标签:
制定:
First:RFC 788 in 1981
Last:RFC 5321 in 2008
端口:
TCP 25(SMTP), TCP 465/587(SMTP_SSL)
功能:
用户客户端:
发送消息:SMTP
接收和管理消息:POP3、IMAP
邮件服务器:
发送和接收消息:SMTP
说明:
SMTP仅定义了消息传输格式(如消息发送者参数),而非消息内容(如消息头和消息体)。
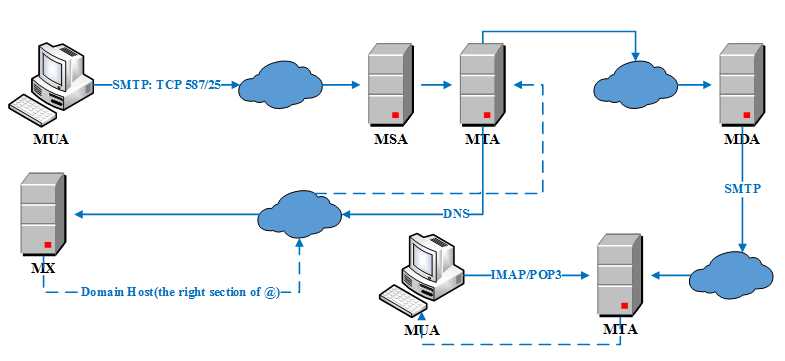
流程描述:
(1) 使用SMTP协议,通过MUA(Mail User Agent)提交邮件到MSA(Mail Submission Agent),然后MSA递送邮件到MTA(Mail Transfer Agent)[通常而言,MSA和MTA是同一邮件服务器上的两个不同例程,其也被称为SMTP服务器]。
(2) MTA通过DNS在MX(Mail Exchanger Record)上查询接收者的邮件服务器。
(3) MTA发送邮件到目标邮件服务器MTA,其间可能是两个MTA直接通信,或者经过多个SMTP服务器,最终到达MDA(Mail Delivery Agent)。
(4) MDA直接递送或者通过SMTP协议,将邮件递送到本地MTA。
(5) 终端应用程序通过IMAP/POP3协议接收和管理邮件。
SMTP由3部分构成:
一个简单的SMTP发送示例(主要为了说明SMTP的3个部分),如sender给receiver1和receiver2发送邮件:
S:表示SMTP服务器 C:表示SMTP客户端
客户端C建立TCP连接后,服务端S通过greeting建立会话(附带服务器的FQDN(Fully Qualified Domain Name)),客户端C通过HELLO响应会话(附带客户端的FQDN)。
# 建立会话 S: 220 smtp.example.com ESMTP Postfix C: HELO client.example.org S: 250 Hello client.example.org, I am glad to meet you # 发送消息 C: MAIL FROM:<sender@example.org> S: 250 Ok C: RCPT TO:<receiver1@example.com> S: 250 Ok C: RCPT TO:<receiver2@example.com> S: 250 Ok C: DATA S: 354 End data with <CR><LF>.<CR><LF> C: From: "Sender Example" <sender@example.org> C: To: "Receiver1 Example" <receiver1@example.com> C: Cc: receiver2@example.com C: Date: Tue, 15 January 2008 16:02:43 -0500 C: Subject: Test message C: C: Hello Receiver1. C: This is a test message with 5 header fields and 4 lines in the message body. C: Your friend, C: Sender C: . S: 250 Ok: queued as 12345 C: QUIT S: 221 Bye {The server closes the connection}
python中邮件发送使用smtplib模块,其一般流程为:初始化连接->发送邮件->退出。其中包含的类有SMTP,SMTP_SSL,LMTP。如上SMTP中的会话示例在python中对应的部分如下:
C: HELO client.example.org --- SMTP.helo([hostname]): 使用HELO向SMTP服务器标识自己。 S: 250 Hello client.example.org, I am glad to meet you --- SMTP.verify(address):服务器用来验证地址的有效性,返回一个元组(250,相关地址)或者(>=400, 错误消息字符串)。 C: MAIL FROM:<sender@example.org> --- low-level methods: mail() C: RCPT TO:<receiver1@example.com> --- low-level methods: rcpt() C: DATA --- low-level methods: data() C: QUIT --- SMTP.quit(): 终止会话,关闭连接。
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 from __future__ import print_function 3 from __future__ import with_statement 4 5 6 __author__ = ‘xxx‘ 7 __all__ = [‘BTEmail‘] 8 9 10 import smtplib 11 import sys 12 import os 13 import time 14 import mimetypes 15 from email import encoders 16 from email.header import Header 17 from email.utils import parseaddr, formataddr 18 from email.mime.text import MIMEText 19 from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart 20 from email.mime.image import MIMEImage 21 from email.mime.audio import MIMEAudio 22 from email.mime.base import MIMEBase 23 24 25 # ----- The following information should be in the configuration file. 26 from_addr = ‘xxx@sina.com‘ 27 to_addrs = [‘yyy@126.com‘, ‘zzz@163.com‘] 28 cc_addrs = [‘xxx@sina.com‘, ‘www@qq.com‘] 29 bcc_addrs = [] 30 username = ‘xxx@sina.com‘ 31 password = ‘---‘ 32 # ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 33 34 35 class BTEmail(object): 36 def __init__(self, host=‘smtp.sina.com‘, port=465, username=None, password=None): 37 self.host = host 38 self.port = port 39 self.username = username 40 self.password = password 41 42 @classmethod 43 def _format_addr(cls, envolope_string): 44 # parseaddr() only parses single address or string. 45 (name, addr) = parseaddr(envolope_string) 46 return formataddr(( 47 Header(name, ‘utf-8‘).encode(), 48 addr.encode(‘utf-8‘) if isinstance(addr, unicode) else addr)) 49 50 @classmethod 51 def construct_msg(cls, contentfile, contenttype=‘html‘, charset=‘utf-8‘,
attach_flag=False, attachpath=None): 52 with open(contentfile, ‘rb‘) as fp: 53 content = MIMEText(fp.read(), contenttype, charset) 54 55 if not attach_flag: 56 msg = content 57 else: 58 # Construct root container. 59 msg = MIMEMultipart() 60 # Attach mail contents to the container. 61 msg.attach(content) 62 63 # Attach attachments to the container. 64 for filename in os.listdir(attachpath): 65 item = os.path.join(attachpath, filename) 66 if not os.path.isfile(item): 67 continue 68 # Guess the content type based on the file‘s extension. 69 (ctype, encoding) = mimetypes.guess_type(item) 70 if ctype is None or encoding is not None: 71 ctype = ‘application/octet-stream‘ 72 (maintype, subtype) = ctype.split(‘/‘, 1) 73 74 # Load and encode attachments. 75 """ 76 # Use MIMEBase class construct attachments. 77 with open(item, ‘rb‘) as fp: 78 attachment = MIMEBase(_maintype=maintype, _subtype=subtype) 79 attachment.set_payload(fp.read()) 80 encoders.encode_base64(attachment) 81 """ 82 # Use concrete type class construct attachments. 83 if maintype == ‘text‘: 84 with open(item, ‘rb‘) as fp: 85 attachment = MIMEText(fp.read(), _subtype=subtype) 86 elif maintype == ‘image‘: 87 with open(item, ‘rb‘) as fp: 88 attachment = MIMEImage(fp.read(), _subtype=subtype) 89 elif maintype == ‘audio‘: 90 with open(item, ‘rb‘) as fp: 91 attachment = MIMEAudio(fp.read(), _subtype=subtype) 92 else: 93 with open(item, ‘rb‘) as fp: 94 attachment = MIMEBase(_maintype=maintype, _subtype=subtype) 95 attachment.set_payload(fp.read()) 96 encoders.encode_base64(attachment) 97 98 # Set attachment header. 99 attachment.add_header(‘Content-Disposition‘, ‘attachment‘, filename=filename) 100 msg.attach(attachment) 101 return msg 102 103 @classmethod 104 def make_envolope(cls, msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject=‘A Simple SMTP Demo‘): 105 if msg: 106 msg[‘From‘] = cls._format_addr(u‘BT<%s>‘ % from_addr) 107 # msg[‘To‘] should be a string, not a list. 108 msg[‘To‘] = ‘,‘.join(to_addrs) 109 msg[‘Cc‘] = ‘,‘.join(cc_addrs) 110 msg[‘Bcc‘] = ‘,‘.join(bcc_addrs) 111 msg[‘Subject‘] = Header(u‘主题<%s>‘ % subject, ‘utf-8‘).encode() 112 113 def send_mail(self, from_addr, to_addrs, msg): 114 smtp_server = smtplib.SMTP_SSL() 115 try: 116 #smtp_server.set_debuglevel(True) 117 118 RECONNECT = 10 # Reconnect times. 119 for i in xrange(RECONNECT): 120 try: 121 smtp_server.connect(self.host, self.port) 122 except smtplib.SMTPConnectError: 123 if i < RECONNECT: 124 print(‘Connecting to smtp server...‘) 125 time.sleep(6) 126 continue 127 else: 128 sys.exit(‘Can not connect to smtp server.‘) 129 except smtplib.SMTPServerDisconnected: 130 sys.exit(‘SMTP server is lost.‘) 131 else: 132 break 133 134 try: 135 smtp_server.starttls() 136 except smtplib.SMTPException: 137 print(‘SMTP server does not support the STARTTLS extension.‘) 138 139 try: 140 smtp_server.login(username, password) 141 except smtplib.SMTPAuthenticationError: 142 print(‘Username or Password is incorrect.‘) 143 144 try: 145 refusal_dict = smtp_server.sendmail(from_addr, to_addrs, msg.as_string()) 146 except smtplib.SMTPSenderRefused: 147 sys.exit(‘SMTP server does not accept the %s.‘ % from_addr) 148 except smtplib.SMTPDataError: 149 sys.exit(‘SMTP server replied with an unexpected error code .‘) 150 else: 151 if refusal_dict: 152 print(‘*****SMTP server rejects the following recipients:*****‘) 153 print(list(refusal_dict.items())) 154 print(‘*******************************************************‘) 155 finally: 156 smtp_server.quit() 157 158 159 def main(): 160 # Send text/plain email. 161 """ 162 email_obj = BTEmail(host=‘smtp.sina.com‘, port=465, username=username, password=password) 163 msg = email_obj.construct_msg(r‘content\mail.txt‘, ‘plain‘, ‘utf-8‘) 164 email_obj.make_envolope(msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject=‘This is a plain text mail.‘) 165 email_obj.send_mail(from_addr, to_addrs + cc_addrs, msg) 166 """ 167 168 # Send text/html email. 169 """ 170 email_obj = BTEmail(host=‘smtp.sina.com‘, port=465, username=username, password=password) 171 msg = email_obj.construct_msg(r‘content\mail.html‘, ‘html‘, ‘utf-8‘) 172 email_obj.make_envolope(msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject=‘This is a html mail.‘) 173 email_obj.send_mail(from_addr, to_addrs + cc_addrs, msg) 174 """ 175 176 # Send email with attachments. 177 email_obj = BTEmail(host=‘smtp.sina.com‘, port=465, username=username, password=password) 178 msg = email_obj.construct_msg(r‘content\mail.html‘, ‘html‘, ‘utf-8‘, attach_flag=True, attachpath=r‘attachment‘) 179 email_obj.make_envolope(msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject=‘A html mail with attachments.‘) 180 email_obj.send_mail(from_addr, to_addrs + cc_addrs, msg) 181 182 183 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 184 main()
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/benxintuzi/p/5514613.html