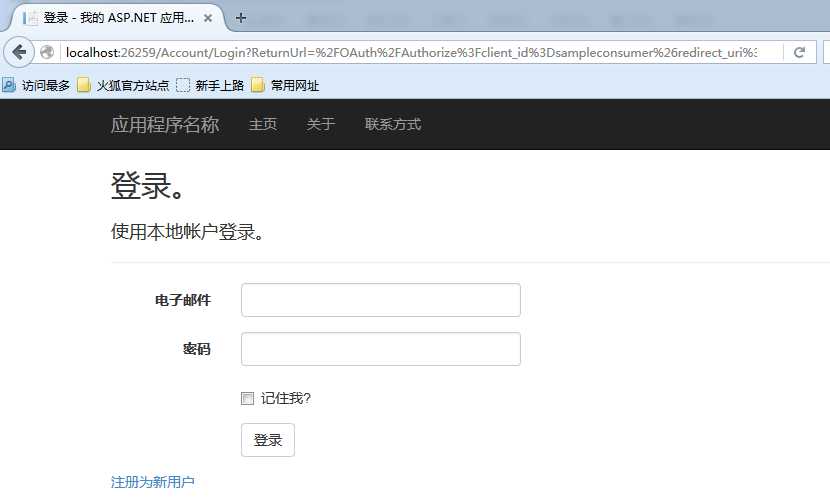
再次运行,就会跳转到登录页面了:
这里我们想使用OpenID登录,所以使用另外一个登录页面:
在Models目录下的AccountViewModels中添加:

public class LogOnModel { [Required] [Display(Name="OpenID")] public string UserSuppliedIdentifier { get; set; } [Display(Name="Remember me?")] public bool RememberMe { get; set; } }
在AccountController中添加:

[HttpPost] [AllowAnonymous] [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public async Task<ActionResult> Login(LogOnModel model, string returnUrl) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { var rp = new OpenIdRelyingParty(); var request = await rp.CreateRequestAsync(model.UserSuppliedIdentifier, Realm.AutoDetect, new Uri(Request.Url, Url.Action("Authenticate"))); if (request != null) { if (returnUrl != null) { request.AddCallbackArguments("returnUrl", returnUrl); } var response = await request.GetRedirectingResponseAsync(); Response.ContentType = response.Content.Headers.ContentType.ToString(); return response.AsActionResult(); } else { ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "The identifier you supplied is not recognized as a valid OpenID Identifier."); } } // If we got this far, something failed, redisplay form return View(model); } [AllowAnonymous] public async Task<ActionResult> Authenticate(string returnUrl) { var rp = new OpenIdRelyingParty(); var response = await rp.GetResponseAsync(Request); if (response != null) { switch (response.Status) { case AuthenticationStatus.Authenticated: // Make sure we have a user account for this guy. string identifier = response.ClaimedIdentifier; // convert to string so LinqToSQL expression parsing works. if (MvcApplication.DataContext.Users.FirstOrDefault(u => u.OpenIDClaimedIdentifier == identifier) == null) { MvcApplication.DataContext.Users.Add(new User { OpenIDFriendlyIdentifier = response.FriendlyIdentifierForDisplay, OpenIDClaimedIdentifier = response.ClaimedIdentifier, }); } FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie(response.ClaimedIdentifier, false); return this.Redirect(returnUrl ?? Url.Action("Index", "Home")); default: ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, "An error occurred during login."); break; } } return this.View("LogOn"); }
这里的[AllowAnonymous]很重要,没有这个的话无法正常提交请求
运行网站
跳转到登录页面:
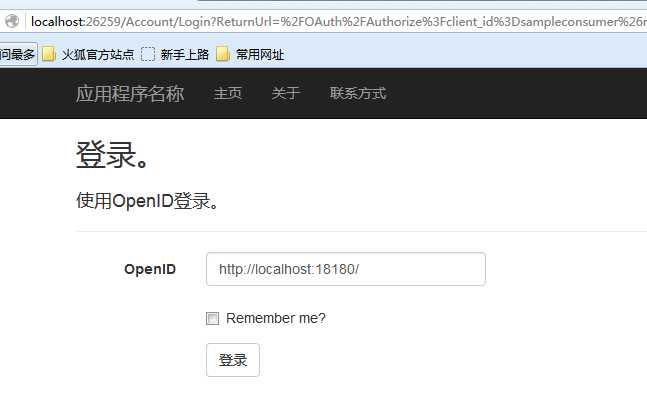
这里需要有一个OpenID的提供者,此时我们使用客户端来提供OpenID服务(假设服务端和客户端都是内网的,直接用客户端的登录授权)
下面需要改造客户端,这里坑比较多,需要注意:
首先修改HomeController:

public ActionResult Index() { if (Request.AcceptTypes.Contains("application/xrds+xml")) { ViewData["OPIdentifier"] = true; return View("Xrds"); } return View(); } public ActionResult Xrds() { ViewData["OPIdentifier"] = true; return View(); }
加入Xrds页面:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <xrds:XRDS xmlns:xrds="xri://$xrds" xmlns:openid="http://openid.net/xmlns/1.0" xmlns="xri://$xrd*($v*2.0)"> <XRD> <Service priority="10"> @if (ViewData["OPIdentifier"] != null) { <Type>http://specs.openid.net/auth/2.0/server</Type> } else { <Type>http://specs.openid.net/auth/2.0/signon</Type> } <Type>http://openid.net/extensions/sreg/1.1</Type> <Type>http://axschema.org/contact/email</Type> @*Add these types when and if the Provider supports the respective aspects of the UI extension. <Type>http://specs.openid.net/extensions/ui/1.0/mode/popup</Type> <Type>http://specs.openid.net/extensions/ui/1.0/lang-pref</Type> <Type>http://specs.openid.net/extensions/ui/1.0/icon</Type>*@ <URI>@(new Uri(Request.Url, Response.ApplyAppPathModifier("~/OpenId/Provider")))</URI> </Service> @if (ViewData["OPIdentifier"] == null) { <Service priority="20"> <Type>http://openid.net/signon/1.0</Type> <Type>http://openid.net/extensions/sreg/1.1</Type> <Type>http://axschema.org/contact/email</Type> <URI>@(new Uri(Request.Url, Response.ApplyAppPathModifier("~/OpenId/Provider")))</URI> </Service> } </XRD> </xrds:XRDS> @{ Layout = null;} @{ Response.ContentType = "application/xrds+xml"; }
新增OpenIdController:

[ValidateInput(false)] public async Task<ActionResult> Provider() { return View(); }
OpenId的Provider页面:

@{ ViewBag.Title = "Provider"; } <h2>Provider</h2> <p> This page expects to receive OpenID authentication messages to allow users to log into other web sites. </p>
稍后我们要对这两处进行修改。
先关注Xrds页面:
这里要注意最后两行,而且一定要把这两行放到最后,否则生成的xml就会出现换行,在服务端验证就会报错
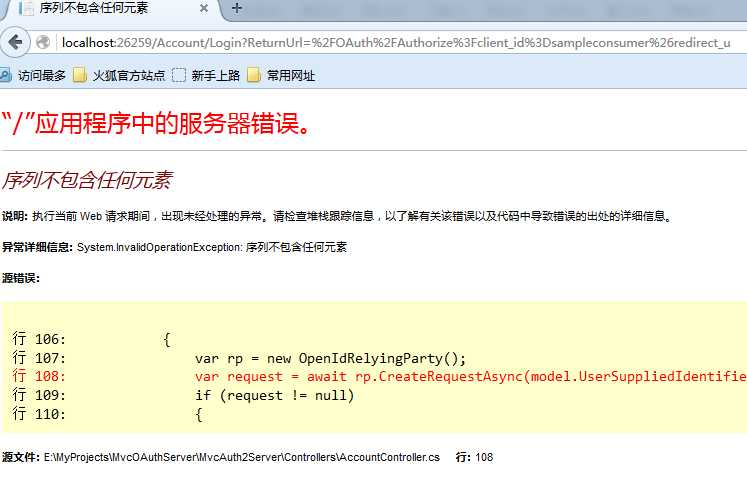
跟源码发现问题在这里:
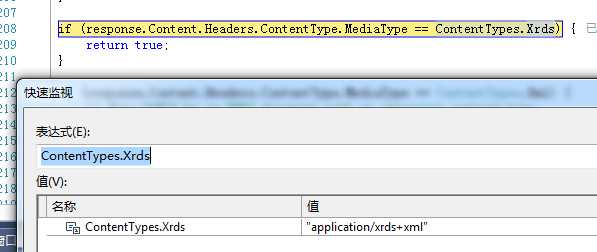
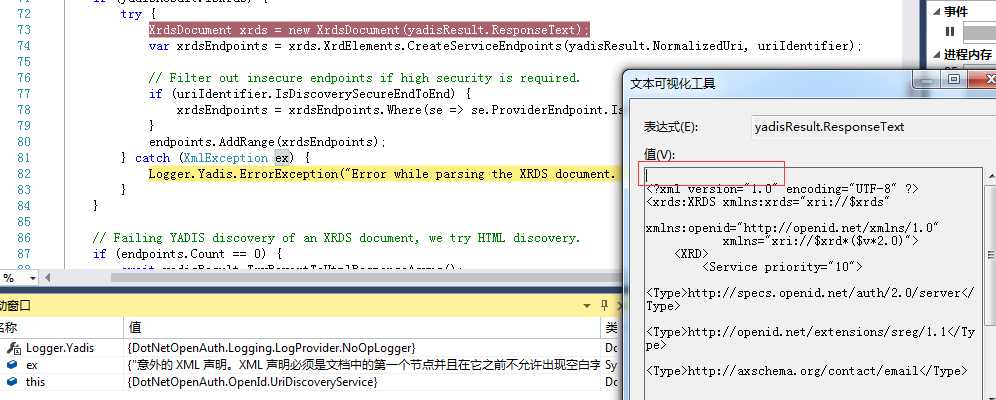
修改后发现生成的xml一直有第一行的空白,元凶在这里:
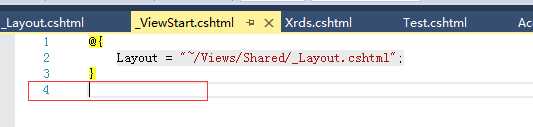
把这个第4行删掉,再次运行就看到如下页面了:
接下来实现OpenId。
修改OpenIdController:

public class OpenIdController : Controller { internal static OpenIdProvider OpenIdProvider = new OpenIdProvider(); public IFormsAuthentication FormsAuth { get; private set; } [ValidateInput(false)] public async Task<ActionResult> Provider() { IRequest request = await OpenIdProvider.GetRequestAsync(this.Request, this.Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); if (request != null) { // Some requests are automatically handled by DotNetOpenAuth. If this is one, go ahead and let it go. if (request.IsResponseReady) { var response = await OpenIdProvider.PrepareResponseAsync(request, this.Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); Response.ContentType = response.Content.Headers.ContentType.ToString(); return response.AsActionResult(); } // This is apparently one that the host (the web site itself) has to respond to. ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest = (IHostProcessedRequest)request; // If PAPE requires that the user has logged in recently, we may be required to challenge the user to log in. var papeRequest = ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest.GetExtension<PolicyRequest>(); if (papeRequest != null && papeRequest.MaximumAuthenticationAge.HasValue) { TimeSpan timeSinceLogin = DateTime.UtcNow - this.FormsAuth.SignedInTimestampUtc.Value; if (timeSinceLogin > papeRequest.MaximumAuthenticationAge.Value) { // The RP wants the user to have logged in more recently than he has. // We‘ll have to redirect the user to a login screen. return this.RedirectToAction("LogOn", "Account", new { returnUrl = this.Url.Action("ProcessAuthRequest") }); } } return await this.ProcessAuthRequest(); } else { // No OpenID request was recognized. This may be a user that stumbled on the OP Endpoint. return this.View(); } } public async Task<ActionResult> ProcessAuthRequest() { if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest == null) { return this.RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } // Try responding immediately if possible. ActionResult response = await this.AutoRespondIfPossibleAsync(); if (response != null) { return response; } // We can‘t respond immediately with a positive result. But if we still have to respond immediately... if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest.Immediate) { // We can‘t stop to prompt the user -- we must just return a negative response. return await this.SendAssertion(); } return this.RedirectToAction("AskUser"); } /// <summary> /// Displays a confirmation page. /// </summary> /// <returns>The response for the user agent.</returns> [Authorize] public async Task<ActionResult> AskUser() { if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest == null) { // Oops... precious little we can confirm without a pending OpenID request. return this.RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } // The user MAY have just logged in. Try again to respond automatically to the RP if appropriate. ActionResult response = await this.AutoRespondIfPossibleAsync(); if (response != null) { return response; } if (!ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest.IsDirectedIdentity && !this.UserControlsIdentifier(ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest)) { return this.Redirect(this.Url.Action("LogOn", "Account", new { returnUrl = this.Request.Url })); } this.ViewData["Realm"] = ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest.Realm; return this.View(); } [HttpPost, Authorize, ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public async Task<ActionResult> AskUserResponse(bool confirmed) { if (!ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest.IsDirectedIdentity && !this.UserControlsIdentifier(ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest)) { // The user shouldn‘t have gotten this far without controlling the identifier we‘d send an assertion for. return new HttpStatusCodeResult((int)HttpStatusCode.BadRequest); } if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingAnonymousRequest != null) { ProviderEndpoint.PendingAnonymousRequest.IsApproved = confirmed; } else if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest != null) { ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest.IsAuthenticated = confirmed; } else { throw new InvalidOperationException("There‘s no pending authentication request!"); } return await this.SendAssertion(); } /// <summary> /// Attempts to formulate an automatic response to the RP if the user‘s profile allows it. /// </summary> /// <returns>The ActionResult for the caller to return, or <c>null</c> if no automatic response can be made.</returns> private async Task<ActionResult> AutoRespondIfPossibleAsync() { // If the odds are good we can respond to this one immediately (without prompting the user)... if (await ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest.IsReturnUrlDiscoverableAsync(OpenIdProvider.Channel.HostFactories, this.Response.ClientDisconnectedToken) == RelyingPartyDiscoveryResult.Success && User.Identity.IsAuthenticated && this.HasUserAuthorizedAutoLogin(ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest)) { // Is this is an identity authentication request? (as opposed to an anonymous request)... if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest != null) { // If this is directed identity, or if the claimed identifier being checked is controlled by the current user... if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest.IsDirectedIdentity || this.UserControlsIdentifier(ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest)) { ProviderEndpoint.PendingAuthenticationRequest.IsAuthenticated = true; return await this.SendAssertion(); } } // If this is an anonymous request, we can respond to that too. if (ProviderEndpoint.PendingAnonymousRequest != null) { ProviderEndpoint.PendingAnonymousRequest.IsApproved = true; return await this.SendAssertion(); } } return null; } /// <summary> /// Sends a positive or a negative assertion, based on how the pending request is currently marked. /// </summary> /// <returns>An MVC redirect result.</returns> public async Task<ActionResult> SendAssertion() { var pendingRequest = ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest; var authReq = pendingRequest as IAuthenticationRequest; var anonReq = pendingRequest as IAnonymousRequest; ProviderEndpoint.PendingRequest = null; // clear session static so we don‘t do this again if (pendingRequest == null) { throw new InvalidOperationException("There‘s no pending authentication request!"); } // Set safe defaults if somehow the user ended up (perhaps through XSRF) here before electing to send data to the RP. if (anonReq != null && !anonReq.IsApproved.HasValue) { anonReq.IsApproved = false; } if (authReq != null && !authReq.IsAuthenticated.HasValue) { authReq.IsAuthenticated = false; } if (authReq != null && authReq.IsAuthenticated.Value) { if (authReq.IsDirectedIdentity) { authReq.LocalIdentifier = Models.User.GetClaimedIdentifierForUser(User.Identity.Name); } if (!authReq.IsDelegatedIdentifier) { authReq.ClaimedIdentifier = authReq.LocalIdentifier; } } // Respond to AX/sreg extension requests only on a positive result. if ((authReq != null && authReq.IsAuthenticated.Value) || (anonReq != null && anonReq.IsApproved.Value)) { // Look for a Simple Registration request. When the AXFetchAsSregTransform behavior is turned on // in the web.config file as it is in this sample, AX requests will come in as SReg requests. var claimsRequest = pendingRequest.GetExtension<ClaimsRequest>(); if (claimsRequest != null) { var claimsResponse = claimsRequest.CreateResponse(); // This simple respond to a request check may be enhanced to only respond to an individual attribute // request if the user consents to it explicitly, in which case this response extension creation can take // place in the confirmation page action rather than here. if (claimsRequest.Email != DemandLevel.NoRequest) { claimsResponse.Email = User.Identity.Name + "@dotnetopenauth.net"; } pendingRequest.AddResponseExtension(claimsResponse); } // Look for PAPE requests. var papeRequest = pendingRequest.GetExtension<PolicyRequest>(); if (papeRequest != null) { var papeResponse = new PolicyResponse(); if (papeRequest.MaximumAuthenticationAge.HasValue) { papeResponse.AuthenticationTimeUtc = this.FormsAuth.SignedInTimestampUtc; } pendingRequest.AddResponseExtension(papeResponse); } } var response = await OpenIdProvider.PrepareResponseAsync(pendingRequest, this.Response.ClientDisconnectedToken); Response.ContentType = response.Content.Headers.ContentType.ToString(); return response.AsActionResult(); } /// <summary> /// Determines whether the currently logged in user has authorized auto login to the requesting relying party. /// </summary> /// <param name="request">The incoming request.</param> /// <returns> /// <c>true</c> if it is safe to respond affirmatively to this request and all extensions /// without further user confirmation; otherwise, <c>false</c>. /// </returns> private bool HasUserAuthorizedAutoLogin(IHostProcessedRequest request) { // TODO: host should implement this method meaningfully, consulting their user database. // Make sure the user likes the RP if (true/*User.UserLikesRP(request.Realm))*/) { // And make sure the RP is only asking for information about the user that the user has granted before. if (true/*User.HasGrantedExtensions(request)*/) { // For now for the purposes of the sample, we‘ll disallow auto-logins when an sreg request is present. if (request.GetExtension<ClaimsRequest>() != null) { return false; } return true; } } // If we aren‘t sure the user likes this site and is willing to disclose the requested info, return false // so the user has the opportunity to explicity choose whether to share his/her info. return false; } /// <summary> /// Checks whether the logged in user controls the OP local identifier in the given authentication request. /// </summary> /// <param name="authReq">The authentication request.</param> /// <returns><c>true</c> if the user controls the identifier; <c>false</c> otherwise.</returns> private bool UserControlsIdentifier(IAuthenticationRequest authReq) { if (authReq == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("authReq"); } if (User == null || User.Identity == null) { return false; } Uri userLocalIdentifier = Models.User.GetClaimedIdentifierForUser(User.Identity.Name); // Assuming the URLs on the web server are not case sensitive (on Windows servers they almost never are), // and usernames aren‘t either, compare the identifiers without case sensitivity. // No reason to do this for the PPID identifiers though, since they *can* be case sensitive and are highly // unlikely to be typed in by the user anyway. return string.Equals(authReq.LocalIdentifier.ToString(), userLocalIdentifier.ToString(), StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) || authReq.LocalIdentifier == PpidGeneration.PpidIdentifierProvider.GetIdentifier(userLocalIdentifier, authReq.Realm); } }
新增Code文件夹和两个类:

public interface IFormsAuthentication { string SignedInUsername { get; } DateTime? SignedInTimestampUtc { get; } void SignIn(string userName, bool createPersistentCookie); void SignOut(); }

internal static class Util { internal static Uri GetAppPathRootedUri(string value) { string appPath = HttpContext.Current.Request.ApplicationPath.ToLowerInvariant(); if (!appPath.EndsWith("/")) { appPath += "/"; } return new Uri(HttpContext.Current.Request.Url, appPath + value); } }
添加引用:
在Models文件夹中添加User:

internal class User { internal static Uri ClaimedIdentifierBaseUri { get { return Util.GetAppPathRootedUri("user/"); } } internal static Uri GetClaimedIdentifierForUser(string username) { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(username)) { throw new ArgumentNullException("username"); } return new Uri(ClaimedIdentifierBaseUri, username.ToLowerInvariant()); } internal static string GetUserFromClaimedIdentifier(Uri claimedIdentifier) { Regex regex = new Regex(@"/user/([^/\?]+)"); Match m = regex.Match(claimedIdentifier.AbsoluteUri); if (!m.Success) { throw new ArgumentException(); } return m.Groups[1].Value; } internal static Uri GetNormalizedClaimedIdentifier(Uri uri) { return GetClaimedIdentifierForUser(GetUserFromClaimedIdentifier(uri)); } }
添加UserController,因为后面还会调用User里的Xrds,可以看到这里的Xrds做了两次验证,把原来Views/home 下的Xrds.cshtml移到Shared目录下,这样就可以共享

public class UserController : Controller { /// <summary> /// Identities the specified id. /// </summary> /// <param name="id">The username or anonymous identifier.</param> /// <param name="anon">if set to <c>true</c> then <paramref name="id"/> represents an anonymous identifier rather than a username.</param> /// <returns>The view to display.</returns> public ActionResult Identity(string id, bool anon) { if (!anon) { var redirect = this.RedirectIfNotNormalizedRequestUri(id); if (redirect != null) { return redirect; } } if (Request.AcceptTypes != null && Request.AcceptTypes.Contains("application/xrds+xml")) { return View("Xrds"); } if (!anon) { this.ViewData["username"] = id; } return View(); } public ActionResult Xrds(string id) { return View(); } private ActionResult RedirectIfNotNormalizedRequestUri(string user) { Uri normalized = Models.User.GetClaimedIdentifierForUser(user); if (Request.Url != normalized) { return Redirect(normalized.AbsoluteUri); } return null; } }
修改RegisterRoutes:

public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}"); routes.MapRoute( name: "User identities", url: "user/{id}/{action}", defaults: new { controller = "User", action = "Identity", id = string.Empty, anon = false }); routes.MapRoute( name: "PPID identifiers", url: "anon", defaults: new { controller = "User", action = "Identity", id = string.Empty, anon = true }); routes.MapRoute( name: "Default", url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } ); }
这里需要注意的是这里的配置,因为这里我们的用户是邮箱注册的,回调的时候是这样的:http://localhost:18180/user/123@123.com
直接访问这个地址会发现找不到页面:
需要在web.config中修改配置:

<system.webServer>
<modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests="true">
<remove name="FormsAuthentication" />
</modules>
</system.webServer>
这里一定要注意添加localhost到whitelistHosts

<messaging relaxSslRequirements="true"> <untrustedWebRequest> <whitelistHosts> <!-- Uncomment to enable communication with localhost (should generally not activate in production!) --> <add name="localhost" /> </whitelistHosts> </untrustedWebRequest> </messaging>
否则会报这个错误,
"The URL ‘http://localhost:18180/‘ is rated unsafe and cannot be requested this way."
当然这是跟源码才能得到的错误,不跟源码的话只有一个错误页面:
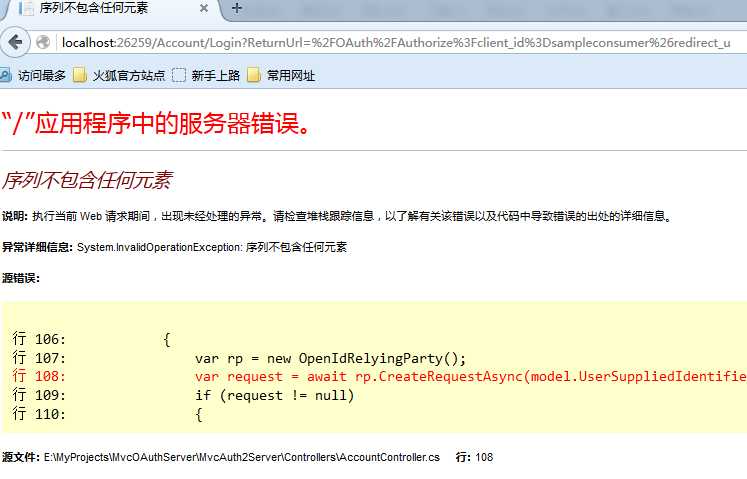
修改后运行跳转到登录页面:
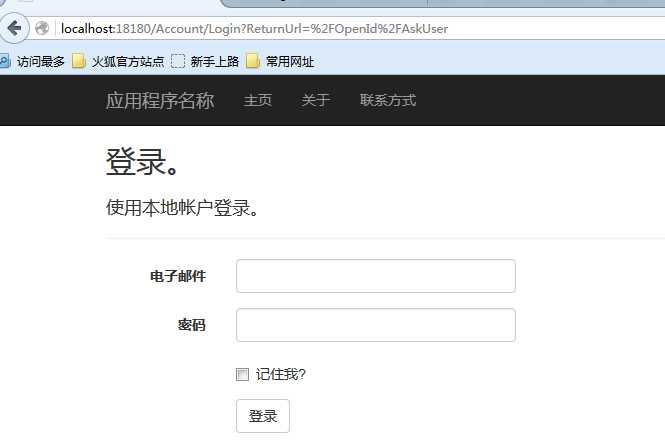
登录后跳转:
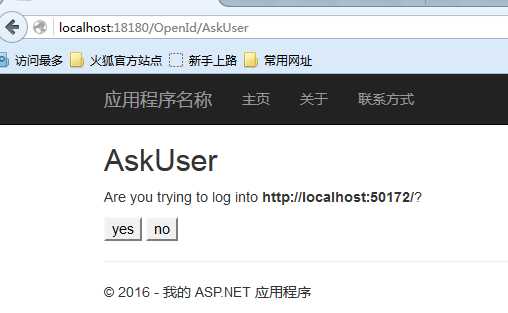
这里又需要注意了,比如在客户端我们是用1@1.com来登录的,那么在客户端的Identity.Name就是1@1.com,服务端用默认的登录会直接取这个1@1.com,那么在这里就不匹配了:

public static User LoggedInUser { get { return DataContext.Users.SingleOrDefault(user => user.OpenIDClaimedIdentifier == HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name); } }
接下来修改这些地方:
1.删除ManagerConroller
2.Startup中注销外部登录

public partial class Startup { public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app) { //ConfigureAuth(app); } }
3.web.config中修改configSections、system.web.authentication、system.webServer.modules、dotNetOpenAuth如下:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- For more information on how to configure your ASP.NET application, please visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=301880 --> <configuration> <configSections> <!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 --> <section name="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" requirePermission="false" /> <sectionGroup name="dotNetOpenAuth" type="DotNetOpenAuth.Configuration.DotNetOpenAuthSection, DotNetOpenAuth.Core"> <section name="messaging" type="DotNetOpenAuth.Configuration.MessagingElement, DotNetOpenAuth.Core" requirePermission="false" allowLocation="true" /> <section name="reporting" type="DotNetOpenAuth.Configuration.ReportingElement, DotNetOpenAuth.Core" requirePermission="false" allowLocation="true" /> <section name="oauth" type="DotNetOpenAuth.Configuration.OAuthElement, DotNetOpenAuth.OAuth" requirePermission="false" allowLocation="true" /> <section name="openid" type="DotNetOpenAuth.Configuration.OpenIdElement, DotNetOpenAuth.OpenId" requirePermission="false" allowLocation="true" /> <sectionGroup name="oauth2" type="DotNetOpenAuth.Configuration.OAuth2SectionGroup, DotNetOpenAuth.OAuth2"> <section name="authorizationServer" type="DotNetOpenAuth.Configuration.OAuth2AuthorizationServerSection, DotNetOpenAuth.OAuth2.AuthorizationServer" requirePermission="false" allowLocation="true"/> </sectionGroup> </sectionGroup></configSections> <connectionStrings> <add name="DefaultConnection" connectionString="Data Source=(LocalDb)\MSSQLLocalDB;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\MvcAuth2Server-2016.mdf;Initial Catalog=MvcAuth2Server-2016;Integrated Security=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> </connectionStrings> <appSettings> <add key="webpages:Version" value="3.0.0.0" /> <add key="webpages:Enabled" value="false" /> <add key="ClientValidationEnabled" value="true" /> <add key="UnobtrusiveJavaScriptEnabled" value="true" /> </appSettings> <system.web> <authentication mode="Forms"> <forms loginUrl="~/Account/Login" timeout="2880"/> </authentication> <compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5.2" /> <httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5.2" /> </system.web> <system.webServer> <!--<modules> <remove name="FormsAuthentication" /> </modules>--> <modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests="true"/> </system.webServer> <runtime> <assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1"> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="Microsoft.Owin.Security" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-3.0.1.0" newVersion="3.0.1.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="Microsoft.Owin.Security.OAuth" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-3.0.1.0" newVersion="3.0.1.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="Microsoft.Owin.Security.Cookies" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-3.0.1.0" newVersion="3.0.1.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="Microsoft.Owin" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-3.0.1.0" newVersion="3.0.1.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="Newtonsoft.Json" culture="neutral" publicKeyToken="30ad4fe6b2a6aeed" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-6.0.0.0" newVersion="6.0.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Optimization" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-1.1.0.0" newVersion="1.1.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="WebGrease" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-1.5.2.14234" newVersion="1.5.2.14234" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Helpers" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-3.0.0.0" newVersion="3.0.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Mvc" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-5.2.3.0" newVersion="5.2.3.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.WebPages" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-3.0.0.0" newVersion="3.0.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> </assemblyBinding> <!-- This prevents the Windows Event Log from frequently logging that HMAC1 is being used (when the other party needs it). --><legacyHMACWarning enabled="0" /><!-- When targeting ASP.NET MVC 3, this assemblyBinding makes MVC 1 and 2 references relink to MVC 3 so libraries such as DotNetOpenAuth that compile against MVC 1 will work with it. <assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1"> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Mvc" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-3.0.0.0" newVersion="3.0.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> </assemblyBinding> --></runtime> <entityFramework> <defaultConnectionFactory type="System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.LocalDbConnectionFactory, EntityFramework"> <parameters> <parameter value="mssqllocaldb" /> </parameters> </defaultConnectionFactory> <providers> <provider invariantName="System.Data.SqlClient" type="System.Data.Entity.SqlServer.SqlProviderServices, EntityFramework.SqlServer" /> </providers> </entityFramework> <system.codedom> <compilers> <compiler language="c#;cs;csharp" extension=".cs" type="Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform.CSharpCodeProvider, Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" warningLevel="4" compilerOptions="/langversion:6 /nowarn:1659;1699;1701" /> <compiler language="vb;vbs;visualbasic;vbscript" extension=".vb" type="Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform.VBCodeProvider, Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" warningLevel="4" compilerOptions="/langversion:14 /nowarn:41008 /define:_MYTYPE=\"Web\" /optionInfer+" /> </compilers> </system.codedom> <system.net> <defaultProxy enabled="true" /> <settings> <!-- This setting causes .NET to check certificate revocation lists (CRL) before trusting HTTPS certificates. But this setting tends to not be allowed in shared hosting environments. --> <!--<servicePointManager checkCertificateRevocationList="true"/>--> </settings> </system.net> <dotNetOpenAuth> <messaging relaxSslRequirements="true"> <untrustedWebRequest> <whitelistHosts> <!-- Uncomment to enable communication with localhost (should generally not activate in production!) --> <add name="localhost" /> </whitelistHosts> </untrustedWebRequest> </messaging> <!-- Allow DotNetOpenAuth to publish usage statistics to library authors to improve the library. --> <reporting enabled="true" /> <oauth2> <authorizationServer> </authorizationServer> </oauth2> </dotNetOpenAuth> <uri> <!-- The uri section is necessary to turn on .NET 3.5 support for IDN (international domain names), which is necessary for OpenID urls with unicode characters in the domain/host name. It is also required to put the Uri class into RFC 3986 escaping mode, which OpenID and OAuth require. --> <idn enabled="All" /> <iriParsing enabled="true" /> </uri></configuration>
这样就会使用DotNetOpenAuth的认证登录了:
确定后就看到授权页面了:
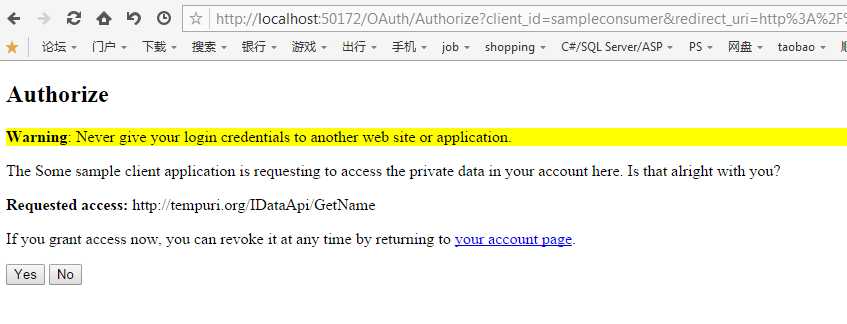
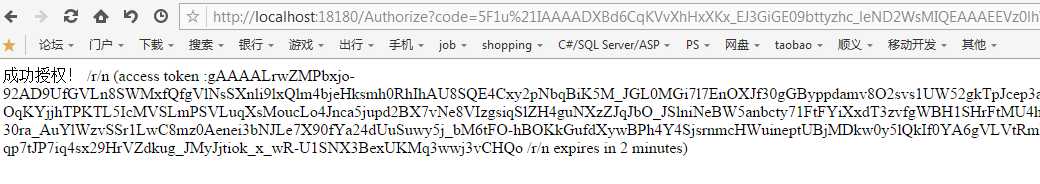
此时再看数据库记录:
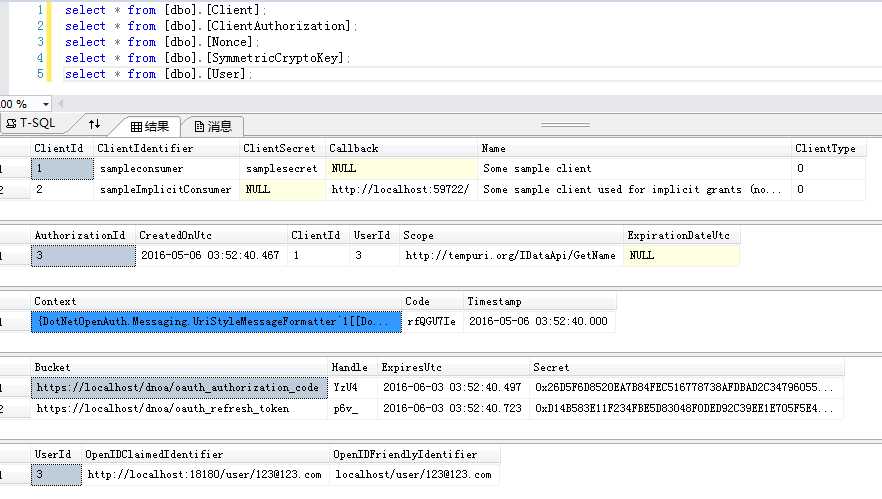
到这里基本就OK了。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/uptothesky/p/5459284.html