标签:
本章介绍Hibernate的基础知识,结合例子说明。
Hibernate是一个开放源代码的对象关系映射框架,它对JDBC进行了非常轻量级的对象封装,它将POJO与数据库表建立映射关系,是一个全自动的orm框架,通过操作POJO,对数据表中的数据进行增,删,改,查等操作。
hibernate简单应用流程图:
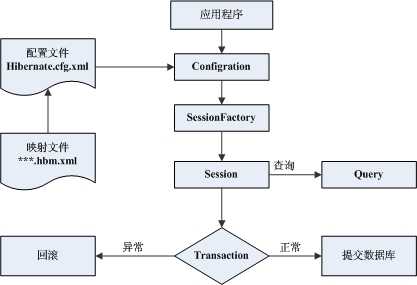
实例环境:hibernate3.6.10,mysql
代码结构:
关键代码:

package com.alfred.bean; import java.sql.Date; public class Person { private Long id; private String username; private Integer age; private Date birthday; public Person() { } public Person(String username, int age, Date birthday) { this.username = username; this.age = age; this.birthday = birthday; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } }

package com.alfred.bean; import java.sql.Timestamp; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity @Table(name = "employee") public class Employee { private Long id; private String fullname; private Integer workyear; private Timestamp employdate; public Employee() { } public Employee(String fullname, Integer workyear, Timestamp employdate) { this.fullname = fullname; this.workyear = workyear; this.employdate = employdate; } @GenericGenerator(name = "generator", strategy = "increment") @Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "generator") @Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false) public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } @Column(name = "fullname", length = 32) public String getFullname() { return fullname; } public void setFullname(String fullname) { this.fullname = fullname; } @Column(name = "workyear") public Integer getWorkyear() { return workyear; } public void setWorkyear(Integer workyear) { this.workyear = workyear; } @Column(name = "employ_date") public Timestamp getEmploydate() { return employdate; } public void setEmploydate(Timestamp employdate) { this.employdate = employdate; } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- <hibernate-mapping>一般不去配置,采用默认即可 default-cascade="none":默认的级联风格,表与表联动. default-lazy="true":默认延迟加载 --> <hibernate-mapping> <!-- <class>:使用class元素定义一个持久化类. name="com.alfred.bean.Person":持久化类的java全限定名; table="person":对应数据库表名; mutable="true":默认为true,设置为false时则不可以被应用程序更新或删除; dynamic-insert="false":默认为false,动态插入非空值字段; dynamic-update="false":默认为false,动态修改那些有改变过的字段,而不用修改所有字段; select-before-update="false":默认为false,在修改之前先做一次查询,与用户的值进行对比,有变化都会真正更新; optimistic-lock="version":默认为version(检查version/timestamp字段),取值:all(检查全部字段)、dirty(只检查修改过的字段)、 none(不使用乐观锁定),此参数主要用来处理并发,每条值都有固定且唯一的版本,版本为最新时才能执行操作; --> <class name="com.alfred.bean.Person" table="person"> <!-- <id>:定义了该属性到数据库表主键字段的映射. name="id":标识属性的名字; column="id":表主键字段的名字,如果不填写与name一样; --> <id name="id" column="id"> <!-- <generator>:指定主键由什么生成. 例如: uuid:唯一标识符. (32位,长度大,占用空间大,跨数据库,不用访问数据库就生成主键值,所以效率高且能保证唯一性,移植非常方便,推荐使用.) native:由hibernate根据使用的数据库自行判断采用identity、hilo、sequence其中一种作为主键生成方式,灵活性很强。如果能支持identity则使用identity,如果支持sequence则使用sequence. (例如:MySQL使用identity,Oracle使用sequence.注:如果Hibernate自动选择sequence或者hilo,则所有的表的主键都会从Hibernate默认的sequence或hilo表中取。并且,有的数据库对于默认情况主键生成测试的支持,效率并不是很高。) assigned:指用户手工填入. increment:hibernate会先select max(id)的值加1作为id值. --> <generator class="increment"/> </id> <!-- <property>:为类定义一个持久化的javaBean风格的属性. name="username":标识属性的名字,以小写字母开头; column="username":表主键字段的名字,如果不填写与name一样; update="true"/insert="true":默认为true,表示可以被更新或插入; --> <property name="username" column="username" type="string" /> <property name="age" column="age" type="int" /> <property name="birthday" column="birthday" type="timestamp" /> </class> </hibernate-mapping>

package com.alfred.util; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; public class HibernateUtil { private static SessionFactory sf; static{ sf = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); } public static Session openSession(){ return sf.openSession(); } public static void closeSession(Session s){ s.close(); } public static void closeSessionFactory(){ sf.close(); } }

package com.alfred.main; import java.sql.Date; import java.sql.Timestamp; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import com.alfred.bean.Employee; import com.alfred.bean.Person; import com.alfred.util.HibernateUtil; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person("alfred", 22, new Date(System .currentTimeMillis())); Employee employee = new Employee("Alfred_Emp",3,new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())); Session session = HibernateUtil.openSession(); Transaction tr = session.beginTransaction(); try { session.save(person); session.save(employee); tr.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); tr.rollback(); } finally { HibernateUtil.closeSession(session); } //关闭sessionfactory,结束程序 HibernateUtil.closeSessionFactory(); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- 数据库的基本连接信息 --> <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/hibernate_db</property> <property name="connection.username">root</property> <property name="connection.password">123456</property> <!-- sql方言 根据不同的数据库有所区别 --> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect</property> <!-- 在标准输出流中输出所有执行的sql --> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <!-- 格式化输出的sql <property name="format_sql">true</property> --> <!-- 映射文件 --> <mapping resource="com/alfred/bean/Person.hbm.xml"/> <!-- 使用注释方式 --> <mapping class="com.alfred.bean.Employee" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
实例中使用了两种方式配置hibernate对象关系映射,Person使用映射文件方式配置,Employee使用注释方式配置。
hibernate配置文件hibernate.cfg.xml默认放置于根目录下,使用new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();获取hibernate的会话工厂,通过源码可以看到configure()空参方法是到根目录下获取 hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件。
public Configuration configure() throws HibernateException { configure( "/hibernate.cfg.xml" ); return this; }
new Configuration().configure()有几个重载方法,在自定义hibernate配置文件的时候可以通过这些重载方法载入配置文件。
例如:
自定义配置文件newcfg.xml,可以通过以下方式载入
private static SessionFactory sf; static{ sf = new Configuration().configure("/hibernate/newcfg.xml").buildSessionFactory(); }
hibernate的配置文件hibernate.cfg.xml,在根hibernate-configuration下配置session-factory,一个session-factory对应一个数据库会话工厂,如果项目中需要连接使用多个数据库,那么连接的数据库数目等于配置的session-factory数目。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/alfredinchange/p/5572778.html