标签:
1.冒泡排序:(面试常考)
static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1; j++) {
if (a[j]>a[j+1]) {
temp =a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
2.String处理字符串常用方法
int length();--获取字符串长度 -----和集合区分, int size();
int indexOf(String str);--返回此字符串中第一次出现的索引
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String another);--比较两个字符串,不区分大小写 -----验证码
String subString(int beginIndex) 获取一段字符串,从beginIndex开始到结尾
String subString(int beginIndex,int endIndex) 获取一段字符串,从beginIndex开始到endIndex结尾(不含endIndex所指字符)
String[] split(String regex) 分割字符串,返回分割后的字符串数组
3.继承,封装,多态简单总结
继承:
通过继承实现代码复用。Java中所有的类都是通过直接或间接地继承java.lang.Object类得到的。
继承而得到的类称为子类,被继承的类称为父类。子类不能继承父类中访问权限为private的成员变量和方法。
子类可以重写父类的方法,及命名与父类同名的成员变量。
但Java不支持多重继承,即一个类从多个超类派生的能力。
封装:属性私有化,提供getter和setter访问私有属性 ----常用
多态存在的三个必要条件:
一、要有继承;
二、要有重写;
三、父类引用指向子类对象。
4.八个封装类
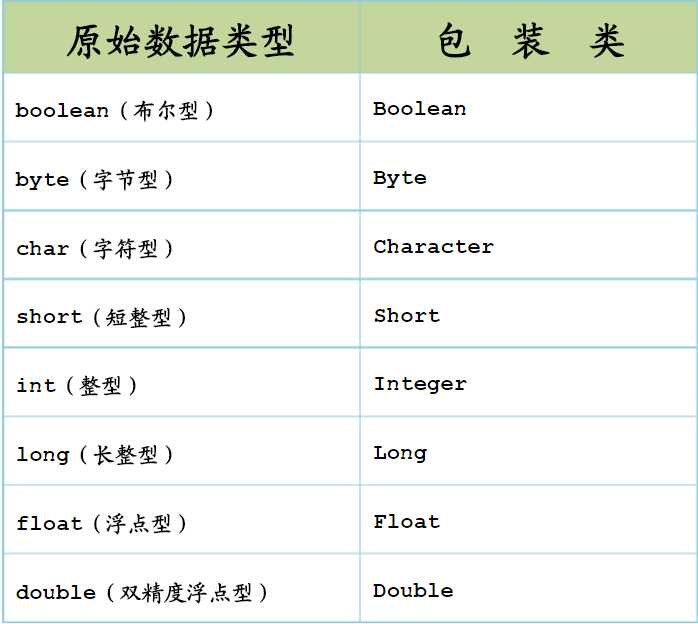
5.装箱和拆箱:
http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3780005.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liucldq/p/5551508.html