标签:
上篇文章介绍了mapReduce这个聚合操作。本篇将继续学习,db有了,collection和document也有,基本上够用了,但是随着项目上线后,发现业务数据越来越多,查询效率越来越慢,这时就需要分析慢查询记录了。如何开启慢查询记录?就是本篇文章介绍的内容了。
[MongoDB]索引
首先添加测试数据,添加100w吧。
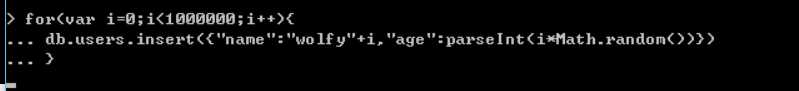
插入时间比较长,你可以通过服务端,查看日志
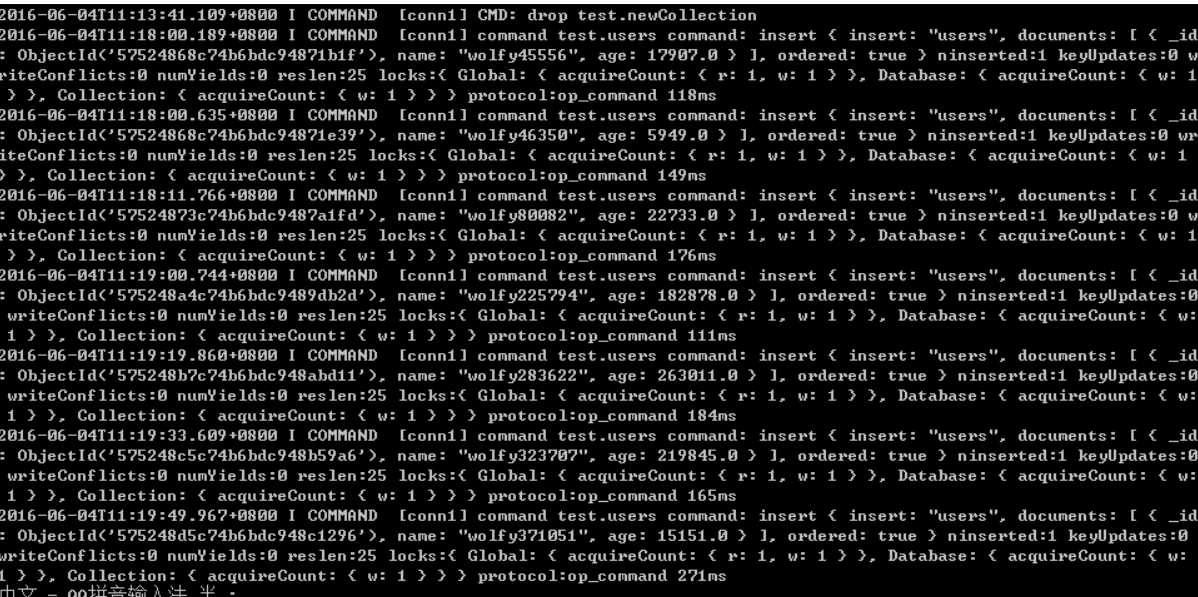
时间比较久,就插入这么多吧,能说明问题就行
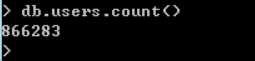
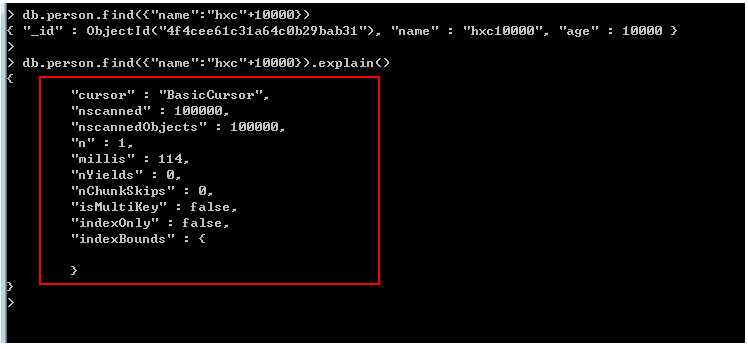
首先需要分析是否需要建立索引,之前的版本可以通过expalin函数进行查看,不过当前使用的版本,通过该函数给出的结果是下面的情况。通过下图的indexFilterSet只能看到没有使用索引,其他的信息并不能帮到我们。
下面这张是@一线码农 园友的图片 可以对比一下 原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2012/02/29/2372699.html
不过还有另外的一种方式,通过Profiling ,可以在服务端启动的时候加上该参数,–profile=级别。
也可以通过客户端db.setProfilingLevel(级别) 命令来实时配置。可以通过db.getProfilingLevel()命令来获取当前的Profile级别。
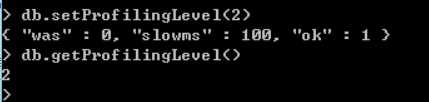
level有三种级别
0 – 不开启
1 – 记录慢命令 (默认为>100ms)
2 – 记录所有命令
参数为1的时候,默认的慢命令是大于100ms,当然也可以进行设置
db.setProfilingLevel( level , slowms )
db.setProfilingLevel( 1 , 120 );
Mongodb Profile 记录是直接存在系统db里的,记录位置 system.profile ,我们只要查询这个Collection的记录就可以获取到我们的 Profile 记录了。
执行查询,然后执行profile
> db.users.find({"name":"wolfy"+66666})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5752486fc74b6bdc94876d95"), "name" : "wolfy66666", "age" : 13471 }
> db.system.profile.find()
分析结果
{ "op": "query", "ns": "test.system.profile", "query": { "find": "system.profile", "filter": { } }, "keysExamined": 0, "docsExamined": 0, "cursorExhausted": true, "keyUpdates": 0, "writeConflicts": 0, "numYield": 0, "locks": { "Global": { "acquireCount": { "r": NumberLong(2) } }, "Database": { "acquireCount": { "r": NumberLong(1) } }, "Collection": { "acquireCount": { "r": NumberLong(1) } } }, "nreturned": 0, "responseLength": 110, "protocol": "op_command", "millis": 0, "execStats": { "stage": "COLLSCAN", "filter": { "$and": [ ] }, "nReturned": 0, "executionTimeMillisEstimate": 0, "works": 2, "advanced": 0, "needTime": 1, "needYield": 0, "saveState": 0, "restoreState": 0, "isEOF": 1, "invalidates": 0, "direction": "forward", "docsExamined": 0 }, "ts": ISODate("2016-06-04T03:56:35.706Z"), "client": "127.0.0.1", "allUsers": [ ], "user": "" }{ "op": "query", "ns": "test.users", "query": { "find": "users", "filter": { "name": "wolfy66666" } }, "keysExamined": 0, "docsExamined": 866283, "cursorExhausted": true, "keyUpdates": 0, "writeConflicts": 0, "numYield": 6767, "locks": { "Global": { "acquireCount": { "r": NumberLong(13536) } }, "Database": { "acquireCount": { "r": NumberLong(6768) } }, "Collection": { "acquireCount": { "r": NumberLong(6768) } } }, "nreturned": 1, "responseLength": 160, "protocol": "op_command", "millis": 339, "execStats": { "stage": "COLLSCAN", "filter": { "name": { "$eq": "wolfy66666" } }, "nReturned": 1, "executionTimeMillisEstimate": 310, "works": 866285, "advanced": 1, "needTime": 866283, "needYield": 0, "saveState": 6767, "restoreState": 6767, "isEOF": 1, "invalidates": 0, "direction": "forward", "docsExamined": 866283 }, "ts": ISODate("2016-06-04T03:57:10.206Z"), "client": "127.0.0.1", "allUsers": [ ], "user": "" }
通过下面的命令可以查看最新的记录
db.system.profile.find().sort({$natural:-1})
还有一种更简洁的查看方式
show profile
该命令可以查看最近的5条记录
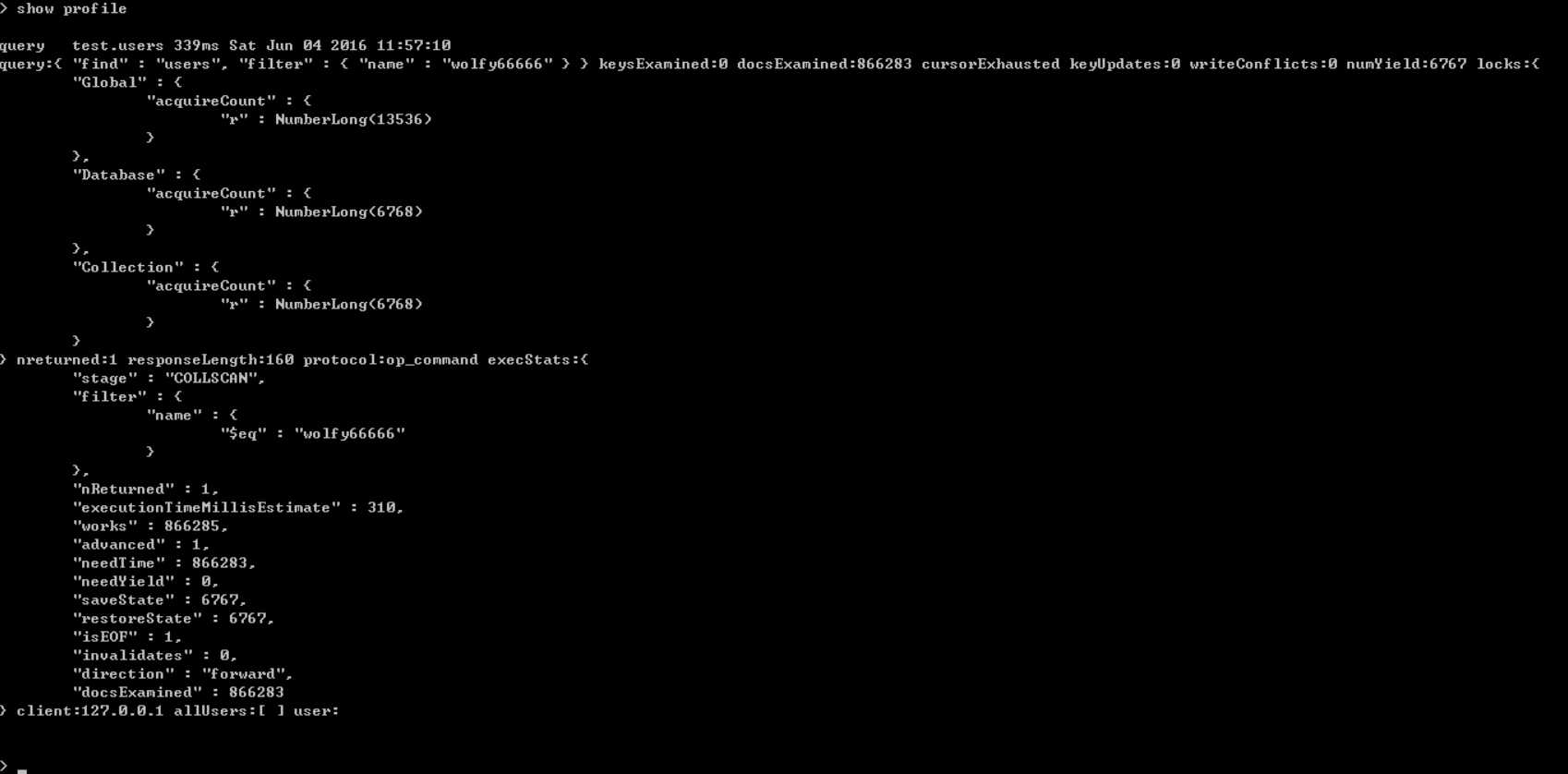
profile提供的信息内容解释
ts:该命令在何时执行。
millis:执行耗时,以毫秒为单位。
op:什么操作。
query:设置的查询条件。
nReturned:返回的条数。
docsExamined:文档扫描条数。
上面列举了profile的使用方法,以及常用的几个分析结果进行解释。感兴趣的可以使用增删改查练练手,尝试一下。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wolf-sun/p/5558530.html