标签:style blog class code java tar
C#部分:
1.C#中集合有三种,数组类,ArrayList,和字典键值对类,一般也可以自定义集合,但是自定义集合的类型也只有这三类。
2.自定义集合实现三类集合的方法:前两者需要继承CollectionBase类,Array需要使用List属性,ArrayList需要使用InnerList属性,后一种,继承DictionaryBase类,使用Dictionary属性。

public class myCollect : CollectionBase { public void Add(int a) { List.Add(a); } public void Remove(int a) { List.Remove(a); } //实现索引器 public int this[int index] { get { return (int)List[index]; } set { List[index] = value; } } }

public class myDic : DictionaryBase { public void Add(string key, Object value) { Dictionary.Add(key, value); } public void Remove(string key) { Dictionary.Remove(key); } //实现索引器 public string this[string key] { get { return (string)Dictionary[key]; } set { Dictionary[key] = value; } } }
3.自定义的集合会自动实现foreach循环迭代器,而有时我们自定义的类或类的集合需要迭代,那么我们就需要手动继承IEnumerable接口,并实现该接口中的IEnumerator接口。
这种自己手动添加迭代器的方法比较繁杂,不容易理解,这里只列出具体步骤:
a.继承IEnumerable接口,然后类中实现 public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()方法
b.实现继承了IEnumberator接口的迭代类,类中实现public bool MoveNext方法和public object Current属性
c. 完成迭代器后,使用时通过判断MoveNext方法的返回值,确定是否迭代,并用Current属性保存当前被迭代到对象的引用
d.反复c步骤的过程,直到MoveNext返回false,迭代结束。
4.yield return迭代器的出现简化了手动继承IEnumerable接口的繁琐性,使用比较简单。

class user { public string name; public int key; public string Name { get { return this.name; } set { this.name = value; } } public int Key { get { return this.key; } set { this.key = value; } } public IEnumerable foo() { yield return this.name; yield return this.key; } } class test { public static void Main(String[] args) { user us=new user(); us.Name="jack"; us.Key=123; foreach (var item in us.foo()) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey(); } }
5.C#的对象复制也分为深度复制和浅度复制,浅度复制需在类的方法中调用MemberwiseClone函数实现。深度方法则和JavaScript类似,也是用new相同类型对象并迭代赋值实现。
6.C#可以对某些运算符进行重载,比如下面的案例:

public class person { public int age; public int Age { get { return this.age; } set { this.age = value; } } public static person operator +(person a, person b) { person c = new person(); c.age = a.age + b.age; return c; } } class test { public static void Main(String[] args) { var a = new person(); var b = new person(); a.age = 3; b.age = 4; var c = new person(); c = a + b; Console.WriteLine(c.Age); Console.ReadKey(); } }
运算符重载事项: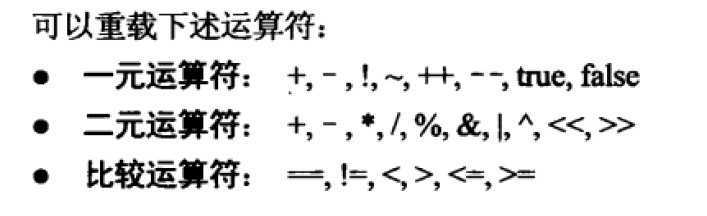
比较运算符的重载需要
成对重载,同时重载==和!=时,需要重写该类的Equals方法和GetHashCode方法。其中GetHashCode方法返回的是int类型的8位数字编码,表示该类的唯一性。
7.IComparable接口和IComparer接口负责实现对象之间的比较,前者是obj1.ComparaTo(obj2)方法的借口,后者是object.Compare(object a,object b)方法的载体。
8.每次重写ICmparable接口时都要重写== <= >= <> !=这些运算符。同样,每次重写== 都要重写Equals方法,重写Equals方法时也要重写GetHashCode方法。这些都是连锁反应。为什么重写Equals需要重写GetHashCode方法?因为每个对象的散列码即哈希编码都是唯一的,两个对象如果相等,那么这两个对象的散列码必须相同,所以,有必要维护这个协定。注意:相等的对象有相同的散列码,反之则不成立。因为散列码实质就是该对象在内存中的地址,所以谁知道你下次程序运行你的对象分配的地址是什么呢?
9.C#中==表示值类型的值是否相等和引用类型的引用地址是否相等。而Equals则表示两个变量是否是对同一个对象的引用,即堆中的内容是否相同。
java部分:
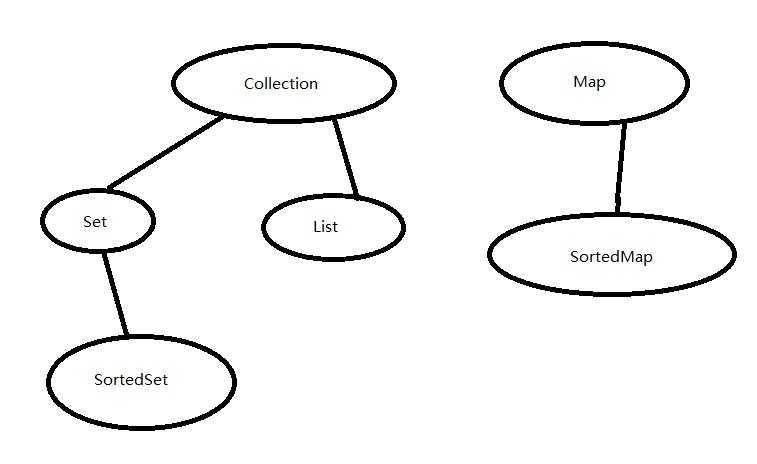
1.java中集合通过Collection接口和Map接口来派生,前者表示线性序列,后者是键值到值的映射。
2.Collection分为Set和List,Set表示不重复的元素集合,List表示一个可包含重复元素的有序集合。
3.Set还可以派生出SortedSet,表示可排序的集合。
4.Map也可以派生出SortedMap,表示可排序的映射。
C#&Java重学笔记(集合比较和转换),布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style blog class code java tar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/JhoneLee/p/3712315.html