标签:
《算法导论》第二版中在讨论斐波那契堆之前还讨论了二项堆,但是第三版中已经把这块的内容放到思考题中,究极原因我想大概是二项堆只是个引子,目的是为了引出斐波那契堆,便于理解,而且许多经典的算法实现都是基于斐波那契堆,譬如计算最小生成树问题和寻找单源最短路径问题等,此时再把二项堆单独作为一章来讲显然没有必要。类似的堆结构还有很多,如左倾堆,斜堆,二项堆等,下次我打算开一篇博客来记录下它们的异同点。
一、摊还分析(第十七章)
这些高级的数据结构的性能分析一般是基于一个技术——摊还分析,可以理解成一种时间复杂度的分析方法。它的提出是基于这样一个事实:并不能总以最坏情况来衡量一个算法的性能,因为最坏情况并不总会发生,而且在绝大多数应用中最坏情况出现的次数是极小的。从字面意思上理解这种分析方法,就是将一系列操作所需要的时间平均分摊到每一个操作上,使得每一个操作,在最坏情况下,具有平均性能。这样的分析方法看上去有点像平均情况分析,但其实有着本质的不同,其一,摊还分析是通过求一系列操作的平均时间来评价某一操作的性能,即使其中某一操作的代价很高,都能保证它们具有较低的平均性能,而平均情况分析则是单独针对某一操作来评价;其二,摊还分析不涉及概率计算,只是对一个整体求平均值,而平均情况则不然,代价高的操作自然占总开销的概率就大。
要理解的是,摊还分析强调的是一个“操作序列”,一般低级的数据结构操作都用不到这种分析方法,而高级的数据结构,说白了,就是结合多种低级数据结构形成的,因此在对这些数据结构进行操作时,涉及到一个序列的操作,而其中可能存在每个操作的时间复杂度都不一样,有的很高,有的又几乎可以忽略,所以采用这种摊还分析方法更加适合分析这些数据结构的操作性能。就以本文将要说的斐波那契堆来说,这种堆结构是由“堆排序”中所用到的最小堆组成,至于为什么叫这个名字,是由斐波那契堆上每个节点的度所决定的——其具有斐波那契数列的性质(具体可以看书本的推导)。另外,再来看一个书上提出的例子——栈操作:
1 Multi-Pop(S, k) 2 while not Stack-Empty(S) and k > 0 3 POP(S) 4 k = k - 1
其中,POP()操作的代价是1,假设栈的大小最大为n,一般的时间复杂度的分析方法是:Multi-Pop()操作在最坏情况下的代价为O(n),那么假设有n个这样的操作,则最坏情况下时间复杂度就为O(n^2),虽然这种分析方法是正确的,但通过单独分析每个操作的最坏情况代价得到的操作序列的最坏情况时间O(n^2)并不是一个确界。如果使用摊还分析方法(方法有三种,具体可以查看书本,此处不做详述),则可以得到更好的上界。分析如下:从整体上来看,n个Multi-Pop()序列的操作,最多进行n次,因为POP()的次数最多与栈的大小相等,有多少个元素就POP多少次,即使有n次的操作也是如此。所以,n次序列的操作,代价至多为O(n),任意一个操作的平均时间就为O(n)/n=O(1),这个就是Multi-Pop()的摊还代价。
二、斐波那契堆
1、斐波那契堆由一组最小堆序有根树组成,其中每棵树必须满足最小堆的性质;
2、每个最小堆用一个双循环链表连接起来,称为根链表;
3、斐波那契堆是一种合并堆,除了支持可合并堆的五种操作之外(Make-Heap, Insert, Minimum, Extract_min, Union),还支持Decrease_Key和Delete两种操作;
4、斐波那契堆是为了改进普通二叉堆Union操作( O(n) )而提出的一种可合并堆,除了Union操作,普通二叉堆都能在最坏情况时间为O(lgn)下完成,但斐波那契堆所有操作均能在常数摊还时间下完成,除了Extract_min和Delete操作。
5、斐波那契堆在优化加速图算法中有很大的用途。比如用于解决诸如最小生成树、寻找单源最短路径等问题的快速算法都要用到斐波那契堆。
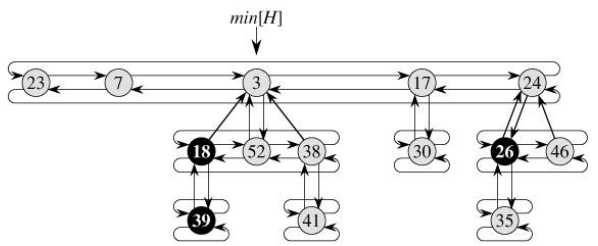
6、斐波那契堆具有以下属性:
1)根节点的孩子节点也组成一个双循环链表,称为孩子链表;
2)每个节点有指向父亲节点,指向某一个孩子节点,指向左兄弟节点和有兄弟节点的指针;
3)H.min指向根链表中的最小节点;
4)H.n表示节点数目
5)每个节点x有两个属性: x.degree表示节点的度; x.mark则用来标识一个非根结点是否已经失去 了一个孩子(这样的结点,不能在夺其子女了,可能要进行一些其它的特别操作),该标志主要用于删除操作。下面看一个斐波那契堆的内存结构图(引自:斐波那契堆之图文解析)
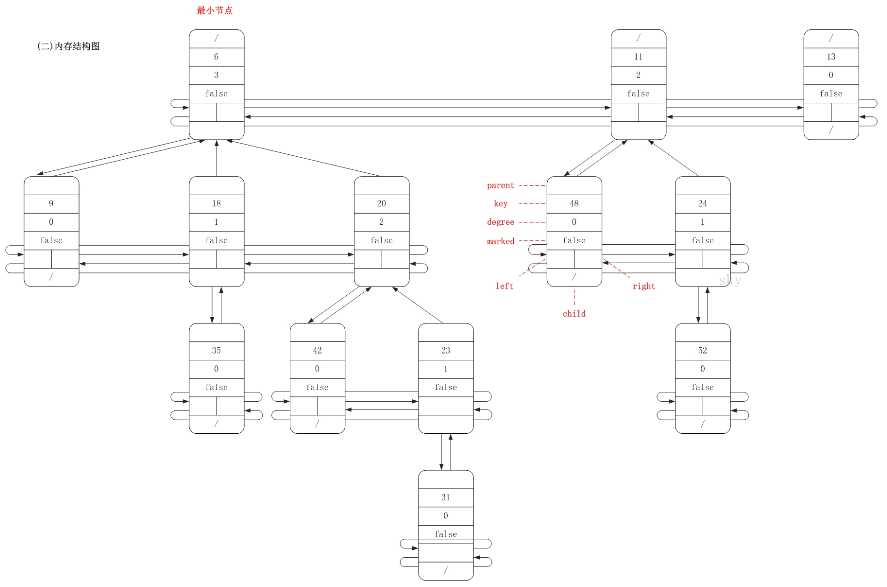
1 template<typename Data, typename Key> 2 class FibHeapNode 3 { 4 public: 5 template<typename D, typename K> friend class FibHeap; 6 FibHeapNode() {} 7 FibHeapNode( Data d, Key k): 8 myKey( k ), 9 myData( d ), 10 degree( 0 ), 11 marked( false ), 12 child( NULL ) 13 { 14 prev = next = this; //doubly linked circular list 15 } 16 17 Key key() const 18 { 19 return myKey; 20 } 21 22 Data data() const 23 { 24 return myData; 25 } 26 28 private: 29 Key myKey; 30 Data myData; 31 32 unsigned int degree; //节点的孩子节点数 33 bool marked; //标识一个节点的孩子节点是否被删除过,用于decreaseKey 操作 34 35 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *prev; //双循环链表的上一个节点 36 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *next; //双循环链表的下一个节点 37 38 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *child; //孩子链表中的第 39 一个节点 40 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *parent;//父节点 41 };
下面是斐波那契堆类的定义:
1 template<typename Data, typename Key> 2 class FibHeap 3 { 4 public: 5 FibHeap() {} 6 FibHeap(): rootWithMinKey( NULL ), nCount( 0 ), maxDegree( 0 ) { } 7 8 ~FibHeap(){ 9 10 } 11 12 13 private: 14 typedef FibHeapNode<Data, Key>* pNode; 15 16 pNode rootWithMinKey; 17 unsigned int nCount; 18 unsigned int maxDegree; 19 };
三、斐波那契堆动态集合的操作
其中最难的,也是最麻烦的可能就是Extrac_min()和Decrease_key()操作了,书上对于这两个操作也是写得很详细,具体的我就不再赘述了,我相信认真照着书本上推导,一个下午绝对可以搞定,如果确实难以吃下,推荐一个博客:斐波那契堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现,其图文并茂的方式可能比书上更浅显易懂一点,感谢作者。下面附上自己借鉴这个作者所写的程序:

#ifndef _FIBONACCI_HEAP_H_ #define _FIBONACCI_HEAP_H_ template<typename Data, typename Key> class FibHeapNode { public: template<typename D, typename K> friend class FibHeap; FibHeapNode() {} FibHeapNode( Data d, Key k): myKey( k ), myData( d ), degree( 0 ), marked( false ), child( NULL ) { prev = next = this; //doubly linked circular list } Key key() const { return myKey; } Data data() const { return myData; } public: bool isSingle() const { return ( this == this->next ); } //插入一个节点或节点链表 void Insert( FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *other ) { if ( !other ) return; //for example: given 1->2->3->1, insert a->b->c->a after node 3; //result: 1->2->3->a->b->c->1 this->next->prev = other->prev; other->prev->next = this->next; this->next = other; other->prev = this; } //删除当前节点 void RemoveNode() { this->prev->next = this->next; this->next->prev = this->prev; this->next = this->prev = this; } //连接其他节点到当前节点 void addChild( FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *other ) { if ( !child ) child = other; else child->Insert( other ); //更新相应的信息 other->parent = this; other->marked = false; degree ++; } //删除孩子节点 void removeChild( FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *other ) { if ( other->parent != this ) throw string ( "Trying to remove a child from a non-parent!"); //只有一个节点 if ( other->isSingle() ) { if ( child != other ) throw string ("Trying to remove a non-child"); child = NULL; } else { if ( child == other ) { child = other->next; } other->RemoveNode(); } //更新 other->parent = NULL; other->marked = false; degree --; } //<<操作符重载 friend ostream& operator<< ( ostream& out, const FibHeapNode& n) { return ( out << n.myData << ";" << n.myKey ); } //打印树 void printTree( ostream& out ) const { out << myData << ":" << myKey << ":" << degree << ":" << marked; if ( child ) { out << "("; const FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *n = child; do { if ( n== this ) throw string ( "Illegal pointer - node is child of itself"); n->printTree( out ); out << " "; n = n->next; }while ( n != child ); out << ")"; } } void printAll( ostream& out) const { const FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *n = this; do { n->printTree( out ); out << " "; n = n->next; }while ( n != this ); out << endl; } private: Key myKey; Data myData; unsigned int degree; //节点的孩子节点数 bool marked; //标识一个节点的孩子节点是否被删除过,用于decreaseKey 操作 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *prev; //双循环链表的上一个节点 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *next; //双循环链表的下一个节点 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *child; //孩子链表中的第 一个节点 FibHeapNode<Data, Key> *parent;//父节点 }; template<typename Data, typename Key> class FibHeap { public: FibHeap() {} FibHeap(): rootWithMinKey( NULL ), nCount( 0 ), maxDegree( 0 ) { } ~FibHeap(){ } bool empty() const { return nCount == 0; } pNode minimum() const { if ( !rootWithMinKey ) throw string("no minimum element"); return rootWithMinKey; } void printRoots( ostream &out ) const { out << "maxDegree=" << maxDegree << " count=" << count << " roots="; if ( rootWithMinKey ) rootWithMinKey->printAll( out ); else out << endl; } void merge ( const FibHeap& other ) // Fibonacci-Heap-Union { rootWithMinKey->Insert( other.rootWithMinKey ); if ( !rootWithMinKey || ( other.rootWithMinKey && other.rootWithMinKey->key() < rootWithMinKey->key() ) ) this->rootWithMinKey = other.rootWithMinKey; nCount += other.nCount; } pNode insertHeap( Data d, Key k ) { nCount ++; return insertNode( new FibHeapNode<Data, Key>(d, k)); } void removeMinimum() // Fibonacci-Heap-Extract-Min, CONSOLIDATE { if ( !rootWithMinKey ) throw string( "trying to remove from an empty heap" ); /// Phase 1: Make all the removed root‘s children new roots: // Make all children of root new roots: if ( rootWithMinKey->child ) { pNode c = rootWithMinKey->child; do { c->parent = NULL; c = c->next; } while ( c != rootWithMinKey->child ); rootWithMinKey->child = NULL; // removed all children rootWithMinKey->Insert( c ); } /// Phase 2-a: handle the case where we delete the last myKey: if ( rootWithMinKey->next == rootWithMinKey ) { if ( count != 0 ) throw string ( "Internal error: should have 0 keys" ); rootWithMinKey = NULL; return; } /// Phase 2: merge roots with the same degree: vector<pNode> degreeRoots ( maxDegree + 1 ); // make room for a new degree fill ( degreeRoots.begin(), degreeRoots.end(), ( pNode )NULL ); maxDegree = 0; pNode currentPointer = rootWithMinKey->next; unsigned int currentDegree; do { currentDegree = currentPointer->degree; pNode current = currentPointer; currentPointer = currentPointer->next; while ( degreeRoots[currentDegree] ) // merge the two roots with the same degree: { pNode other = degreeRoots[currentDegree]; // another root with the same degree if ( current->key() > other->key() ) swap( other, current ); // now current->key() <= other->key() - make other a child of current: other->RemoveNode(); // remove from list of roots current->addChild( other ); degreeRoots[currentDegree] = NULL; currentDegree++; if ( currentDegree >= degreeRoots.size() ) degreeRoots.push_back( ( pNode )NULL ); } // keep the current root as the first of its degree in the degrees array: degreeRoots[currentDegree] = current; } while ( currentPointer != rootWithMinKey ); /// Phase 3: remove the current root, and calcualte the new rootWithMinKey: delete rootWithMinKey; rootWithMinKey = NULL; unsigned int newMaxDegree = 0; for ( unsigned int d = 0; d < degreeRoots.size(); ++d ) { if ( degreeRoots[d] ) { degreeRoots[d]->next = degreeRoots[d]->prev = degreeRoots[d]; insertNode( degreeRoots[d] ); if ( d > newMaxDegree ) newMaxDegree = d; } } maxDegree = newMaxDegree; } void decreaseKey( pNode node, Key newKey ) { if ( newKey >= node->myKey ) throw string( "Trying to decrease key to a greater key" ); // Update the key and possibly the min key: node->myKey = newKey; // Check if the new key violates the heap invariant: pNode parent = node->parent; if ( !parent ) // root node - just make sure the minimum is correct { if ( newKey < rootWithMinKey->key() ) rootWithMinKey = node; return; // heap invariant not violated - nothing more to do } else if ( parent->key() <= newKey ) { return; // heap invariant not violated - nothing more to do } for( ;; ) { parent->removeChild( node ); insertNode( node ); if ( !parent->parent ) // parent is a root - nothing more to do { break; } else if ( !parent->marked ) // parent is not a root and is not marked - just mark it { parent->marked = true; break; } else { node = parent; parent = parent->parent; continue; } } } void remove( pNode node, Key minusInfinity ) { if ( minusInfinity >= minimum()->key() ) throw string( "2nd argument to remove must be a key that is smaller than all other keys" ); decreaseKey( node, minusInfinity ); removeMinimum(); } protected: pNode insertNode ( pNode newNode ) { if ( !rootWithMinKey ) rootWithMinKey = newNode; else { rootWithMinKey->Insert( newNode ); if ( newNode->key() < rootWithMinKey->key() ) rootWithMinKey = newNode; } return newNode; } private: typedef FibHeapNode<Data, Key>* pNode; pNode rootWithMinKey; unsigned int nCount; unsigned int maxDegree; }; #endif//_FIBONACCI_HEAP_H_
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bakari/p/5486841.html