标签:
Android的View绘制是从根节点(Activity是DecorView)开始,他是一个自上而下的过程。View的绘制经历三个过程:Measure、Layout、Draw。基本流程如下图:
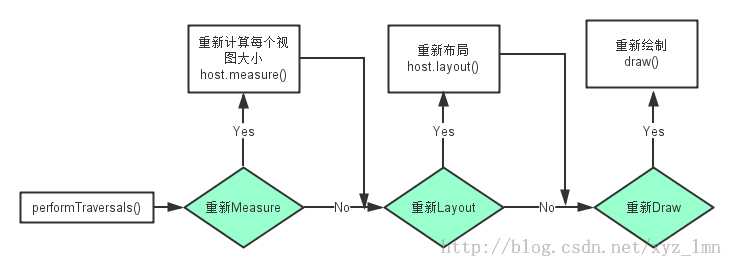
performTraversals函数,具体的可以参考一下源代码:
1 private void performTraversals() { 2 final View host = mView; 3 ... 4 host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); 5 ... 6 host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight()); 7 ... 8 draw(fullRedrawNeeded); 9 }
Measure过程是计算视图大小,View中视图measure过程相关的方法主要有三个:
1 public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 2 protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) 3 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
measure调用onMeasure,onMeasure调用setMeasureDimension,measure,setMeasureDimension是final类型,view的子类不需要重写,onMeasure在view的子类中重写。
measure函数:
1 public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 2 if ((mPrivateFlags & FORCE_LAYOUT) == FORCE_LAYOUT || 3 widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec || 4 heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec) { 5 6 // first clears the measured dimension flag 7 mPrivateFlags &= ~MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET; 8 9 if (ViewDebug.TRACE_HIERARCHY) { 10 ViewDebug.trace(this, ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType.ON_MEASURE); 11 } 12 13 // measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back 14 onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 15 16 // flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise 17 // an exception to warn the developer 18 if ((mPrivateFlags & MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) { 19 throw new IllegalStateException("onMeasure() did not set the" 20 + " measured dimension by calling" 21 + " setMeasuredDimension()"); 22 } 23 24 mPrivateFlags |= LAYOUT_REQUIRED; 25 } 26 27 mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec; 28 mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec; 29 }
onMeasure函数:
1 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 2 setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), 3 getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec)); 4 }
重写onMeasure时,要调用setMeasuredDimension或者super.onMeasure来设置自身的mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight,否则,就会抛出异常.
setMeasuredDimension函数,用来设置view的大小:
1 protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) { 2 mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth; 3 mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight; 4 5 mPrivateFlags |= MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET; 6 }
再看一下onMeasure的getDefaultSize函数:
1 public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) { 2 int result = size; 3 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); 4 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); 5 6 switch (specMode) { 7 case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: 8 result = size; 9 break; 10 case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: 11 case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: 12 result = specSize; 13 break; 14 } 15 return result; 16 }
这里用引入了MeasureSpec类:
1 public static class MeasureSpec { 2 3 private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30; 4 private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT; 5 public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT; 6 public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT; 7 public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT; 8 9 public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) { 10 return size + mode; 11 } 12 13 public static int getMode(int measureSpec) { 14 return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK); 15 } 16 17 public static int getSize(int measureSpec) { 18 return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK); 19 } 20 }
MODE_MASK为30为长度的二进制数,前两位标示Mode,后面的标示Size。MeasureSpec有三种模式分别是UNSPECIFIED, EXACTLY和AT_MOST。
EXACTLY表示父视图希望子视图的大小应该是由specSize的值来决定的,系统默认会按照这个规则来设置子视图的大小,开发人员当然也可以按照自己的意愿设置成任意的大小。
AT_MOST表示子视图最多只能是specSize中指定的大小,开发人员应该尽可能小得去设置这个视图,并且保证不会超过specSize。系统默认会按照这个规则来设置子视图的大小,开发人员当然也可以按照自己的意愿设置成任意的大小。
UNSPECIFIED表示开发人员可以将视图按照自己的意愿设置成任意的大小,没有任何限制。这种情况比较少见,不太会用到。
widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec决定了Mode和Size的值,widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec来自父视图,这两个值都是由父视图经过计算后传递给子视图的,说明父视图会在一定程度上决定子视图的大小。但是最外层的根视图,它的widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec又是从哪里得到的呢?这就需要去分析ViewRoot中的源码了,观察performTraversals()方法可以发现如下代码:
1 childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width); 2 childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
可以看到,这里调用了getRootMeasureSpec()方法去获取widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec的值,注意方法中传入的参数,其中lp.width和lp.height在创建ViewGroup实例的时候就被赋值了,它们都等于MATCH_PARENT。然后看下getRootMeasureSpec()方法中的代码,如下所示:
1 private int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) { 2 int measureSpec; 3 switch (rootDimension) { 4 case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT: 5 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY); 6 break; 7 case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT: 8 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST); 9 break; 10 default: 11 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY); 12 break; 13 } 14 return measureSpec; 15 }
可以看到,这里使用了MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec()方法来组装一个MeasureSpec,当rootDimension参数等于MATCH_PARENT的时候,MeasureSpec的specMode就等于EXACTLY,当rootDimension等于WRAP_CONTENT的时候,MeasureSpec的specMode就等于AT_MOST。并且MATCH_PARENT和WRAP_CONTENT时的specSize都是等于windowSize的,也就意味着根视图总是会充满全屏的。
Measure是一个复杂的过程,因为一个布局中一般都会包含多个子视图,每个视图都需要经历一次measure过程。ViewGroup中定义了一个measureChildren()方法来去测量子视图的大小,如下所示:
1 protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 2 final int size = mChildrenCount; 3 final View[] children = mChildren; 4 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { 5 final View child = children[i]; 6 if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) { 7 measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 8 } 9 } 10 }
这里会去遍历当前布局下的所有子视图,然后逐个调用measureChild()方法来测量相应子视图的大小:
1 protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, 2 int parentHeightMeasureSpec) { 3 final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams(); 4 5 final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, 6 mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width); 7 final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, 8 mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height); 9 10 child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); 11 }
从这里我们可以看到视图的大小是由父视图和子视图共同决定的。子布局里面的android:layout_width和android:layout_height只是期望值,父View大小最终是由DecorView决定。父视图提供尺寸大小的一个能力,子视图最终尺寸与父视图能力、子视图期望的关系如下:
|
父视图能力尺寸 |
子视图期望尺寸 |
子视图最终允许尺寸 |
|
EXACTLY + Size1 |
EXACTLY + Size2 |
EXACTLY + Size2 |
|
EXACTLY + Size1 |
fill_parent/match_parent |
EXACTLY+Size1 |
|
EXACTLY + Size1 |
wrap_content |
AT_MOST+Size1 |
|
AT_MOST+Size1 |
EXACTLY + Size2 |
EXACTLY+Size2 |
|
AT_MOST+Size1 |
fill_parent/match_parent |
AT_MOST+Size1 |
|
AT_MOST+Size1 |
wrap_content |
AT_MOST+Size1 |
|
UNSPECIFIED+Size1 |
EXACTLY + Size2 |
EXACTLY + Size2 |
|
UNSPECIFIED+Size1 |
fill_parent/match_parent |
UNSPECIFIED+0 |
|
UNSPECIFIED+Size1 |
wrap_content |
UNSPECIFIED+0 |
关于视图的measure过程可以阅读以下LinearLayout源码,这样可以更清楚的了解过程。
measure过程确定视图的大小,而layout过程确定视图的位置。loyout是从view的layout方法开始的:
1 public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { 2 int oldL = mLeft; 3 int oldT = mTop; 4 int oldB = mBottom; 5 int oldR = mRight; 6 boolean changed = setFrame(l, t, r, b); 7 if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) { 8 onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); 9 mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED; 10 11 ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo; 12 if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) { 13 ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener> listenersCopy = 14 (ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener>)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone(); 15 int numListeners = listenersCopy.size(); 16 for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) { 17 listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT; 22 }
函数中参数l、t、r、b是指view的左、上、右、底的位置,这几个参数是父视图传入的,而根视图中参数是由performTraversals()方法传入的。
1 host.layout(0, 0, host.mMeasuredWidth, host.mMeasuredHeight);
layout中调用了onLayout方法,在view中onLayout方法是一个空函数,他需要其子类实现。
1 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { 2 }
我们关注一下LinearLayout:
1 @Override 2 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { 3 if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) { 4 layoutVertical(); 5 } else { 6 layoutHorizontal(); 7 } 8 }
1 void layoutVertical() { 2 final int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft; 3 4 int childTop; 5 int childLeft; 6 7 // Where right end of child should go 8 final int width = mRight - mLeft; 9 int childRight = width - mPaddingRight; 10 11 // Space available for child 12 int childSpace = width - paddingLeft - mPaddingRight; 13 14 final int count = getVirtualChildCount(); 15 16 final int majorGravity = mGravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK; 17 final int minorGravity = mGravity & Gravity.RELATIVE_HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK; 18 19 switch (majorGravity) { 20 case Gravity.BOTTOM: 21 // mTotalLength contains the padding already 22 childTop = mPaddingTop + mBottom - mTop - mTotalLength; 23 break; 24 25 // mTotalLength contains the padding already 26 case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL: 27 childTop = mPaddingTop + (mBottom - mTop - mTotalLength) / 2; 28 break; 29 30 case Gravity.TOP: 31 default: 32 childTop = mPaddingTop; 33 break; 34 } 35 36 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 37 final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i); 38 if (child == null) { 39 childTop += measureNullChild(i); 40 } else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) { 41 final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); 42 final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); 43 44 final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = 45 (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); 46 47 int gravity = lp.gravity; 48 if (gravity < 0) { 49 gravity = minorGravity; 50 } 51 final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection(); 52 final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection); 53 switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) { 54 case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL: 55 childLeft = paddingLeft + ((childSpace - childWidth) / 2) 56 + lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin; 57 break; 58 59 case Gravity.RIGHT: 60 childLeft = childRight - childWidth - lp.rightMargin; 61 break; 62 63 case Gravity.LEFT: 64 default: 65 childLeft = paddingLeft + lp.leftMargin; 66 break; 67 } 68 69 if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) { 70 childTop += mDividerHeight; 71 } 72 73 childTop += lp.topMargin; 74 setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child), 75 childWidth, childHeight); 76 childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child); 77 78 i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i); 79 } 80 } 81 }
layout设置了view的位置,还设置了子视图位置,layoutHorizontal()方法中调用了setChildFrame方法:
1 private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) { 2 child.layout(left, top, left + width, top + height); 3 } 4
从上面看出,layout也是一个自上而下的过程,先设置父视图位置,在循环子视图,父视图位置一定程度上决定了子视图位置。
draw过程调用顺序在measure()和layout()之后,同样的,performTraversals()发起的draw过程最终会调用到mView的draw()函数,这里的mView对于Activity来说就是PhoneWindow.DecorView。看一下view类的draw方法:
1 public void draw(Canvas canvas) { 2 final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags; 3 final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE && 4 (mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState); 5 mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN; 6 7 /* 8 * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed 9 * in the appropriate order: 10 * 11 * 1. Draw the background 12 * 2. If necessary, save the canvas‘ layers to prepare for fading 13 * 3. Draw view‘s content 14 * 4. Draw children 15 * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers 16 * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance) 17 */ 18 19 // Step 1, draw the background, if needed 20 int saveCount; 21 22 if (!dirtyOpaque) { 23 final Drawable background = mBackground; 24 if (background != null) { 25 final int scrollX = mScrollX; 26 final int scrollY = mScrollY; 27 28 if (mBackgroundSizeChanged) { 29 background.setBounds(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); 30 mBackgroundSizeChanged = false; 31 } 32 33 if ((scrollX | scrollY) == 0) { 34 background.draw(canvas); 35 } else { 36 canvas.translate(scrollX, scrollY); 37 background.draw(canvas); 38 canvas.translate(-scrollX, -scrollY); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case) 44 final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; 45 boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0; 46 boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0; 47 if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) { 48 // Step 3, draw the content 49 if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); 50 51 // Step 4, draw the children 52 dispatchDraw(canvas); 53 54 // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) 55 onDrawScrollBars(canvas); 56 57 // we‘re done... 58 return; 59 } 60 61 /* 62 * Here we do the full fledged routine... 63 * (this is an uncommon case where speed matters less, 64 * this is why we repeat some of the tests that have been 65 * done above) 66 */ 67 68 boolean drawTop = false; 69 boolean drawBottom = false; 70 boolean drawLeft = false; 71 boolean drawRight = false; 72 73 float topFadeStrength = 0.0f; 74 float bottomFadeStrength = 0.0f; 75 float leftFadeStrength = 0.0f; 76 float rightFadeStrength = 0.0f; 77 78 // Step 2, save the canvas‘ layers 79 int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft; 80 81 final boolean offsetRequired = isPaddingOffsetRequired(); 82 if (offsetRequired) { 83 paddingLeft += getLeftPaddingOffset(); 84 } 85 86 int left = mScrollX + paddingLeft; 87 int right = left + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight - paddingLeft; 88 int top = mScrollY + getFadeTop(offsetRequired); 89 int bottom = top + getFadeHeight(offsetRequired); 90 91 if (offsetRequired) { 92 right += getRightPaddingOffset(); 93 bottom += getBottomPaddingOffset(); 94 } 95 96 final ScrollabilityCache scrollabilityCache = mScrollCache; 97 final float fadeHeight = scrollabilityCache.fadingEdgeLength; 98 int length = (int) fadeHeight; 99 100 // clip the fade length if top and bottom fades overlap 101 // overlapping fades produce odd-looking artifacts 102 if (verticalEdges && (top + length > bottom - length)) { 103 length = (bottom - top) / 2; 104 } 105 106 // also clip horizontal fades if necessary 107 if (horizontalEdges && (left + length > right - length)) { 108 length = (right - left) / 2; 109 } 110 111 if (verticalEdges) { 112 topFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getTopFadingEdgeStrength())); 113 drawTop = topFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; 114 bottomFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getBottomFadingEdgeStrength())); 115 drawBottom = bottomFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; 116 } 117 118 if (horizontalEdges) { 119 leftFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getLeftFadingEdgeStrength())); 120 drawLeft = leftFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; 121 rightFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getRightFadingEdgeStrength())); 122 drawRight = rightFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; 123 } 124 125 saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount(); 126 127 int solidColor = getSolidColor(); 128 if (solidColor == 0) { 129 final int flags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG; 130 131 if (drawTop) { 132 canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags); 133 } 134 135 if (drawBottom) { 136 canvas.saveLayer(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, null, flags); 137 } 138 139 if (drawLeft) { 140 canvas.saveLayer(left, top, left + length, bottom, null, flags); 141 } 142 143 if (drawRight) { 144 canvas.saveLayer(right - length, top, right, bottom, null, flags); 145 } 146 } else { 147 scrollabilityCache.setFadeColor(solidColor); 148 } 149 150 // Step 3, draw the content 151 if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); 152 153 // Step 4, draw the children 154 dispatchDraw(canvas); 155 156 // Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers 157 final Paint p = scrollabilityCache.paint; 158 final Matrix matrix = scrollabilityCache.matrix; 159 final Shader fade = scrollabilityCache.shader; 160 161 if (drawTop) { 162 matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength); 163 matrix.postTranslate(left, top); 164 fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); 165 canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p); 166 } 167 168 if (drawBottom) { 169 matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * bottomFadeStrength); 170 matrix.postRotate(180); 171 matrix.postTranslate(left, bottom); 172 fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); 173 canvas.drawRect(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, p); 174 } 175 176 if (drawLeft) { 177 matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * leftFadeStrength); 178 matrix.postRotate(-90); 179 matrix.postTranslate(left, top); 180 fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); 181 canvas.drawRect(left, top, left + length, bottom, p); 182 } 183 184 if (drawRight) { 185 matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * rightFadeStrength); 186 matrix.postRotate(90); 187 matrix.postTranslate(right, top); 188 fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); 189 canvas.drawRect(right - length, top, right, bottom, p); 190 } 191 192 canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); 193 194 // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) 195 onDrawScrollBars(canvas); 196 }
draw方法分成了6个步骤:
1 /* 2 * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed 3 * in the appropriate order: 4 * 5 * 1. Draw the background 6 * 2. If necessary, save the canvas‘ layers to prepare for fading 7 * 3. Draw view‘s content 8 * 4. Draw children 9 * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers 10 * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance) 11 */
第三部, Draw view‘s content步骤调用了onDraw方法,子类中实现onDraw方法。
第四步,Draw children步骤使用的dispatchDraw方法,这个方法在ViewGroup中有实现。
View或ViewGroup的子类不用再重载ViewGroup中该方法,因为它已经有了默认而且标准的view系统流程。dispatchDraw()内部for循环调用drawChild()分别绘制每一个子视图,而drawChild()内部又会调用draw()函数完成子视图的内部绘制工作。
1 /** 2 * {@inheritDoc} 3 */ 4 @Override 5 protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) { 6 final int count = mChildrenCount; 7 final View[] children = mChildren; 8 int flags = mGroupFlags; 9 10 if ((flags & FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION) != 0 && canAnimate()) { 11 final boolean cache = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE) == FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE; 12 13 final boolean buildCache = !isHardwareAccelerated(); 14 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 15 final View child = children[i]; 16 if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) { 17 final LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams(); 18 attachLayoutAnimationParameters(child, params, i, count); 19 bindLayoutAnimation(child); 20 if (cache) { 21 child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true); 22 if (buildCache) { 23 child.buildDrawingCache(true); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 final LayoutAnimationController controller = mLayoutAnimationController; 30 if (controller.willOverlap()) { 31 mGroupFlags |= FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE; 32 } 33 34 controller.start(); 35 36 mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION; 37 mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE; 38 39 if (cache) { 40 mGroupFlags |= FLAG_CHILDREN_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE; 41 } 42 43 if (mAnimationListener != null) { 44 mAnimationListener.onAnimationStart(controller.getAnimation()); 45 } 46 } 47 48 int saveCount = 0; 49 final boolean clipToPadding = (flags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK; 50 if (clipToPadding) { 51 saveCount = canvas.save(); 52 canvas.clipRect(mScrollX + mPaddingLeft, mScrollY + mPaddingTop, 53 mScrollX + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight, 54 mScrollY + mBottom - mTop - mPaddingBottom); 55 56 } 57 58 // We will draw our child‘s animation, let‘s reset the flag 59 mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION; 60 mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED; 61 62 boolean more = false; 63 final long drawingTime = getDrawingTime(); 64 65 if ((flags & FLAG_USE_CHILD_DRAWING_ORDER) == 0) { 66 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 67 final View child = children[i]; 68 if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) { 69 more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); 70 } 71 } 72 } else { 73 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 74 final View child = children[getChildDrawingOrder(count, i)]; 75 if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) { 76 more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 81 // Draw any disappearing views that have animations 82 if (mDisappearingChildren != null) { 83 final ArrayList<View> disappearingChildren = mDisappearingChildren; 84 final int disappearingCount = disappearingChildren.size() - 1; 85 // Go backwards -- we may delete as animations finish 86 for (int i = disappearingCount; i >= 0; i--) { 87 final View child = disappearingChildren.get(i); 88 more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); 89 } 90 } 91 92 if (debugDraw()) { 93 onDebugDraw(canvas); 94 } 95 96 if (clipToPadding) { 97 canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); 98 } 99 100 // mGroupFlags might have been updated by drawChild() 101 flags = mGroupFlags; 102 103 if ((flags & FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) == FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) { 104 invalidate(true); 105 } 106 107 if ((flags & FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE) == 0 && (flags & FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER) == 0 && 108 mLayoutAnimationController.isDone() && !more) { 109 // We want to erase the drawing cache and notify the listener after the 110 // next frame is drawn because one extra invalidate() is caused by 111 // drawChild() after the animation is over 112 mGroupFlags |= FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER; 113 final Runnable end = new Runnable() { 114 public void run() { 115 notifyAnimationListener(); 116 } 117 }; 118 post(end); 119 } 120 }
上面基本介绍完了View的绘制流程。更多的细节需要在日常学习中总结。
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/xyz_lmn/article/details/20385049
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liyiran/p/5500431.html