标签:
创建一个三角形类,成员变量三边,方法求周长,创建类主类A来测试它。
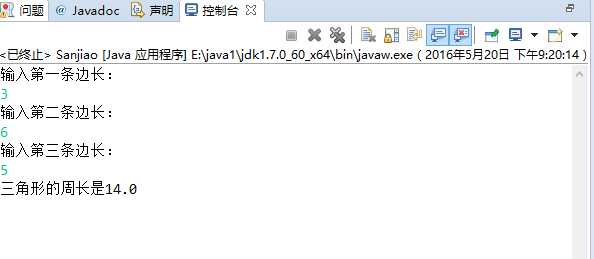
import java.util.*; public class Sanjiao { private double a,b,c; private double n=a+b+c; public Sanjiao(double a, double b, double c) { super(); this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } public double getA() { return a; } public void setA(double a) { this.a = a; } public double getB() { return b; } public void setB(double b) { this.b = b; } public double getC() { return c; } public void setC(double c) { this.c = c; } double doZhouChang() { if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&b+c>a&&a-b<c&&b-c<a&&a-c<b&&a!=0&&b!=0&&c!=0) { return this.n=a+b+c; } else { System.out.println("这不是一个三角形"); } return this.n; } public static void main(String[] args) { Sanjiao san=new Sanjiao(3,4,5); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入第一条边长:"); san.a=sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("输入第二条边长:"); san.b=sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("输入第三条边长:"); san.c=sc.nextDouble(); System.out.println("三角形的周长是"+san.doZhouChang()); } }
按要求编写Java应用程序。
(1)创建一个叫做People的类:
属性:姓名、年龄、性别、身高
行为:说话、计算加法、改名
编写能为所有属性赋值的构造方法;
(2)创建主类:
创建一个对象:名叫“张三”,性别“男”,年龄18岁,身高1.80;
让该对象调用成员方法:
说出“你好!”
计算23+45的值
将名字改为“李四”
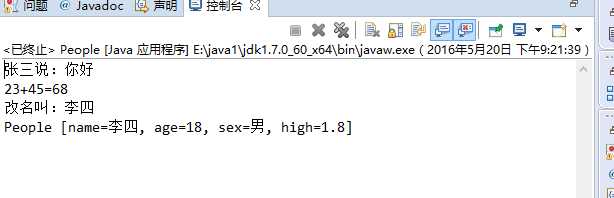
public class People { private String name; private int age; private String sex; private double high; public People(String name, int age, String sex, double high) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.sex = sex; this.high = high; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } void Say() { System.out.println(this.name+"说:你好"); } public int doAddition(int a,int b) { return a+b; } public static void main(String[]args) { People peo=new People("张三",18,"男",1.80); peo.Say(); System.out.println("23+45="+peo.doAddition(23, 45)); peo.setName("李四"); System.out.println("改名叫:"+peo.name); System.out.println(peo.toString()); } @Override public String toString() { return "People [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + ", high=" + high + "]"; } }
按要求编写Java应用程序。
(1)创建一个叫做机动车的类:
属性:车牌号(String),车速(int),载重量(double)
功能:加速(车速自增)、减速(车速自减)、修改车牌号,查询车的载重量。
编写两个构造方法:一个没有形参,在方法中将车牌号设置“XX1234”,速
度设置为100,载重量设置为100;另一个能为对象的所有属性赋值;
(2)创建主类:
在主类中创建两个机动车对象。
创建第一个时调用无参数的构造方法,调用成员方法使其车牌为“辽
A9752”,并让其加速。
创建第二个时调用有参数的构造方法,使其车牌为“辽B5086”,车速为150,
载重为200,并让其减速。
输出两辆车的所有信息
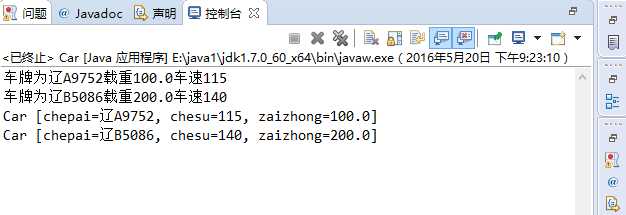
public class Car { private String chepai; private int chesu; private double zaizhong; public int getJiaSu(int n) { return this.chesu+=n; } public int getJianSu(int n) { return this.chesu-=n; } public Car() { chepai="XX1234"; chesu=100; zaizhong=100; } public Car(String chepai, int chesu, double zaizhong) { super(); this.chepai = chepai; this.chesu = chesu; this.zaizhong = zaizhong; } public double getZaizhong() { return zaizhong; } public void setZaizhong(double zaizhong) { this.zaizhong = zaizhong; } public int getChesu() { return chesu; } public void setChesu(int chesu) { this.chesu = chesu; } public String getChepai() { return chepai; } public void setChepai(String chepai) { this.chepai = chepai; } public static void main(String[]args) { Car car1=new Car(); car1.chepai="辽A9752"; System.out.println("车牌为"+car1.getChepai()+"载重"+car1.getZaizhong()+"车速"+car1.getJiaSu(15)); Car car2=new Car("辽B5086",150,200); System.out.println("车牌为"+car2.getChepai()+"载重"+car2.getZaizhong()+"车速"+car2.getJianSu(10)); System.out.println(car1.toString()); System.out.println(car2.toString()); } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [chepai=" + chepai + ", chesu=" + chesu + ", zaizhong=" + zaizhong + "]"; } }
创建一个Point类,有成员变量x,y,方法getX(),setX(),还有一个构造方
法初始化x和y。创建类主类A来测试它。
public class Point { private int x; private int y; public int getX() { return x; } public void setX(int x) { this.x = x; } public int getY() { return y; } public void setY(int y) { this.y = y; } public Point(int x, int y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } }
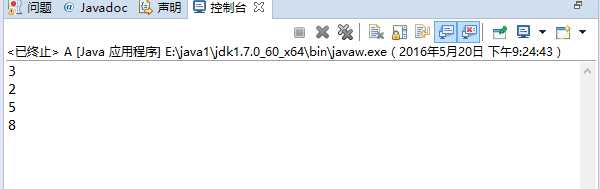
public class A { public static void main(String[] args) { Point p=new Point(3,2); System.out.println(p.getX()); System.out.println(p.getY()); p.setX(5); System.out.println(p.getX()); p.setY(8); System.out.println(p.getY()); } }
首先,编写一个类ChongZai,该类中有3个重载的方法void print();其次,
再编写一个主类来测试ChongZai类的功能。
public class ChongZai { public void print(int a,int b) { System.out.println(a-b); } public void print(double a,double b) { System.out.println(a-b); } public void print(int a,int b,int c) { System.out.println(a-b-c); } public static void main (String[]args) { ChongZai n=new ChongZai(); n.print(5, 6); n.print(3.2, 5.6); n.print(98, 32, 10); } }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wallan/p/5513481.html