标签:
输入输出流
File
使用路径字符串来创建File类实例,相关方法见API,文件路径可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径,但系统会根据用户的工作路径来解释相对路径,需要留意.
可以getName(),getAbsoluteFile(),getParent(),list()等等
IO流
分为输入流和输出流,其中输入流以InputStream和Reader作为基类,输出流以OutputStream和Writer作为基类,它们都属于抽象类,不可直接创建实例。
分为字节流和字符流,字节流操作单位是8位的字节,而字符流操作的单位是16位的字符。
分为节点流和处理流,其中节点流是直接访问数据源的底层操作,处理流是对底层的数据流进行封装,而且封装好的流非常好用。
流的概念详解
所有流都是从InputStream/Reader、OutputStream/Writer四个基类中派生,都提供方法记录指针移动
InputStream
int read() 读取单个字节,返回实际读取的字节,访问的字节数据直接转为int
int read(byte[] b) 最多读取b.length()个字节,存储在b中。
int read(byte[] b,int off,int len) 从输入流中最多读取len个字节,存储在b数组中,从off位置开始,返回实际读取的字符数量,这里是返回数量,不是read()放回读取的数据。
Writer
void write(int c) 将单个字符写入输出流
void write(byte[] buf) 将buf写入输出流
void write(byte[] buf,int off,int len) 将buf从off开始写入len个字符
其中字符流以字符作为操作单位,可以字符串来代替字符数组故Writer还包括
void write(String str)
void write(String str,int off,int len)
记得执行结束后显式关闭输出流close(),或者使用java7之后的try(){}cath{}语句自动关闭
Windows平台的换行符是\r\n,UNIX/Linux等平台为\n
常用的节点流
1. FileWriter/FileOutputStream,FileReader/FileInputStream
显然FileWriter是以字节方式,读取文本非常方便
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class FileWriterTest { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 try{ 6 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("poem.txt"); 7 fw.write("小草\r\n"); 8 fw.write("离离原上草\r\n"); 9 fw.write("一岁一枯荣\r\n"); 10 fw.write("野火烧不尽\r\n"); 11 fw.write("春风吹又生\r\n"); 12 }catch(IOException e) 13 { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 17 } 18 }
2.ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream
可以以二进制形式存储自定义的对象,注意该对象必须implements Serializable,读写时先用文件流,再用对象流进行处理
核心代码
//读入操作
FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream(new File("对象.txt"));
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(fi); Student[] studentReader = (Student[])oi.readObject(); oi.close();
//写出操作
File file = new File("对象.txt"); FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream(file); ObjectOutputStream oo = new ObjectOutputStream(fo); oo.writeObject(student); oo.close();
完整代码(使用windowsbuilder插件)

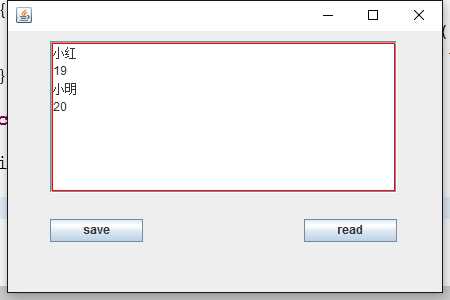
1 package Object; 2 3 import java.awt.Color; 4 import java.awt.EventQueue; 5 import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; 6 import java.awt.event.ActionListener; 7 import java.io.File; 8 import java.io.FileInputStream; 9 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 10 import java.io.IOException; 11 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 12 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 13 14 import javax.swing.JButton; 15 import javax.swing.JFrame; 16 import javax.swing.JScrollPane; 17 import javax.swing.JTextArea; 18 import javax.swing.ScrollPaneConstants; 19 import javax.swing.border.BevelBorder; 20 21 public class ObjectDemo { 22 23 private JFrame frame; 24 public Student[] student; 25 private JTextArea textArea; 26 /** 27 * Launch the application. 28 */ 29 public static void main(String[] args) { 30 EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() { 31 public void run() { 32 try { 33 ObjectDemo window = new ObjectDemo(); 34 window.frame.setVisible(true); 35 } catch (Exception e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 } 39 }); 40 } 41 42 /** 43 * Create the application. 44 */ 45 public ObjectDemo() { 46 initialize(); 47 } 48 49 /** 50 * Initialize the contents of the frame. 51 */ 52 private void initialize() { 53 frame = new JFrame(); 54 frame.setBounds(100, 100, 450, 300); 55 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 56 frame.getContentPane().setLayout(null); 57 58 JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(); 59 scrollPane.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(ScrollPaneConstants.VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER); 60 scrollPane.setViewportBorder(new BevelBorder(BevelBorder.LOWERED, new Color(255, 0, 0), null, Color.RED, null)); 61 scrollPane.setBounds(42, 10, 347, 152); 62 frame.getContentPane().add(scrollPane); 63 64 textArea = new JTextArea(); 65 scrollPane.setViewportView(textArea); 66 67 JButton btnSave = new JButton("save"); 68 btnSave.setBounds(42, 188, 93, 23); 69 btnSave.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){ 70 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ 71 saveActionPerformed(); 72 } 73 74 }); 75 frame.getContentPane().add(btnSave); 76 77 JButton btnRead = new JButton("read"); 78 btnRead.setBounds(296, 188, 93, 23); 79 btnRead.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){ 80 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ 81 readActionPerformed(); 82 } 83 }); 84 frame.getContentPane().add(btnRead); 85 86 student = new Student[]{new Student("小红","19"),new Student("小明","20")}; 87 for(Student student1 : student) 88 { 89 this.textArea.append(student1.getName()+"\n"); 90 this.textArea.append(student1.getAge()+"\n"); 91 } 92 } 93 protected void saveActionPerformed() 94 { 95 try{ 96 this.textArea.setText(null); 97 File file = new File("对象.txt"); 98 FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream(file); 99 ObjectOutputStream oo = new ObjectOutputStream(fo); 100 oo.writeObject(student); 101 oo.close(); 102 }catch(IOException ioe) 103 { 104 ioe.printStackTrace(); 105 } 106 } 107 protected void readActionPerformed() 108 { 109 try{ 110 FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream(new File("对象.txt")); 111 ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(fi); 112 Student[] studentReader = (Student[])oi.readObject(); 113 oi.close(); 114 for(Student student : studentReader) 115 { 116 this.textArea.append(student.getName()+"\n"); 117 this.textArea.append(student.getAge()+"\n"); 118 } 119 120 }catch(Exception ioe) 121 { 122 ioe.printStackTrace(); 123 } 124 } 125 }
好用的处理流
1 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.io.PrintStream; 4 public class PrintStreamTest { 5 public static void main(String[] args) 6 { 7 try{ 8 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("PrintStreamTest.txt"); 9 PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(fos); 10 ps.println("想写入什么就写入什么"); 11 ps.println(new PrintStreamTest()); 12 ps.close(); 13 14 15 }catch(IOException ioe) 16 { 17 ioe.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 } 20 }
非常强大的输出处理流,System.out就是PrintStream型,其print方法可以说是想写入什么就写入什么
而且只需关闭最上层的处理流,下层的会自动关闭。
小结
计算机的文件通常分为文本文件和二进制文件,显然字节处理方式较强大,因为字节可以转为字符,但需要考虑用合适的方式来转为字符。比如Windows简体中文默认是GBK字符集,而linux下默认是UTF-8。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ajmd/p/5474523.html