标签:
应掌握内容:
1. AOP的全名
2. AOP的实现原理[静态代理和动态代理]
3. 注解方式的配置
4. 通知类型
A. 每种通知的特点和使用方式
B. 获取各种数据,方便日后操作
5. 执行表达式的方式
6. XML方式的配置
7. 如何加载属性文件和注意事项
8. 如何引入资源文件,为什么只用引入资源文件
AOP的概念: 在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。
利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
百科地址: http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=bKr5CSAi8R-_3G4ai3NUvsldjm3bQfnbV7O1LKrOyLafbJyyXr-PO6_9t7lHJDfnhQ7oWRkApHJXTEg3VY0Jh8TXrvS1v41JXmz0xg8pYuG
模拟开发情景:
项目经理,我根据客户的需求[预先定义好了接口],让程序员A某完成业务功能,加法运算和减法运算!实现对应的接口功能! 代码如下,定义好接口
//对核心业务进行实现: package com.shxt.core.impl; import com.shxt.core.OperationService; public class OperationServiceImpl implements OperationService { @Override public int add(int i, int j) { int result = i+j; return result; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { int result = i-j; return result; } }
//核心业务: package com.shxt.core; public interface OperationService { public int add(int i ,int j); public int sub(int i ,int j); }
项目经理调用,客户看到我们做东西,感觉不是他想要,应该给他看到你传递数据和结果的显示[重新写一下核心代码,复制] public class OperationServiceImpl implements OperationService { @Override public int add(int i, int j) { System.out.println("加法传递的参数为: i="+i+",j="+j); int result = i+j; System.out.println("运行结果为--->>>>"+result); return result; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { System.out.println("减法传递的参数为: i="+i+",j="+j); int result = i-j; System.out.println("运行结果为--->>>>"+result); return result; } }
又出情况了:项目经理又去给客户看这东西,不需要看到参数和结果,使用静态代理完成
package com.shxt.core.impl; import com.shxt.core.OperationService; //实现接口,但是不对核心代码做任何的改变,只是增加功能而已 public class OperationLogServiceImpl implements OperationService { OperationServiceImpl osi = new OperationServiceImpl();//--->>>注意这里 @Override public int add(int i, int j) { System.out.println("加法传递的参数为: i="+i+",j="+j);//1.新增功能 int result = osi.add(i, j);//调用核心代码 System.out.println("运行结果为--->>>>"+result);//2.新增功能 return result; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { System.out.println("减法传递的参数为: i="+i+",j="+j);//1.新增功能 int result = osi.sub(i, j);//调用核心代码 System.out.println("运行结果为--->>>>"+result);//2.新增功能 return result; } }
测试类代码为: public class RunTest { private OperationService os = null; @Before public void init(){ os = new OperationLogServiceImpl(); } @Test public void 测试加法运算(){ int result = os.add(2, 3); } @Test public void 测试减法运算(){ int result = os.sub(4, 1); } }
又出情况了: 客户需要乘法的操作,相应的实现类需要进行修改,缺点: 被动
解释一下动态代理:自行补充
AOP的底层,就是通过Java的动态代理【自学内容】来实现,理解在不改变原来代码的情况下,增加新的功能。
搭建环境:需要在额外的20个jar包外,多引用3个jar包 http://www.mvnrepository.com/

<!-- 核心配置文件配置 --> <!-- 开启Spring注解 --> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- 扫描,如果多个包使用空格或者逗号 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.shxt"/> <!-- 启动AspectJ注解 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
@Component @Aspect //定义切面 public class LogAspect { @Around(value="execution(public int com.shxt.core.OperationService.add(int,int))") public Object test01(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ System.out.println("*******"); Object result = null; try { result = joinPoint.proceed(); } catch (Throwable e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } } 代码说明:--->>>>
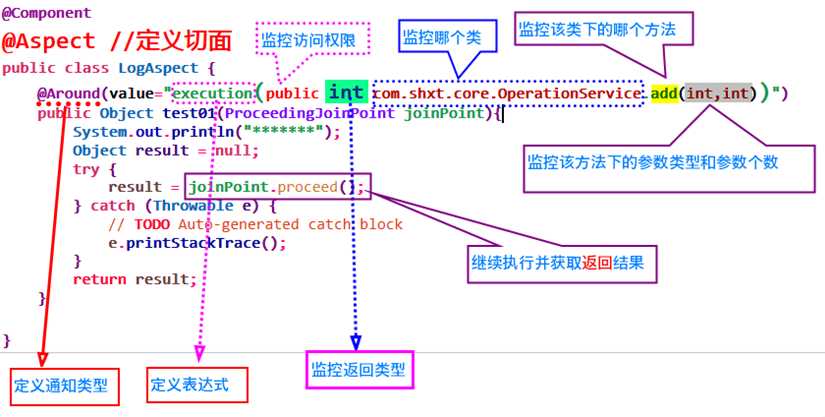
表达式使用说明:
/**
* 表达式当中:可以使用 && 等价于 and || 等价于 or ! 非
* 重点说明 : "execution(public * com..service.*Service.*(..))"
* 第一个 * 代表任意的放回类型 int void String Object
* 第二个 .. 任意层次 .*.service 代表一个层次
* 第三个 *Service 要查找以Service结束的类
* 第四个 * 代表该类下的所有方法 还可以这样写:add* query*
* 第五个 .. 代表任意个的参数和任意类型,如何制定,应该如下 (int,String)
* */
//第五种通知--->>>环绕通知@Around:包含前置通知,返回通知,异常通知,后置通知 //能力越大责任越大,消耗越大 --->>> 慎重使用 @Around(value="execution(public * com..core.*Service.*(..))") public Object test01(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ Object result = null; try { System.out.println("第一种通知--->>>前置通知@Before-->>不管出现任何状况,都会执行处理");//功能1 result = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("第二种通知--->>>返回通知[经常会用]@AfterReturning-->>有且只有正常执行后,才可以执行相关处理-->>"+result);//业务2 } catch (Throwable e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("第三种通知--->>>异常通知-->>只有出现异常的情况下才处理相关的程序-->>"+e.getMessage());//异常处理 } System.out.println("第四种通知--->>>后置通知@After-->>不管出现任何状况,都会执行处理"+result);//收尾功能 return result; }


前置通知介绍:
/* * 练习题一:前置通知只能监控加法或者减法 */ //定义一个前置通知的切入点 @Pointcut("execution(* com.shxt.core.*Service.add(int,int))||execution(* com.shxt.core.*Service.sub(int,int))") public void beforeAdvice(){} @Before(value="beforeAdvice()") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){ System.out.println("前置通知:无法获取到结果集"); System.out.println("传递的参数:"+Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs())); System.out.println("不知道:"+joinPoint.getKind()); System.out.println("获取接口对应-全路径:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName()); System.out.println("获取接口对应-简写"+joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName()); System.out.println("执行的方法名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); System.out.println("获取代理实现类的--全路径:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName()); System.out.println("获取代理实现类的--简写:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName()); }
返回通知介绍:
//定义一个返回通知的切入点 @Pointcut("execution(* com.shxt.core.*Service.add(int,int))") public void returningAdvice(){} @AfterReturning(value="returningAdvice()",returning="shxt") public void returning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object shxt){ System.out.println("返回通知:可以获取到结果集--需要注意形参跟returning的字串一样:"+shxt); }
后置通知介绍:
//定义一个后置通知的切入点 @Pointcut("execution(* com.shxt.core.*Service.add(int,int))") public void afterAdvice(){} @After(value="afterAdvice()") public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint){ System.out.println("后置通知:无法获取到结果集"); }
异常通知介绍:
//定义一个异常通知的切入点 @Pointcut("execution(* com.shxt.core.*Service.*(int,int))") public void thorwingAdvice(){} @AfterThrowing(value="thorwingAdvice()",throwing="ex") public void thorwing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception ex){ System.out.println("异常通知通:"+ex.getMessage()); }
私人定制异常: 跟自己的项目情况,可以对异常做特殊的处理 @Pointcut("execution(* com.shxt.core.*Service.*(int,int))") public void thorwingAdvice(){} @AfterThrowing(value="thorwingAdvice()",throwing="ex") public void thorwing(JoinPoint joinPoint,RbacException ex){ System.out.println("异常通知:"+ex.getMessage()); }
注解的推荐方法
/* * 前置通知: * 1.监控OperationServiceImpl的运行 * 2.不监控MyServiceImpl的运行 * */ //第一种 //@Pointcut("execution(public * com..core.impl.OperationServiceImpl.*(..))") //第二种 //@Pointcut("execution(public * com..core.*Service.*(..))&&!execution(public * com..impl.MyServiceImpl.*(..))") //第三种[推荐] 定义多个切入点进行罗列,之后可以根据实际开发的情况,进行各种组合! @Pointcut("execution(public * com..core.*Service.*(..))") public void shxt01(){} @Pointcut("bean(myServiceImpl)") public void shxt02(){} @Before("shxt01()&&!shxt02()") public void test01(){ System.out.println("***前置通知***"); } /* * 后置通知: * 1.监控所有的运行 * */ @After("shxt01()") public void test02(){ System.out.println("***后置通知***"); }
XML配置方式
public class LogAspect { public void test01(){ System.out.println("***前置通知***"); } public void test02(){ System.out.println("===悟空==="); } }
<bean id="logAspect" class="com.shxt.aspect.LogAspect"/><!-- @Component -->
<!--
配置AOP
当通知类型一致的时候,如果有多个切面,可以使用order进行排序!
注意引用关系
-->
<aop:config >
<!-- 定义切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="logAspect" order="2"><!-- @Aspect -->
<!-- 切入点 @Pointcut-->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com..*Service.*(..))" id="serviceMethodPointCut"/>
<!-- 前置通知 @Before-->
<aop:before method="test01" pointcut-ref="serviceMethodPointCut"/>
</aop:aspect>
<!-- 定义切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="logAspect" order="1">
<!-- 切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com..*Service.*(..))" id="serviceMethodPointCut2"/>
<aop:before method="test02" pointcut-ref="serviceMethodPointCut2"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
优化代码,定义多个切入点
public class LogAspect { public void test01(){ System.out.println("***前置通知***"); } public void test02(Object shxt){ System.out.println("===悟空==="+shxt); } }
<!-- 配置AOP --> <aop:config > <!-- 切入点 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com..*Service.*(..))" id="serviceMethodPointCut"/> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com..*Service.*(..))" id="serviceMethodPointCut2"/> <!-- 定义切面 --> <aop:aspect ref="logAspect" order="2"> <aop:before method="test01" pointcut-ref="serviceMethodPointCut"/> </aop:aspect> <aop:aspect ref="logAspect" order="1"> <aop:after-returning method="test02" returning="shxt" pointcut-ref="serviceMethodPointCut2"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
附录:请查看API文档,对自己很有收获
XML方式
execution[执行表达式] - 匹配方法执行的连接点,这是Spring AOP的工作时,你将使用的主要切入点指示符,一定要知道*和..的使用
within - 限定匹配特定的连接某些类型的内点(使用Spring AOP的时候,在匹配的类型中定义的方法的执行),也可以说是对execution的一种简写方式。
this[当前对象] - 限定匹配特定的连接点,其中bean reference(Spring AOP的代理)是指定类型的目标的一个实例(方法使用Spring AOP时执行) - 匹配特定的连接点(方法的执行使用Spring AOP的时候)的限制的目标对象(被代理应用对象)是给定类型的一个实例
args - 限定匹配特定的连接点(方法使用Spring AOP时执行),其中参数是指定类型的实例
注解方式
@target - 限定匹配(使用Spring AOP的时候方法的执行),其中类执行对象的具有给定类型@args的注释的连接点 - 匹配特定的连接点(方法的执行使用Spring AOP的时候)的限制其中,通过实际参数的运行时类型有指定类型的注解。
@within - 限定匹配(使用Spring AOP的时候,类型与指定注解方法的执行)具有给定的注释类型中的连接点
@annotation - 限定匹配特定的连接点,其中连接点(在Spring AOP的时候方法的执行)的主体具有给定的注释
还有那个bean的使用,还记得不??????
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lusid/p/5482329.html