标签:
一.简介
迷宫求解:类似图的DFS。具体的算法思路可以参考书上的50、51页,不过书上只说了粗略的算法,实现起来还是有很多细节需要注意。大多数只是给了个抽象的名字,甚至参数类型,返回值也没说的很清楚,所以很多需要自己揣摩。这也体现了算法和程序设计语言的特点,算法更侧重本质的描述,而任何编程语言都要照顾到实现的细节以及数据类型等语法方面的需求。
表达式求值:
[编码中。。。。]
二.头文件
迷宫求解:

1 //3_2_maze.h 2 /** 3 author:zhaoyu 4 email:zhaoyu1995.com@gmail.com 5 date:2016-6-8 6 note:realize my textbook <<数据结构(C语言版)>> 7 */ 8 //Page 51 9 #ifndef _3_2_MAZE_H 10 #define _3_2_MAZE_H 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <cstdlib> 13 #include <cstring> 14 #include "head.h" 15 #define STACK_INIT_SIZE 200//存储空间的初始分配值 16 #define STACKINCREMENT 10//存储空间分配增量 17 #define WALL -1 18 #define PATH 1 19 #define PASSED -2 20 #define UNREACHABLE -3 21 #define FINALPATH -4 22 #define NMAX 50 23 char Map[NMAX][NMAX]; 24 typedef struct{ 25 int x; 26 int y; 27 }PosType; 28 typedef struct node_1{ 29 int x, y; 30 struct node_1 *next; 31 }MazeType; 32 typedef struct{ 33 int ord;//通道块在路径上的序号 34 PosType seat;//通道块在迷宫中的位置 35 int direction;//从此通道块走向下一通道块的方向 36 }SElemType; 37 typedef struct{ 38 SElemType *base;//在栈构造之前和销毁之后,base 值为 NULL 39 SElemType *top;//栈顶指针 40 int stacksize;//当前已分配的存储空间,以元素为单位 41 }SqStack; 42 Status InitStack(SqStack &S) 43 { 44 //构造一个空栈 S 45 S.base = (SElemType *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE*sizeof(SElemType)); 46 if (!S.base) 47 { 48 exit(OVERFLOW); 49 } 50 S.top = S.base; 51 S.stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE; 52 return OK; 53 }//InitStack 54 void Assign_PosType(PosType &a, PosType b) 55 { 56 a.x = b.x; 57 a.y = b.y; 58 }//Assign_PosType 59 Status Pass(PosType pos) 60 {//可能写的不对,注意 61 if (PATH == Map[pos.x][pos.y]) 62 { 63 return TRUE; 64 } 65 else 66 { 67 return FALSE; 68 } 69 }//Pass 70 void FoorPrint(PosType pos) 71 { 72 Map[pos.x][pos.y] = PASSED; 73 } 74 void Assign_SELemType(SElemType &e, int x, PosType pos, int y) 75 { 76 e.ord = x; 77 Assign_PosType(e.seat, pos); 78 e.direction = y; 79 } 80 Status Push(SqStack &S, SElemType e) 81 { 82 //插入元素 e 为新的栈顶元素 83 if (S.top - S.base >= S.stacksize) 84 {//栈满,追加存储空间 85 S.base = (SElemType *)realloc(S.base, 86 (S.stacksize+STACKINCREMENT)*sizeof(SElemType)); 87 if (!S.base) 88 { 89 exit(OVERFLOW); 90 } 91 S.top = S.base + S.stacksize; 92 S.stacksize += STACKINCREMENT; 93 } 94 //*S.top++ = e; 95 Assign_SELemType(*S.top++, e.ord, e.seat, e.direction); 96 return OK; 97 }//Push 98 PosType NextPos(PosType pos, int direction) 99 { 100 PosType temp; 101 switch (direction) 102 { 103 case 1: 104 { 105 temp.x = pos.x; 106 temp.y = pos.y+1; 107 break; 108 } 109 case 2: 110 { 111 temp.x = pos.x + 1; 112 temp.y = pos.y; 113 break; 114 } 115 case 3: 116 { 117 temp.x = pos.x; 118 temp.y = pos.y - 1; 119 break; 120 } 121 case 4: 122 { 123 temp.x = pos.x - 1; 124 temp.y = pos.y; 125 break; 126 } 127 } 128 //加一个越界检查 129 return temp; 130 } 131 Status StackEmpty(SqStack S) 132 { 133 //若 S 为空栈, 则返回 TRUE, 否则返回 FALSE 134 if (S.base == S.top) 135 { 136 return TRUE; 137 } 138 else 139 { 140 return FALSE; 141 } 142 } 143 Status Pop(SqStack &S, SElemType &e) 144 { 145 //若栈不空,则删除 S 的栈顶元素,用 e 返回其 146 //值,并返回OK;否则返回ERROR 147 if (S.top == S.base) 148 { 149 return ERROR; 150 } 151 //e = *--S.top; 152 S.top--; 153 Assign_SELemType(e, (*S.top).ord, (*S.top).seat, (*S.top).direction); 154 return OK; 155 }//Pop 156 void FootPrint(PosType pos) 157 { 158 Map[pos.x][pos.y] = PASSED; 159 } 160 void MarkPrint(PosType pos) 161 { 162 Map[pos.x][pos.y] = UNREACHABLE; 163 } 164 void MakeMap(int size) 165 { 166 memset(Map, 0, sizeof(Map)); 167 char ch; 168 getchar(); 169 for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) 170 { 171 for (int j = 1; j <= size; j++) 172 { 173 scanf("%c", &ch); 174 if (‘X‘ == ch) 175 { 176 Map[i][j] = UNREACHABLE; 177 } 178 else 179 { 180 Map[i][j] = PATH; 181 } 182 } 183 //attention ‘\n‘ 184 getchar(); 185 } 186 //Print maze 187 for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) 188 { 189 for (int j = 1; j <= size; j++) 190 { 191 if (UNREACHABLE == Map[i][j]) 192 { 193 printf("X"); 194 } 195 else 196 { 197 printf(" "); 198 } 199 } 200 printf("\n"); 201 } 202 } 203 void PrintPath(SqStack S, int size) 204 { 205 SElemType e; 206 SqStack temp; 207 while (!StackEmpty(S)) 208 { 209 Pop(S, e); 210 Map[e.seat.x][e.seat.y] = FINALPATH; 211 } 212 for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) 213 { 214 for (int j = 1; j <= size; j++) 215 { 216 if (UNREACHABLE == Map[i][j]) 217 { 218 printf("X"); 219 } 220 else if (FINALPATH == Map[i][j]) 221 { 222 printf("O"); 223 } 224 else 225 { 226 printf(" "); 227 } 228 } 229 printf("\n"); 230 } 231 } 232 Status MazePath(MazeType maze, PosType start, PosType end, int size) 233 { 234 //若迷宫 maze 中存在从入口 start 到出口 end 的通道, 235 //则求得一条存放在栈中(从栈底到栈顶),并返回 TRUE, 236 //否则返回 FALSE 237 SqStack S; 238 InitStack(S); 239 //curpos = start 240 PosType curpos; 241 Assign_PosType(curpos, start);//设定当前位置为入口位置 242 int curstep = 1;//探索第一步 243 SElemType e; 244 do{ 245 if (TRUE == Pass(curpos)) 246 {//当前位置可以通过 247 FootPrint(curpos);//留下足迹 248 //e = (curstep, curpos, 1); 249 Assign_SELemType(e, curstep, curpos, 1); 250 Push(S, e);//加入路径 251 if (curpos.x == end.x && curpos.y == end.y) 252 { 253 //打印路径 254 printf("PATH EXIST\n"); 255 PrintPath(S ,size); 256 return TRUE; 257 } 258 curpos = NextPos(curpos, 1);//下一位置是当前位置的东邻 259 curstep++;//探索下一步 260 } 261 else 262 { 263 if (!StackEmpty(S)) 264 { 265 Pop(S, e); 266 while (4 == e.direction && !StackEmpty(S)) 267 { 268 MarkPrint(e.seat); 269 Pop(S, e);//留下不能通过的标记,并退回一步 270 } 271 if (e.direction < 4) 272 { 273 e.direction++; 274 Push(S, e); 275 curpos = NextPos(e.seat, e.direction); 276 } 277 } 278 } 279 }while (!StackEmpty(S)); 280 281 } 282 #endif
表达式求值:
三.CPP文件
迷宫求解:

1 #include "3_2_maze.h" 2 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 3 { 4 freopen("map.txt", "r", stdin); 5 printf("Map\n"); 6 int size; 7 scanf("%d", &size); 8 MakeMap(size); 9 PosType start, end; 10 scanf("%d%d", &start.x, &start.y); 11 printf("start:\tx:%d\ty:%d\n", start.x, start.y); 12 scanf("%d%d", &end.x, &end.y); 13 printf("end:\tx:%d\ty:%d\n", end.x, end.y); 14 MazeType maze;//un useded for me 15 MazePath(maze, start, end, size); 16 //PrintPath(size); 17 return 0; 18 }
表达式求值:
四.测试
迷宫求解:
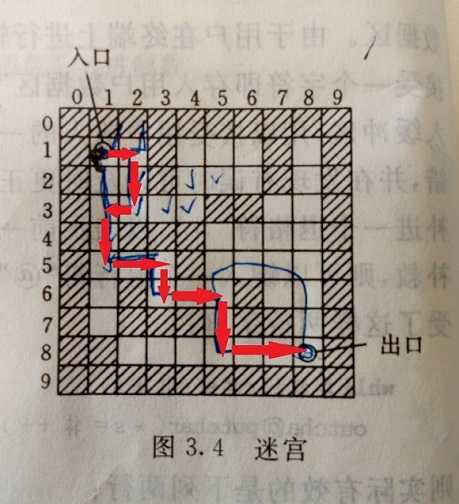
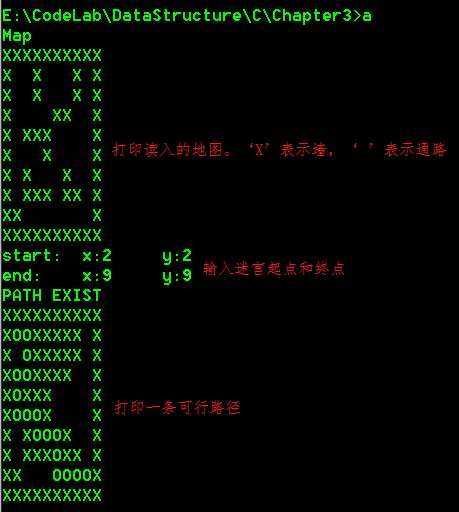
表达式求值:
五.迷宫求解的输入文件map.txt

10 XXXXXXXXXX XOOXOOOXOX XOOXOOOXOX XOOOOXXOOX XOXXXOOOOX XOOOXOOOOX XOXOOOXOOX XOXXXOXXOX XXOOOOOOOX XXXXXXXXXX 2 2 9 9
数据结构算法C语言实现(八)--- 3.2栈的应用举例:迷宫求解与表达式求值
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoyu1995/p/5569391.html