标签:
网络爬虫(又被称为网页蜘蛛,网络机器人,在FOAF社区中间,更经常的称为网页追逐者),是一种按照一定的规则,自动的抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本。
一、urllib简介
python3中的urllib模块相对于Python2做了很大的改变,原来的urllib、urllib2、urlparse和robotparse模块被去掉了,新的urllib模块分为5个子模块,改变日志文件内容如下:
a new urllib package was created. It consists of code from urllib, urllib2, urlparse, and robotparser. The old modules have all been removed. The new package has five submodules: urllib.parse, urllib.request, urllib.response, urllib.error, and urllib.robotparser. The urllib.request.urlopen() function uses the url opener from urllib2. (Note that the unittests have not been renamed for the beta, but they will be renamed in the future.)
使用help()可以查看Python3中的urllib模块:
>>> import urllib
>>> help(urllib)
Help on package urllib:
NAME
urllib
MODULE REFERENCE
http://docs.python.org/3.5/library/urllib
The following documentation is automatically generated from the Python
source files. It may be incomplete, incorrect or include features that
are considered implementation detail and may vary between Python
implementations. When in doubt, consult the module reference at the
location listed above.
PACKAGE CONTENTS
error
parse
request
response
robotparser
FILE
/usr/local/python35/lib/python3.5/urllib/__init__.py

"""Exception classes raised by urllib. The base exception class is URLError, which inherits from OSError. It doesn‘t define any behavior of its own, but is the base class for all exceptions defined in this package. HTTPError is an exception class that is also a valid HTTP response instance. It behaves this way because HTTP protocol errors are valid responses, with a status code, headers, and a body. In some contexts, an application may want to handle an exception like a regular response. """ import urllib.response __all__ = [‘URLError‘, ‘HTTPError‘, ‘ContentTooShortError‘] # do these error classes make sense? # make sure all of the OSError stuff is overridden. we just want to be # subtypes. class URLError(OSError): # URLError is a sub-type of OSError, but it doesn‘t share any of # the implementation. need to override __init__ and __str__. # It sets self.args for compatibility with other EnvironmentError # subclasses, but args doesn‘t have the typical format with errno in # slot 0 and strerror in slot 1. This may be better than nothing. def __init__(self, reason, filename=None): self.args = reason, self.reason = reason if filename is not None: self.filename = filename def __str__(self): return ‘<urlopen error %s>‘ % self.reason class HTTPError(URLError, urllib.response.addinfourl): """Raised when HTTP error occurs, but also acts like non-error return""" __super_init = urllib.response.addinfourl.__init__ def __init__(self, url, code, msg, hdrs, fp): self.code = code self.msg = msg self.hdrs = hdrs self.fp = fp self.filename = url # The addinfourl classes depend on fp being a valid file # object. In some cases, the HTTPError may not have a valid # file object. If this happens, the simplest workaround is to # not initialize the base classes. if fp is not None: self.__super_init(fp, hdrs, url, code) def __str__(self): return ‘HTTP Error %s: %s‘ % (self.code, self.msg) def __repr__(self): return ‘<HTTPError %s: %r>‘ % (self.code, self.msg) # since URLError specifies a .reason attribute, HTTPError should also # provide this attribute. See issue13211 for discussion. @property def reason(self): return self.msg @property def headers(self): return self.hdrs @headers.setter def headers(self, headers): self.hdrs = headers class ContentTooShortError(URLError): """Exception raised when downloaded size does not match content-length.""" def __init__(self, message, content): URLError.__init__(self, message) self.content = content

"""Parse (absolute and relative) URLs. urlparse module is based upon the following RFC specifications. RFC 3986 (STD66): "Uniform Resource Identifiers" by T. Berners-Lee, R. Fielding and L. Masinter, January 2005. RFC 2732 : "Format for Literal IPv6 Addresses in URL‘s by R.Hinden, B.Carpenter and L.Masinter, December 1999. RFC 2396: "Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI)": Generic Syntax by T. Berners-Lee, R. Fielding, and L. Masinter, August 1998. RFC 2368: "The mailto URL scheme", by P.Hoffman , L Masinter, J. Zawinski, July 1998. RFC 1808: "Relative Uniform Resource Locators", by R. Fielding, UC Irvine, June 1995. RFC 1738: "Uniform Resource Locators (URL)" by T. Berners-Lee, L. Masinter, M. McCahill, December 1994 RFC 3986 is considered the current standard and any future changes to urlparse module should conform with it. The urlparse module is currently not entirely compliant with this RFC due to defacto scenarios for parsing, and for backward compatibility purposes, some parsing quirks from older RFCs are retained. The testcases in test_urlparse.py provides a good indicator of parsing behavior. """ import re import sys import collections __all__ = ["urlparse", "urlunparse", "urljoin", "urldefrag", "urlsplit", "urlunsplit", "urlencode", "parse_qs", "parse_qsl", "quote", "quote_plus", "quote_from_bytes", "unquote", "unquote_plus", "unquote_to_bytes", "DefragResult", "ParseResult", "SplitResult", "DefragResultBytes", "ParseResultBytes", "SplitResultBytes"] # A classification of schemes (‘‘ means apply by default) uses_relative = [‘ftp‘, ‘http‘, ‘gopher‘, ‘nntp‘, ‘imap‘, ‘wais‘, ‘file‘, ‘https‘, ‘shttp‘, ‘mms‘, ‘prospero‘, ‘rtsp‘, ‘rtspu‘, ‘‘, ‘sftp‘, ‘svn‘, ‘svn+ssh‘] uses_netloc = [‘ftp‘, ‘http‘, ‘gopher‘, ‘nntp‘, ‘telnet‘, ‘imap‘, ‘wais‘, ‘file‘, ‘mms‘, ‘https‘, ‘shttp‘, ‘snews‘, ‘prospero‘, ‘rtsp‘, ‘rtspu‘, ‘rsync‘, ‘‘, ‘svn‘, ‘svn+ssh‘, ‘sftp‘, ‘nfs‘, ‘git‘, ‘git+ssh‘] uses_params = [‘ftp‘, ‘hdl‘, ‘prospero‘, ‘http‘, ‘imap‘, ‘https‘, ‘shttp‘, ‘rtsp‘, ‘rtspu‘, ‘sip‘, ‘sips‘, ‘mms‘, ‘‘, ‘sftp‘, ‘tel‘] # These are not actually used anymore, but should stay for backwards # compatibility. (They are undocumented, but have a public-looking name.) non_hierarchical = [‘gopher‘, ‘hdl‘, ‘mailto‘, ‘news‘, ‘telnet‘, ‘wais‘, ‘imap‘, ‘snews‘, ‘sip‘, ‘sips‘] uses_query = [‘http‘, ‘wais‘, ‘imap‘, ‘https‘, ‘shttp‘, ‘mms‘, ‘gopher‘, ‘rtsp‘, ‘rtspu‘, ‘sip‘, ‘sips‘, ‘‘] uses_fragment = [‘ftp‘, ‘hdl‘, ‘http‘, ‘gopher‘, ‘news‘, ‘nntp‘, ‘wais‘, ‘https‘, ‘shttp‘, ‘snews‘, ‘file‘, ‘prospero‘, ‘‘] # Characters valid in scheme names scheme_chars = (‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz‘ ‘ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ‘ ‘0123456789‘ ‘+-.‘) # XXX: Consider replacing with functools.lru_cache MAX_CACHE_SIZE = 20 _parse_cache = {} def clear_cache(): """Clear the parse cache and the quoters cache.""" _parse_cache.clear() _safe_quoters.clear() # Helpers for bytes handling # For 3.2, we deliberately require applications that # handle improperly quoted URLs to do their own # decoding and encoding. If valid use cases are # presented, we may relax this by using latin-1 # decoding internally for 3.3 _implicit_encoding = ‘ascii‘ _implicit_errors = ‘strict‘ def _noop(obj): return obj def _encode_result(obj, encoding=_implicit_encoding, errors=_implicit_errors): return obj.encode(encoding, errors) def _decode_args(args, encoding=_implicit_encoding, errors=_implicit_errors): return tuple(x.decode(encoding, errors) if x else ‘‘ for x in args) def _coerce_args(*args): # Invokes decode if necessary to create str args # and returns the coerced inputs along with # an appropriate result coercion function # - noop for str inputs # - encoding function otherwise str_input = isinstance(args[0], str) for arg in args[1:]: # We special-case the empty string to support the # "scheme=‘‘" default argument to some functions if arg and isinstance(arg, str) != str_input: raise TypeError("Cannot mix str and non-str arguments") if str_input: return args + (_noop,) return _decode_args(args) + (_encode_result,) # Result objects are more helpful than simple tuples class _ResultMixinStr(object): """Standard approach to encoding parsed results from str to bytes""" __slots__ = () def encode(self, encoding=‘ascii‘, errors=‘strict‘): return self._encoded_counterpart(*(x.encode(encoding, errors) for x in self)) class _ResultMixinBytes(object): """Standard approach to decoding parsed results from bytes to str""" __slots__ = () def decode(self, encoding=‘ascii‘, errors=‘strict‘): return self._decoded_counterpart(*(x.decode(encoding, errors) for x in self)) class _NetlocResultMixinBase(object): """Shared methods for the parsed result objects containing a netloc element""" __slots__ = () @property def username(self): return self._userinfo[0] @property def password(self): return self._userinfo[1] @property def hostname(self): hostname = self._hostinfo[0] if not hostname: hostname = None elif hostname is not None: hostname = hostname.lower() return hostname @property def port(self): port = self._hostinfo[1] if port is not None: port = int(port, 10) # Return None on an illegal port if not ( 0 <= port <= 65535): return None return port class _NetlocResultMixinStr(_NetlocResultMixinBase, _ResultMixinStr): __slots__ = () @property def _userinfo(self): netloc = self.netloc userinfo, have_info, hostinfo = netloc.rpartition(‘@‘) if have_info: username, have_password, password = userinfo.partition(‘:‘) if not have_password: password = None else: username = password = None return username, password @property def _hostinfo(self): netloc = self.netloc _, _, hostinfo = netloc.rpartition(‘@‘) _, have_open_br, bracketed = hostinfo.partition(‘[‘) if have_open_br: hostname, _, port = bracketed.partition(‘]‘) _, _, port = port.partition(‘:‘) else: hostname, _, port = hostinfo.partition(‘:‘) if not port: port = None return hostname, port class _NetlocResultMixinBytes(_NetlocResultMixinBase, _ResultMixinBytes): __slots__ = () @property def _userinfo(self): netloc = self.netloc userinfo, have_info, hostinfo = netloc.rpartition(b‘@‘) if have_info: username, have_password, password = userinfo.partition(b‘:‘) if not have_password: password = None else: username = password = None return username, password @property def _hostinfo(self): netloc = self.netloc _, _, hostinfo = netloc.rpartition(b‘@‘) _, have_open_br, bracketed = hostinfo.partition(b‘[‘) if have_open_br: hostname, _, port = bracketed.partition(b‘]‘) _, _, port = port.partition(b‘:‘) else: hostname, _, port = hostinfo.partition(b‘:‘) if not port: port = None return hostname, port from collections import namedtuple _DefragResultBase = namedtuple(‘DefragResult‘, ‘url fragment‘) _SplitResultBase = namedtuple(‘SplitResult‘, ‘scheme netloc path query fragment‘) _ParseResultBase = namedtuple(‘ParseResult‘, ‘scheme netloc path params query fragment‘) # For backwards compatibility, alias _NetlocResultMixinStr # ResultBase is no longer part of the documented API, but it is # retained since deprecating it isn‘t worth the hassle ResultBase = _NetlocResultMixinStr # Structured result objects for string data class DefragResult(_DefragResultBase, _ResultMixinStr): __slots__ = () def geturl(self): if self.fragment: return self.url + ‘#‘ + self.fragment else: return self.url class SplitResult(_SplitResultBase, _NetlocResultMixinStr): __slots__ = () def geturl(self): return urlunsplit(self) class ParseResult(_ParseResultBase, _NetlocResultMixinStr): __slots__ = () def geturl(self): return urlunparse(self) # Structured result objects for bytes data class DefragResultBytes(_DefragResultBase, _ResultMixinBytes): __slots__ = () def geturl(self): if self.fragment: return self.url + b‘#‘ + self.fragment else: return self.url class SplitResultBytes(_SplitResultBase, _NetlocResultMixinBytes): __slots__ = () def geturl(self): return urlunsplit(self) class ParseResultBytes(_ParseResultBase, _NetlocResultMixinBytes): __slots__ = () def geturl(self): return urlunparse(self) # Set up the encode/decode result pairs def _fix_result_transcoding(): _result_pairs = ( (DefragResult, DefragResultBytes), (SplitResult, SplitResultBytes), (ParseResult, ParseResultBytes), ) for _decoded, _encoded in _result_pairs: _decoded._encoded_counterpart = _encoded _encoded._decoded_counterpart = _decoded _fix_result_transcoding() del _fix_result_transcoding def urlparse(url, scheme=‘‘, allow_fragments=True): """Parse a URL into 6 components: <scheme>://<netloc>/<path>;<params>?<query>#<fragment> Return a 6-tuple: (scheme, netloc, path, params, query, fragment). Note that we don‘t break the components up in smaller bits (e.g. netloc is a single string) and we don‘t expand % escapes.""" url, scheme, _coerce_result = _coerce_args(url, scheme) splitresult = urlsplit(url, scheme, allow_fragments) scheme, netloc, url, query, fragment = splitresult if scheme in uses_params and ‘;‘ in url: url, params = _splitparams(url) else: params = ‘‘ result = ParseResult(scheme, netloc, url, params, query, fragment) return _coerce_result(result) def _splitparams(url): if ‘/‘ in url: i = url.find(‘;‘, url.rfind(‘/‘)) if i < 0: return url, ‘‘ else: i = url.find(‘;‘) return url[:i], url[i+1:] def _splitnetloc(url, start=0): delim = len(url) # position of end of domain part of url, default is end for c in ‘/?#‘: # look for delimiters; the order is NOT important wdelim = url.find(c, start) # find first of this delim if wdelim >= 0: # if found delim = min(delim, wdelim) # use earliest delim position return url[start:delim], url[delim:] # return (domain, rest) def urlsplit(url, scheme=‘‘, allow_fragments=True): """Parse a URL into 5 components: <scheme>://<netloc>/<path>?<query>#<fragment> Return a 5-tuple: (scheme, netloc, path, query, fragment). Note that we don‘t break the components up in smaller bits (e.g. netloc is a single string) and we don‘t expand % escapes.""" url, scheme, _coerce_result = _coerce_args(url, scheme) allow_fragments = bool(allow_fragments) key = url, scheme, allow_fragments, type(url), type(scheme) cached = _parse_cache.get(key, None) if cached: return _coerce_result(cached) if len(_parse_cache) >= MAX_CACHE_SIZE: # avoid runaway growth clear_cache() netloc = query = fragment = ‘‘ i = url.find(‘:‘) if i > 0: if url[:i] == ‘http‘: # optimize the common case scheme = url[:i].lower() url = url[i+1:] if url[:2] == ‘//‘: netloc, url = _splitnetloc(url, 2) if ((‘[‘ in netloc and ‘]‘ not in netloc) or (‘]‘ in netloc and ‘[‘ not in netloc)): raise ValueError("Invalid IPv6 URL") if allow_fragments and ‘#‘ in url: url, fragment = url.split(‘#‘, 1) if ‘?‘ in url: url, query = url.split(‘?‘, 1) v = SplitResult(scheme, netloc, url, query, fragment) _parse_cache[key] = v return _coerce_result(v) for c in url[:i]: if c not in scheme_chars: break else: # make sure "url" is not actually a port number (in which case # "scheme" is really part of the path) rest = url[i+1:] if not rest or any(c not in ‘0123456789‘ for c in rest): # not a port number scheme, url = url[:i].lower(), rest if url[:2] == ‘//‘: netloc, url = _splitnetloc(url, 2) if ((‘[‘ in netloc and ‘]‘ not in netloc) or (‘]‘ in netloc and ‘[‘ not in netloc)): raise ValueError("Invalid IPv6 URL") if allow_fragments and ‘#‘ in url: url, fragment = url.split(‘#‘, 1) if ‘?‘ in url: url, query = url.split(‘?‘, 1) v = SplitResult(scheme, netloc, url, query, fragment) _parse_cache[key] = v return _coerce_result(v) def urlunparse(components): """Put a parsed URL back together again. This may result in a slightly different, but equivalent URL, if the URL that was parsed originally had redundant delimiters, e.g. a ? with an empty query (the draft states that these are equivalent).""" scheme, netloc, url, params, query, fragment, _coerce_result = ( _coerce_args(*components)) if params: url = "%s;%s" % (url, params) return _coerce_result(urlunsplit((scheme, netloc, url, query, fragment))) def urlunsplit(components): """Combine the elements of a tuple as returned by urlsplit() into a complete URL as a string. The data argument can be any five-item iterable. This may result in a slightly different, but equivalent URL, if the URL that was parsed originally had unnecessary delimiters (for example, a ? with an empty query; the RFC states that these are equivalent).""" scheme, netloc, url, query, fragment, _coerce_result = ( _coerce_args(*components)) if netloc or (scheme and scheme in uses_netloc and url[:2] != ‘//‘): if url and url[:1] != ‘/‘: url = ‘/‘ + url url = ‘//‘ + (netloc or ‘‘) + url if scheme: url = scheme + ‘:‘ + url if query: url = url + ‘?‘ + query if fragment: url = url + ‘#‘ + fragment return _coerce_result(url) def urljoin(base, url, allow_fragments=True): """Join a base URL and a possibly relative URL to form an absolute interpretation of the latter.""" if not base: return url if not url: return base base, url, _coerce_result = _coerce_args(base, url) bscheme, bnetloc, bpath, bparams, bquery, bfragment = urlparse(base, ‘‘, allow_fragments) scheme, netloc, path, params, query, fragment = urlparse(url, bscheme, allow_fragments) if scheme != bscheme or scheme not in uses_relative: return _coerce_result(url) if scheme in uses_netloc: if netloc: return _coerce_result(urlunparse((scheme, netloc, path, params, query, fragment))) netloc = bnetloc if not path and not params: path = bpath params = bparams if not query: query = bquery return _coerce_result(urlunparse((scheme, netloc, path, params, query, fragment))) base_parts = bpath.split(‘/‘) if base_parts[-1] != ‘‘: # the last item is not a directory, so will not be taken into account # in resolving the relative path del base_parts[-1] # for rfc3986, ignore all base path should the first character be root. if path[:1] == ‘/‘: segments = path.split(‘/‘) else: segments = base_parts + path.split(‘/‘) # filter out elements that would cause redundant slashes on re-joining # the resolved_path segments[1:-1] = filter(None, segments[1:-1]) resolved_path = [] for seg in segments: if seg == ‘..‘: try: resolved_path.pop() except IndexError: # ignore any .. segments that would otherwise cause an IndexError # when popped from resolved_path if resolving for rfc3986 pass elif seg == ‘.‘: continue else: resolved_path.append(seg) if segments[-1] in (‘.‘, ‘..‘): # do some post-processing here. if the last segment was a relative dir, # then we need to append the trailing ‘/‘ resolved_path.append(‘‘) return _coerce_result(urlunparse((scheme, netloc, ‘/‘.join( resolved_path) or ‘/‘, params, query, fragment))) def urldefrag(url): """Removes any existing fragment from URL. Returns a tuple of the defragmented URL and the fragment. If the URL contained no fragments, the second element is the empty string. """ url, _coerce_result = _coerce_args(url) if ‘#‘ in url: s, n, p, a, q, frag = urlparse(url) defrag = urlunparse((s, n, p, a, q, ‘‘)) else: frag = ‘‘ defrag = url return _coerce_result(DefragResult(defrag, frag)) _hexdig = ‘0123456789ABCDEFabcdef‘ _hextobyte = None def unquote_to_bytes(string): """unquote_to_bytes(‘abc%20def‘) -> b‘abc def‘.""" # Note: strings are encoded as UTF-8. This is only an issue if it contains # unescaped non-ASCII characters, which URIs should not. if not string: # Is it a string-like object? string.split return b‘‘ if isinstance(string, str): string = string.encode(‘utf-8‘) bits = string.split(b‘%‘) if len(bits) == 1: return string res = [bits[0]] append = res.append # Delay the initialization of the table to not waste memory # if the function is never called global _hextobyte if _hextobyte is None: _hextobyte = {(a + b).encode(): bytes([int(a + b, 16)]) for a in _hexdig for b in _hexdig} for item in bits[1:]: try: append(_hextobyte[item[:2]]) append(item[2:]) except KeyError: append(b‘%‘) append(item) return b‘‘.join(res) _asciire = re.compile(‘([\x00-\x7f]+)‘) def unquote(string, encoding=‘utf-8‘, errors=‘replace‘): """Replace %xx escapes by their single-character equivalent. The optional encoding and errors parameters specify how to decode percent-encoded sequences into Unicode characters, as accepted by the bytes.decode() method. By default, percent-encoded sequences are decoded with UTF-8, and invalid sequences are replaced by a placeholder character. unquote(‘abc%20def‘) -> ‘abc def‘. """ if ‘%‘ not in string: string.split return string if encoding is None: encoding = ‘utf-8‘ if errors is None: errors = ‘replace‘ bits = _asciire.split(string) res = [bits[0]] append = res.append for i in range(1, len(bits), 2): append(unquote_to_bytes(bits[i]).decode(encoding, errors)) append(bits[i + 1]) return ‘‘.join(res) def parse_qs(qs, keep_blank_values=False, strict_parsing=False, encoding=‘utf-8‘, errors=‘replace‘): """Parse a query given as a string argument. Arguments: qs: percent-encoded query string to be parsed keep_blank_values: flag indicating whether blank values in percent-encoded queries should be treated as blank strings. A true value indicates that blanks should be retained as blank strings. The default false value indicates that blank values are to be ignored and treated as if they were not included. strict_parsing: flag indicating what to do with parsing errors. If false (the default), errors are silently ignored. If true, errors raise a ValueError exception. encoding and errors: specify how to decode percent-encoded sequences into Unicode characters, as accepted by the bytes.decode() method. """ parsed_result = {} pairs = parse_qsl(qs, keep_blank_values, strict_parsing, encoding=encoding, errors=errors) for name, value in pairs: if name in parsed_result: parsed_result[name].append(value) else: parsed_result[name] = [value] return parsed_result def parse_qsl(qs, keep_blank_values=False, strict_parsing=False, encoding=‘utf-8‘, errors=‘replace‘): """Parse a query given as a string argument. Arguments: qs: percent-encoded query string to be parsed keep_blank_values: flag indicating whether blank values in percent-encoded queries should be treated as blank strings. A true value indicates that blanks should be retained as blank strings. The default false value indicates that blank values are to be ignored and treated as if they were not included. strict_parsing: flag indicating what to do with parsing errors. If false (the default), errors are silently ignored. If true, errors raise a ValueError exception. encoding and errors: specify how to decode percent-encoded sequences into Unicode characters, as accepted by the bytes.decode() method. Returns a list, as G-d intended. """ qs, _coerce_result = _coerce_args(qs) pairs = [s2 for s1 in qs.split(‘&‘) for s2 in s1.split(‘;‘)] r = [] for name_value in pairs: if not name_value and not strict_parsing: continue nv = name_value.split(‘=‘, 1) if len(nv) != 2: if strict_parsing: raise ValueError("bad query field: %r" % (name_value,)) # Handle case of a control-name with no equal sign if keep_blank_values: nv.append(‘‘) else: continue if len(nv[1]) or keep_blank_values: name = nv[0].replace(‘+‘, ‘ ‘) name = unquote(name, encoding=encoding, errors=errors) name = _coerce_result(name) value = nv[1].replace(‘+‘, ‘ ‘) value = unquote(value, encoding=encoding, errors=errors) value = _coerce_result(value) r.append((name, value)) return r def unquote_plus(string, encoding=‘utf-8‘, errors=‘replace‘): """Like unquote(), but also replace plus signs by spaces, as required for unquoting HTML form values. unquote_plus(‘%7e/abc+def‘) -> ‘~/abc def‘ """ string = string.replace(‘+‘, ‘ ‘) return unquote(string, encoding, errors) _ALWAYS_SAFE = frozenset(b‘ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ‘ b‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz‘ b‘0123456789‘ b‘_.-‘) _ALWAYS_SAFE_BYTES = bytes(_ALWAYS_SAFE) _safe_quoters = {} class Quoter(collections.defaultdict): """A mapping from bytes (in range(0,256)) to strings. String values are percent-encoded byte values, unless the key < 128, and in the "safe" set (either the specified safe set, or default set). """ # Keeps a cache internally, using defaultdict, for efficiency (lookups # of cached keys don‘t call Python code at all). def __init__(self, safe): """safe: bytes object.""" self.safe = _ALWAYS_SAFE.union(safe) def __repr__(self): # Without this, will just display as a defaultdict return "<%s %r>" % (self.__class__.__name__, dict(self)) def __missing__(self, b): # Handle a cache miss. Store quoted string in cache and return. res = chr(b) if b in self.safe else ‘%{:02X}‘.format(b) self[b] = res return res def quote(string, safe=‘/‘, encoding=None, errors=None): """quote(‘abc def‘) -> ‘abc%20def‘ Each part of a URL, e.g. the path info, the query, etc., has a different set of reserved characters that must be quoted. RFC 2396 Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI): Generic Syntax lists the following reserved characters. reserved = ";" | "/" | "?" | ":" | "@" | "&" | "=" | "+" | "$" | "," Each of these characters is reserved in some component of a URL, but not necessarily in all of them. By default, the quote function is intended for quoting the path section of a URL. Thus, it will not encode ‘/‘. This character is reserved, but in typical usage the quote function is being called on a path where the existing slash characters are used as reserved characters. string and safe may be either str or bytes objects. encoding and errors must not be specified if string is a bytes object. The optional encoding and errors parameters specify how to deal with non-ASCII characters, as accepted by the str.encode method. By default, encoding=‘utf-8‘ (characters are encoded with UTF-8), and errors=‘strict‘ (unsupported characters raise a UnicodeEncodeError). """ if isinstance(string, str): if not string: return string if encoding is None: encoding = ‘utf-8‘ if errors is None: errors = ‘strict‘ string = string.encode(encoding, errors) else: if encoding is not None: raise TypeError("quote() doesn‘t support ‘encoding‘ for bytes") if errors is not None: raise TypeError("quote() doesn‘t support ‘errors‘ for bytes") return quote_from_bytes(string, safe) def quote_plus(string, safe=‘‘, encoding=None, errors=None): """Like quote(), but also replace ‘ ‘ with ‘+‘, as required for quoting HTML form values. Plus signs in the original string are escaped unless they are included in safe. It also does not have safe default to ‘/‘. """ # Check if ‘ ‘ in string, where string may either be a str or bytes. If # there are no spaces, the regular quote will produce the right answer. if ((isinstance(string, str) and ‘ ‘ not in string) or (isinstance(string, bytes) and b‘ ‘ not in string)): return quote(string, safe, encoding, errors) if isinstance(safe, str): space = ‘ ‘ else: space = b‘ ‘ string = quote(string, safe + space, encoding, errors) return string.replace(‘ ‘, ‘+‘) def quote_from_bytes(bs, safe=‘/‘): """Like quote(), but accepts a bytes object rather than a str, and does not perform string-to-bytes encoding. It always returns an ASCII string. quote_from_bytes(b‘abc def\x3f‘) -> ‘abc%20def%3f‘ """ if not isinstance(bs, (bytes, bytearray)): raise TypeError("quote_from_bytes() expected bytes") if not bs: return ‘‘ if isinstance(safe, str): # Normalize ‘safe‘ by converting to bytes and removing non-ASCII chars safe = safe.encode(‘ascii‘, ‘ignore‘) else: safe = bytes([c for c in safe if c < 128]) if not bs.rstrip(_ALWAYS_SAFE_BYTES + safe): return bs.decode() try: quoter = _safe_quoters[safe] except KeyError: _safe_quoters[safe] = quoter = Quoter(safe).__getitem__ return ‘‘.join([quoter(char) for char in bs]) def urlencode(query, doseq=False, safe=‘‘, encoding=None, errors=None, quote_via=quote_plus): """Encode a dict or sequence of two-element tuples into a URL query string. If any values in the query arg are sequences and doseq is true, each sequence element is converted to a separate parameter. If the query arg is a sequence of two-element tuples, the order of the parameters in the output will match the order of parameters in the input. The components of a query arg may each be either a string or a bytes type. The safe, encoding, and errors parameters are passed down to the function specified by quote_via (encoding and errors only if a component is a str). """ if hasattr(query, "items"): query = query.items() else: # It‘s a bother at times that strings and string-like objects are # sequences. try: # non-sequence items should not work with len() # non-empty strings will fail this if len(query) and not isinstance(query[0], tuple): raise TypeError # Zero-length sequences of all types will get here and succeed, # but that‘s a minor nit. Since the original implementation # allowed empty dicts that type of behavior probably should be # preserved for consistency except TypeError: ty, va, tb = sys.exc_info() raise TypeError("not a valid non-string sequence " "or mapping object").with_traceback(tb) l = [] if not doseq: for k, v in query: if isinstance(k, bytes): k = quote_via(k, safe) else: k = quote_via(str(k), safe, encoding, errors) if isinstance(v, bytes): v = quote_via(v, safe) else: v = quote_via(str(v), safe, encoding, errors) l.append(k + ‘=‘ + v) else: for k, v in query: if isinstance(k, bytes): k = quote_via(k, safe) else: k = quote_via(str(k), safe, encoding, errors) if isinstance(v, bytes): v = quote_via(v, safe) l.append(k + ‘=‘ + v) elif isinstance(v, str): v = quote_via(v, safe, encoding, errors) l.append(k + ‘=‘ + v) else: try: # Is this a sufficient test for sequence-ness? x = len(v) except TypeError: # not a sequence v = quote_via(str(v), safe, encoding, errors) l.append(k + ‘=‘ + v) else: # loop over the sequence for elt in v: if isinstance(elt, bytes): elt = quote_via(elt, safe) else: elt = quote_via(str(elt), safe, encoding, errors) l.append(k + ‘=‘ + elt) return ‘&‘.join(l) # Utilities to parse URLs (most of these return None for missing parts): # unwrap(‘<URL:type://host/path>‘) --> ‘type://host/path‘ # splittype(‘type:opaquestring‘) --> ‘type‘, ‘opaquestring‘ # splithost(‘//host[:port]/path‘) --> ‘host[:port]‘, ‘/path‘ # splituser(‘user[:passwd]@host[:port]‘) --> ‘user[:passwd]‘, ‘host[:port]‘ # splitpasswd(‘user:passwd‘) -> ‘user‘, ‘passwd‘ # splitport(‘host:port‘) --> ‘host‘, ‘port‘ # splitquery(‘/path?query‘) --> ‘/path‘, ‘query‘ # splittag(‘/path#tag‘) --> ‘/path‘, ‘tag‘ # splitattr(‘/path;attr1=value1;attr2=value2;...‘) -> # ‘/path‘, [‘attr1=value1‘, ‘attr2=value2‘, ...] # splitvalue(‘attr=value‘) --> ‘attr‘, ‘value‘ # urllib.parse.unquote(‘abc%20def‘) -> ‘abc def‘ # quote(‘abc def‘) -> ‘abc%20def‘) def to_bytes(url): """to_bytes(u"URL") --> ‘URL‘.""" # Most URL schemes require ASCII. If that changes, the conversion # can be relaxed. # XXX get rid of to_bytes() if isinstance(url, str): try: url = url.encode("ASCII").decode() except UnicodeError: raise UnicodeError("URL " + repr(url) + " contains non-ASCII characters") return url def unwrap(url): """unwrap(‘<URL:type://host/path>‘) --> ‘type://host/path‘.""" url = str(url).strip() if url[:1] == ‘<‘ and url[-1:] == ‘>‘: url = url[1:-1].strip() if url[:4] == ‘URL:‘: url = url[4:].strip() return url _typeprog = None def splittype(url): """splittype(‘type:opaquestring‘) --> ‘type‘, ‘opaquestring‘.""" global _typeprog if _typeprog is None: _typeprog = re.compile(‘([^/:]+):(.*)‘, re.DOTALL) match = _typeprog.match(url) if match: scheme, data = match.groups() return scheme.lower(), data return None, url _hostprog = None def splithost(url): """splithost(‘//host[:port]/path‘) --> ‘host[:port]‘, ‘/path‘.""" global _hostprog if _hostprog is None: _hostprog = re.compile(‘//([^/?]*)(.*)‘, re.DOTALL) match = _hostprog.match(url) if match: host_port, path = match.groups() if path and path[0] != ‘/‘: path = ‘/‘ + path return host_port, path return None, url def splituser(host): """splituser(‘user[:passwd]@host[:port]‘) --> ‘user[:passwd]‘, ‘host[:port]‘.""" user, delim, host = host.rpartition(‘@‘) return (user if delim else None), host def splitpasswd(user): """splitpasswd(‘user:passwd‘) -> ‘user‘, ‘passwd‘.""" user, delim, passwd = user.partition(‘:‘) return user, (passwd if delim else None) # splittag(‘/path#tag‘) --> ‘/path‘, ‘tag‘ _portprog = None def splitport(host): """splitport(‘host:port‘) --> ‘host‘, ‘port‘.""" global _portprog if _portprog is None: _portprog = re.compile(‘(.*):([0-9]*)$‘, re.DOTALL) match = _portprog.match(host) if match: host, port = match.groups() if port: return host, port return host, None def splitnport(host, defport=-1): """Split host and port, returning numeric port. Return given default port if no ‘:‘ found; defaults to -1. Return numerical port if a valid number are found after ‘:‘. Return None if ‘:‘ but not a valid number.""" host, delim, port = host.rpartition(‘:‘) if not delim: host = port elif port: try: nport = int(port) except ValueError: nport = None return host, nport return host, defport def splitquery(url): """splitquery(‘/path?query‘) --> ‘/path‘, ‘query‘.""" path, delim, query = url.rpartition(‘?‘) if delim: return path, query return url, None def splittag(url): """splittag(‘/path#tag‘) --> ‘/path‘, ‘tag‘.""" path, delim, tag = url.rpartition(‘#‘) if delim: return path, tag return url, None def splitattr(url): """splitattr(‘/path;attr1=value1;attr2=value2;...‘) -> ‘/path‘, [‘attr1=value1‘, ‘attr2=value2‘, ...].""" words = url.split(‘;‘) return words[0], words[1:] def splitvalue(attr): """splitvalue(‘attr=value‘) --> ‘attr‘, ‘value‘.""" attr, delim, value = attr.partition(‘=‘) return attr, (value if delim else None)

"""An extensible library for opening URLs using a variety of protocols The simplest way to use this module is to call the urlopen function, which accepts a string containing a URL or a Request object (described below). It opens the URL and returns the results as file-like object; the returned object has some extra methods described below. The OpenerDirector manages a collection of Handler objects that do all the actual work. Each Handler implements a particular protocol or option. The OpenerDirector is a composite object that invokes the Handlers needed to open the requested URL. For example, the HTTPHandler performs HTTP GET and POST requests and deals with non-error returns. The HTTPRedirectHandler automatically deals with HTTP 301, 302, 303 and 307 redirect errors, and the HTTPDigestAuthHandler deals with digest authentication. urlopen(url, data=None) -- Basic usage is the same as original urllib. pass the url and optionally data to post to an HTTP URL, and get a file-like object back. One difference is that you can also pass a Request instance instead of URL. Raises a URLError (subclass of OSError); for HTTP errors, raises an HTTPError, which can also be treated as a valid response. build_opener -- Function that creates a new OpenerDirector instance. Will install the default handlers. Accepts one or more Handlers as arguments, either instances or Handler classes that it will instantiate. If one of the argument is a subclass of the default handler, the argument will be installed instead of the default. install_opener -- Installs a new opener as the default opener. objects of interest: OpenerDirector -- Sets up the User Agent as the Python-urllib client and manages the Handler classes, while dealing with requests and responses. Request -- An object that encapsulates the state of a request. The state can be as simple as the URL. It can also include extra HTTP headers, e.g. a User-Agent. BaseHandler -- internals: BaseHandler and parent _call_chain conventions Example usage: import urllib.request # set up authentication info authinfo = urllib.request.HTTPBasicAuthHandler() authinfo.add_password(realm=‘PDQ Application‘, uri=‘https://mahler:8092/site-updates.py‘, user=‘klem‘, passwd=‘geheim$parole‘) proxy_support = urllib.request.ProxyHandler({"http" : "http://ahad-haam:3128"}) # build a new opener that adds authentication and caching FTP handlers opener = urllib.request.build_opener(proxy_support, authinfo, urllib.request.CacheFTPHandler) # install it urllib.request.install_opener(opener) f = urllib.request.urlopen(‘http://www.python.org/‘) """ # XXX issues: # If an authentication error handler that tries to perform # authentication for some reason but fails, how should the error be # signalled? The client needs to know the HTTP error code. But if # the handler knows that the problem was, e.g., that it didn‘t know # that hash algo that requested in the challenge, it would be good to # pass that information along to the client, too. # ftp errors aren‘t handled cleanly # check digest against correct (i.e. non-apache) implementation # Possible extensions: # complex proxies XXX not sure what exactly was meant by this # abstract factory for opener import base64 import bisect import email import hashlib import http.client import io import os import posixpath import re import socket import sys import time import collections import tempfile import contextlib import warnings from urllib.error import URLError, HTTPError, ContentTooShortError from urllib.parse import ( urlparse, urlsplit, urljoin, unwrap, quote, unquote, splittype, splithost, splitport, splituser, splitpasswd, splitattr, splitquery, splitvalue, splittag, to_bytes, unquote_to_bytes, urlunparse) from urllib.response import addinfourl, addclosehook # check for SSL try: import ssl except ImportError: _have_ssl = False else: _have_ssl = True __all__ = [ # Classes ‘Request‘, ‘OpenerDirector‘, ‘BaseHandler‘, ‘HTTPDefaultErrorHandler‘, ‘HTTPRedirectHandler‘, ‘HTTPCookieProcessor‘, ‘ProxyHandler‘, ‘HTTPPasswordMgr‘, ‘HTTPPasswordMgrWithDefaultRealm‘, ‘HTTPPasswordMgrWithPriorAuth‘, ‘AbstractBasicAuthHandler‘, ‘HTTPBasicAuthHandler‘, ‘ProxyBasicAuthHandler‘, ‘AbstractDigestAuthHandler‘, ‘HTTPDigestAuthHandler‘, ‘ProxyDigestAuthHandler‘, ‘HTTPHandler‘, ‘FileHandler‘, ‘FTPHandler‘, ‘CacheFTPHandler‘, ‘DataHandler‘, ‘UnknownHandler‘, ‘HTTPErrorProcessor‘, # Functions ‘urlopen‘, ‘install_opener‘, ‘build_opener‘, ‘pathname2url‘, ‘url2pathname‘, ‘getproxies‘, # Legacy interface ‘urlretrieve‘, ‘urlcleanup‘, ‘URLopener‘, ‘FancyURLopener‘, ] # used in User-Agent header sent __version__ = sys.version[:3] _opener = None def urlopen(url, data=None, timeout=socket._GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT, *, cafile=None, capath=None, cadefault=False, context=None): global _opener if cafile or capath or cadefault: if context is not None: raise ValueError( "You can‘t pass both context and any of cafile, capath, and " "cadefault" ) if not _have_ssl: raise ValueError(‘SSL support not available‘) context = ssl.create_default_context(ssl.Purpose.SERVER_AUTH, cafile=cafile, capath=capath) https_handler = HTTPSHandler(context=context) opener = build_opener(https_handler) elif context: https_handler = HTTPSHandler(context=context) opener = build_opener(https_handler) elif _opener is None: _opener = opener = build_opener() else: opener = _opener return opener.open(url, data, timeout) def install_opener(opener): global _opener _opener = opener _url_tempfiles = [] def urlretrieve(url, filename=None, reporthook=None, data=None): """ Retrieve a URL into a temporary location on disk. Requires a URL argument. If a filename is passed, it is used as the temporary file location. The reporthook argument should be a callable that accepts a block number, a read size, and the total file size of the URL target. The data argument should be valid URL encoded data. If a filename is passed and the URL points to a local resource, the result is a copy from local file to new file. Returns a tuple containing the path to the newly created data file as well as the resulting HTTPMessage object. """ url_type, path = splittype(url) with contextlib.closing(urlopen(url, data)) as fp: headers = fp.info() # Just return the local path and the "headers" for file:// # URLs. No sense in performing a copy unless requested. if url_type == "file" and not filename: return os.path.normpath(path), headers # Handle temporary file setup. if filename: tfp = open(filename, ‘wb‘) else: tfp = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False) filename = tfp.name _url_tempfiles.append(filename) with tfp: result = filename, headers bs = 1024*8 size = -1 read = 0 blocknum = 0 if "content-length" in headers: size = int(headers["Content-Length"]) if reporthook: reporthook(blocknum, bs, size) while True: block = fp.read(bs) if not block: break read += len(block) tfp.write(block) blocknum += 1 if reporthook: reporthook(blocknum, bs, size) if size >= 0 and read < size: raise ContentTooShortError( "retrieval incomplete: got only %i out of %i bytes" % (read, size), result) return result def urlcleanup(): """Clean up temporary files from urlretrieve calls.""" for temp_file in _url_tempfiles: try: os.unlink(temp_file) except OSError: pass del _url_tempfiles[:] global _opener if _opener: _opener = None # copied from cookielib.py _cut_port_re = re.compile(r":\d+$", re.ASCII) def request_host(request): """Return request-host, as defined by RFC 2965. Variation from RFC: returned value is lowercased, for convenient comparison. """ url = request.full_url host = urlparse(url)[1] if host == "": host = request.get_header("Host", "") # remove port, if present host = _cut_port_re.sub("", host, 1) return host.lower() class Request: def __init__(self, url, data=None, headers={}, origin_req_host=None, unverifiable=False, method=None): self.full_url = url self.headers = {} self.unredirected_hdrs = {} self._data = None self.data = data self._tunnel_host = None for key, value in headers.items(): self.add_header(key, value) if origin_req_host is None: origin_req_host = request_host(self) self.origin_req_host = origin_req_host self.unverifiable = unverifiable if method: self.method = method @property def full_url(self): if self.fragment: return ‘{}#{}‘.format(self._full_url, self.fragment) return self._full_url @full_url.setter def full_url(self, url): # unwrap(‘<URL:type://host/path>‘) --> ‘type://host/path‘ self._full_url = unwrap(url) self._full_url, self.fragment = splittag(self._full_url) self._parse() @full_url.deleter def full_url(self): self._full_url = None self.fragment = None self.selector = ‘‘ @property def data(self): return self._data @data.setter def data(self, data): if data != self._data: self._data = data # issue 16464 # if we change data we need to remove content-length header # (cause it‘s most probably calculated for previous value) if self.has_header("Content-length"): self.remove_header("Content-length") @data.deleter def data(self): self.data = None def _parse(self): self.type, rest = splittype(self._full_url) if self.type is None: raise ValueError("unknown url type: %r" % self.full_url) self.host, self.selector = splithost(rest) if self.host: self.host = unquote(self.host) def get_method(self): """Return a string indicating the HTTP request method.""" default_method = "POST" if self.data is not None else "GET" return getattr(self, ‘method‘, default_method) def get_full_url(self): return self.full_url def set_proxy(self, host, type): if self.type == ‘https‘ and not self._tunnel_host: self._tunnel_host = self.host else: self.type= type self.selector = self.full_url self.host = host def has_proxy(self): return self.selector == self.full_url def add_header(self, key, val): # useful for something like authentication self.headers[key.capitalize()] = val def add_unredirected_header(self, key, val): # will not be added to a redirected request self.unredirected_hdrs[key.capitalize()] = val def has_header(self, header_name): return (header_name in self.headers or header_name in self.unredirected_hdrs) def get_header(self, header_name, default=None): return self.headers.get( header_name, self.unredirected_hdrs.get(header_name, default)) def remove_header(self, header_name): self.headers.pop(header_name, None) self.unredirected_hdrs.pop(header_name, None) def header_items(self): hdrs = self.unredirected_hdrs.copy() hdrs.update(self.headers) return list(hdrs.items()) class OpenerDirector: def __init__(self): client_version = "Python-urllib/%s" % __version__ self.addheaders = [(‘User-agent‘, client_version)] # self.handlers is retained only for backward compatibility self.handlers = [] # manage the individual handlers self.handle_open = {} self.handle_error = {} self.process_response = {} self.process_request = {} def add_handler(self, handler): if not hasattr(handler, "add_parent"): raise TypeError("expected BaseHandler instance, got %r" % type(handler)) added = False for meth in dir(handler): if meth in ["redirect_request", "do_open", "proxy_open"]: # oops, coincidental match continue i = meth.find("_") protocol = meth[:i] condition = meth[i+1:] if condition.startswith("error"): j = condition.find("_") + i + 1 kind = meth[j+1:] try: kind = int(kind) except ValueError: pass lookup = self.handle_error.get(protocol, {}) self.handle_error[protocol] = lookup elif condition == "open": kind = protocol lookup = self.handle_open elif condition == "response": kind = protocol lookup = self.process_response elif condition == "request": kind = protocol lookup = self.process_request else: continue handlers = lookup.setdefault(kind, []) if handlers: bisect.insort(handlers, handler) else: handlers.append(handler) added = True if added: bisect.insort(self.handlers, handler) handler.add_parent(self) def close(self): # Only exists for backwards compatibility. pass def _call_chain(self, chain, kind, meth_name, *args): # Handlers raise an exception if no one else should try to handle # the request, or return None if they can‘t but another handler # could. Otherwise, they return the response. handlers = chain.get(kind, ()) for handler in handlers: func = getattr(handler, meth_name) result = func(*args) if result is not None: return result def open(self, fullurl, data=None, timeout=socket._GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT): # accept a URL or a Request object if isinstance(fullurl, str): req = Request(fullurl, data) else: req = fullurl if data is not None: req.data = data req.timeout = timeout protocol = req.type # pre-process request meth_name = protocol+"_request" for processor in self.process_request.get(protocol, []): meth = getattr(processor, meth_name) req = meth(req) response = self._open(req, data) # post-process response meth_name = protocol+"_response" for processor in self.process_response.get(protocol, []): meth = getattr(processor, meth_name) response = meth(req, response) return response def _open(self, req, data=None): result = self._call_chain(self.handle_open, ‘default‘, ‘default_open‘, req) if result: return result protocol = req.type result = self._call_chain(self.handle_open, protocol, protocol + ‘_open‘, req) if result: return result return self._call_chain(self.handle_open, ‘unknown‘, ‘unknown_open‘, req) def error(self, proto, *args): if proto in (‘http‘, ‘https‘): # XXX http[s] protocols are special-cased dict = self.handle_error[‘http‘] # https is not different than http proto = args[2] # YUCK! meth_name = ‘http_error_%s‘ % proto http_err = 1 orig_args = args else: dict = self.handle_error meth_name = proto + ‘_error‘ http_err = 0 args = (dict, proto, meth_name) + args result = self._call_chain(*args) if result: return result if http_err: args = (dict, ‘default‘, ‘http_error_default‘) + orig_args return self._call_chain(*args) # XXX probably also want an abstract factory that knows when it makes # sense to skip a superclass in favor of a subclass and when it might # make sense to include both def build_opener(*handlers): """Create an opener object from a list of handlers. The opener will use several default handlers, including support for HTTP, FTP and when applicable HTTPS. If any of the handlers passed as arguments are subclasses of the default handlers, the default handlers will not be used. """ opener = OpenerDirector() default_classes = [ProxyHandler, UnknownHandler, HTTPHandler, HTTPDefaultErrorHandler, HTTPRedirectHandler, FTPHandler, FileHandler, HTTPErrorProcessor, DataHandler] if hasattr(http.client, "HTTPSConnection"): default_classes.append(HTTPSHandler) skip = set() for klass in default_classes: for check in handlers: if isinstance(check, type): if issubclass(check, klass): skip.add(klass) elif isinstance(check, klass): skip.add(klass) for klass in skip: default_classes.remove(klass) for klass in default_classes: opener.add_handler(klass()) for h in handlers: if isinstance(h, type): h = h() opener.add_handler(h) return opener class BaseHandler: handler_order = 500 def add_parent(self, parent): self.parent = parent def close(self): # Only exists for backwards compatibility pass def __lt__(self, other): if not hasattr(other, "handler_order"): # Try to preserve the old behavior of having custom classes # inserted after default ones (works only for custom user # classes which are not aware of handler_order). return True return self.handler_order < other.handler_order class HTTPErrorProcessor(BaseHandler): """Process HTTP error responses.""" handler_order = 1000 # after all other processing def http_response(self, request, response): code, msg, hdrs = response.code, response.msg, response.info() # According to RFC 2616, "2xx" code indicates that the client‘s # request was successfully received, understood, and accepted. if not (200 <= code < 300): response = self.parent.error( ‘http‘, request, response, code, msg, hdrs) return response https_response = http_response class HTTPDefaultErrorHandler(BaseHandler): def http_error_default(self, req, fp, code, msg, hdrs): raise HTTPError(req.full_url, code, msg, hdrs, fp) class HTTPRedirectHandler(BaseHandler): # maximum number of redirections to any single URL # this is needed because of the state that cookies introduce max_repeats = 4 # maximum total number of redirections (regardless of URL) before # assuming we‘re in a loop max_redirections = 10 def redirect_request(self, req, fp, code, msg, headers, newurl): """Return a Request or None in response to a redirect. This is called by the http_error_30x methods when a redirection response is received. If a redirection should take place, return a new Request to allow http_error_30x to perform the redirect. Otherwise, raise HTTPError if no-one else should try to handle this url. Return None if you can‘t but another Handler might. """ m = req.get_method() if (not (code in (301, 302, 303, 307) and m in ("GET", "HEAD") or code in (301, 302, 303) and m == "POST")): raise HTTPError(req.full_url, code, msg, headers, fp) # Strictly (according to RFC 2616), 301 or 302 in response to # a POST MUST NOT cause a redirection without confirmation # from the user (of urllib.request, in this case). In practice, # essentially all clients do redirect in this case, so we do # the same. # be conciliant with URIs containing a space newurl = newurl.replace(‘ ‘, ‘%20‘) CONTENT_HEADERS = ("content-length", "content-type") newheaders = dict((k, v) for k, v in req.headers.items() if k.lower() not in CONTENT_HEADERS) return Request(newurl, headers=newheaders, origin_req_host=req.origin_req_host, unverifiable=True) # Implementation note: To avoid the server sending us into an # infinite loop, the request object needs to track what URLs we # have already seen. Do this by adding a handler-specific # attribute to the Request object. def http_error_302(self, req, fp, code, msg, headers): # Some servers (incorrectly) return multiple Location headers # (so probably same goes for URI). Use first header. if "location" in headers: newurl = headers["location"] elif "uri" in headers: newurl = headers["uri"] else: return # fix a possible malformed URL urlparts = urlparse(newurl) # For security reasons we don‘t allow redirection to anything other # than http, https or ftp. if urlparts.scheme not in (‘http‘, ‘https‘, ‘ftp‘, ‘‘): raise HTTPError( newurl, code, "%s - Redirection to url ‘%s‘ is not allowed" % (msg, newurl), headers, fp) if not urlparts.path: urlparts = list(urlparts) urlparts[2] = "/" newurl = urlunparse(urlparts) newurl = urljoin(req.full_url, newurl) # XXX Probably want to forget about the state of the current # request, although that might interact poorly with other # handlers that also use handler-specific request attributes new = self.redirect_request(req, fp, code, msg, headers, newurl) if new is None: return # loop detection # .redirect_dict has a key url if url was previously visited. if hasattr(req, ‘redirect_dict‘): visited = new.redirect_dict = req.redirect_dict if (visited.get(newurl, 0) >= self.max_repeats or len(visited) >= self.max_redirections): raise HTTPError(req.full_url, code, self.inf_msg + msg, headers, fp) else: visited = new.redirect_dict = req.redirect_dict = {} visited[newurl] = visited.get(newurl, 0) + 1 # Don‘t close the fp until we are sure that we won‘t use it # with HTTPError. fp.read() fp.close() return self.parent.open(new, timeout=req.timeout) http_error_301 = http_error_303 = http_error_307 = http_error_302 inf_msg = "The HTTP server returned a redirect error that would " "lead to an infinite loop.\n" "The last 30x error message was:\n" def _parse_proxy(proxy): """Return (scheme, user, password, host/port) given a URL or an authority. If a URL is supplied, it must have an authority (host:port) component. According to RFC 3986, having an authority component means the URL must have two slashes after the scheme. """ scheme, r_scheme = splittype(proxy) if not r_scheme.startswith("/"): # authority scheme = None authority = proxy else: # URL if not r_scheme.startswith("//"): raise ValueError("proxy URL with no authority: %r" % proxy) # We have an authority, so for RFC 3986-compliant URLs (by ss 3. # and 3.3.), path is empty or starts with ‘/‘ end = r_scheme.find("/", 2) if end == -1: end = None authority = r_scheme[2:end] userinfo, hostport = splituser(authority) if userinfo is not None: user, password = splitpasswd(userinfo) else: user = password = None return scheme, user, password, hostport class ProxyHandler(BaseHandler): # Proxies must be in front handler_order = 100 def __init__(self, proxies=None): if proxies is None: proxies = getproxies() assert hasattr(proxies, ‘keys‘), "proxies must be a mapping" self.proxies = proxies for type, url in proxies.items(): setattr(self, ‘%s_open‘ % type, lambda r, proxy=url, type=type, meth=self.proxy_open: meth(r, proxy, type)) def proxy_open(self, req, proxy, type): orig_type = req.type proxy_type, user, password, hostport = _parse_proxy(proxy) if proxy_type is None: proxy_type = orig_type if req.host and proxy_bypass(req.host): return None if user and password: user_pass = ‘%s:%s‘ % (unquote(user), unquote(password)) creds = base64.b64encode(user_pass.encode()).decode("ascii") req.add_header(‘Proxy-authorization‘, ‘Basic ‘ + creds) hostport = unquote(hostport) req.set_proxy(hostport, proxy_type) if orig_type == proxy_type or orig_type == ‘https‘: # let other handlers take care of it return None else: # need to start over, because the other handlers don‘t # grok the proxy‘s URL type # e.g. if we have a constructor arg proxies like so: # {‘http‘: ‘ftp://proxy.example.com‘}, we may end up turning # a request for http://acme.example.com/a into one for # ftp://proxy.example.com/a return self.parent.open(req, timeout=req.timeout) class HTTPPasswordMgr: def __init__(self): self.passwd = {} def add_password(self, realm, uri, user, passwd): # uri could be a single URI or a sequence if isinstance(uri, str): uri = [uri] if realm not in self.passwd: self.passwd[realm] = {} for default_port in True, False: reduced_uri = tuple( [self.reduce_uri(u, default_port) for u in uri]) self.passwd[realm][reduced_uri] = (user, passwd) def find_user_password(self, realm, authuri): domains = self.passwd.get(realm, {}) for default_port in True, False: reduced_authuri = self.reduce_uri(authuri, default_port) for uris, authinfo in domains.items(): for uri in uris: if self.is_suburi(uri, reduced_authuri): return authinfo return None, None def reduce_uri(self, uri, default_port=True): """Accept authority or URI and extract only the authority and path.""" # note HTTP URLs do not have a userinfo component parts = urlsplit(uri) if parts[1]: # URI scheme = parts[0] authority = parts[1] path = parts[2] or ‘/‘ else: # host or host:port scheme = None authority = uri path = ‘/‘ host, port = splitport(authority) if default_port and port is None and scheme is not None: dport = {"http": 80, "https": 443, }.get(scheme) if dport is not None: authority = "%s:%d" % (host, dport) return authority, path def is_suburi(self, base, test): """Check if test is below base in a URI tree Both args must be URIs in reduced form. """ if base == test: return True if base[0] != test[0]: return False common = posixpath.commonprefix((base[1], test[1])) if len(common) == len(base[1]): return True return False class HTTPPasswordMgrWithDefaultRealm(HTTPPasswordMgr): def find_user_password(self, realm, authuri): user, password = HTTPPasswordMgr.find_user_password(self, realm, authuri) if user is not None: return user, password return HTTPPasswordMgr.find_user_password(self, None, authuri) class HTTPPasswordMgrWithPriorAuth(HTTPPasswordMgrWithDefaultRealm): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): self.authenticated = {} super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) def add_password(self, realm, uri, user, passwd, is_authenticated=False): self.update_authenticated(uri, is_authenticated) # Add a default for prior auth requests if realm is not None: super().add_password(None, uri, user, passwd) super().add_password(realm, uri, user, passwd) def update_authenticated(self, uri, is_authenticated=False): # uri could be a single URI or a sequence if isinstance(uri, str): uri = [uri] for default_port in True, False: for u in uri: reduced_uri = self.reduce_uri(u, default_port) self.authenticated[reduced_uri] = is_authenticated def is_authenticated(self, authuri): for default_port in True, False: reduced_authuri = self.reduce_uri(authuri, default_port) for uri in self.authenticated: if self.is_suburi(uri, reduced_authuri): return self.authenticated[uri] class AbstractBasicAuthHandler: # XXX this allows for multiple auth-schemes, but will stupidly pick # the last one with a realm specified. # allow for double- and single-quoted realm values # (single quotes are a violation of the RFC, but appear in the wild) rx = re.compile(‘(?:.*,)*[ \t]*([^ \t]+)[ \t]+‘ ‘realm=(["\‘]?)([^"\‘]*)\\2‘, re.I) # XXX could pre-emptively send auth info already accepted (RFC 2617, # end of section 2, and section 1.2 immediately after "credentials" # production). def __init__(self, password_mgr=None): if password_mgr is None: password_mgr = HTTPPasswordMgr() self.passwd = password_mgr self.add_password = self.passwd.add_password def http_error_auth_reqed(self, authreq, host, req, headers): # host may be an authority (without userinfo) or a URL with an # authority # XXX could be multiple headers authreq = headers.get(authreq, None) if authreq: scheme = authreq.split()[0] if scheme.lower() != ‘basic‘: raise ValueError("AbstractBasicAuthHandler does not" " support the following scheme: ‘%s‘" % scheme) else: mo = AbstractBasicAuthHandler.rx.search(authreq) if mo: scheme, quote, realm = mo.groups() if quote not in [‘"‘,"‘"]: warnings.warn("Basic Auth Realm was unquoted", UserWarning, 2) if scheme.lower() == ‘basic‘: return self.retry_http_basic_auth(host, req, realm) def retry_http_basic_auth(self, host, req, realm): user, pw = self.passwd.find_user_password(realm, host) if pw is not None: raw = "%s:%s" % (user, pw) auth = "Basic " + base64.b64encode(raw.encode()).decode("ascii") if req.get_header(self.auth_header, None) == auth: return None req.add_unredirected_header(self.auth_header, auth) return self.parent.open(req, timeout=req.timeout) else: return None def http_request(self, req): if (not hasattr(self.passwd, ‘is_authenticated‘) or not self.passwd.is_authenticated(req.full_url)): return req if not req.has_header(‘Authorization‘): user, passwd = self.passwd.find_user_password(None, req.full_url) credentials = ‘{0}:{1}‘.format(user, passwd).encode() auth_str = base64.standard_b64encode(credentials).decode() req.add_unredirected_header(‘Authorization‘, ‘Basic {}‘.format(auth_str.strip())) return req def http_response(self, req, response): if hasattr(self.passwd, ‘is_authenticated‘): if 200 <= response.code < 300: self.passwd.update_authenticated(req.full_url, True) else: self.passwd.update_authenticated(req.full_url, False) return response https_request = http_request https_response = http_response class HTTPBasicAuthHandler(AbstractBasicAuthHandler, BaseHandler): auth_header = ‘Authorization‘ def http_error_401(self, req, fp, code, msg, headers): url = req.full_url response = self.http_error_auth_reqed(‘www-authenticate‘, url, req, headers) return response class ProxyBasicAuthHandler(AbstractBasicAuthHandler, BaseHandler): auth_header = ‘Proxy-authorization‘ def http_error_407(self, req, fp, code, msg, headers): # http_error_auth_reqed requires that there is no userinfo component in # authority. Assume there isn‘t one, since urllib.request does not (and # should not, RFC 3986 s. 3.2.1) support requests for URLs containing # userinfo. authority = req.host response = self.http_error_auth_reqed(‘proxy-authenticate‘, authority, req, headers) return response # Return n random bytes. _randombytes = os.urandom class AbstractDigestAuthHandler: # Digest authentication is specified in RFC 2617. # XXX The client does not inspect the Authentication-Info header # in a successful response. # XXX It should be possible to test this implementation against # a mock server that just generates a static set of challenges. # XXX qop="auth-int" supports is shaky def __init__(self, passwd=None): if passwd is None: passwd = HTTPPasswordMgr() self.passwd = passwd self.add_password = self.passwd.add_password self.retried = 0 self.nonce_count = 0 self.last_nonce = None def reset_retry_count(self): self.retried = 0 def http_error_auth_reqed(self, auth_header, host, req, headers): authreq = headers.get(auth_header, None) if self.retried > 5: # Don‘t fail endlessly - if we failed once, we‘ll probably # fail a second time. Hm. Unless the Password Manager is # prompting for the information. Crap. This isn‘t great # but it‘s better than the current ‘repeat until recursion # depth exceeded‘ approach <wink> raise HTTPError(req.full_url, 401, "digest auth failed", headers, None) else: self.retried += 1 if authreq: scheme = authreq.split()[0] if scheme.lower() == ‘digest‘: return self.retry_http_digest_auth(req, authreq) elif scheme.lower() != ‘basic‘: raise ValueError("AbstractDigestAuthHandler does not support" " the following scheme: ‘%s‘" % scheme) def retry_http_digest_auth(self, req, auth): token, challenge = auth.split(‘ ‘, 1) chal = parse_keqv_list(filter(None, parse_http_list(challenge))) auth = self.get_authorization(req, chal) if auth: auth_val = ‘Digest %s‘ % auth if req.headers.get(self.auth_header, None) == auth_val: return None req.add_unredirected_header(self.auth_header, auth_val) resp = self.parent.open(req, timeout=req.timeout) return resp def get_cnonce(self, nonce): # The cnonce-value is an opaque # quoted string value provided by the client and used by both client # and server to avoid chosen plaintext attacks, to provide mutual # authentication, and to provide some message integrity protection. # This isn‘t a fabulous effort, but it‘s probably Good Enough. s = "%s:%s:%s:" % (self.nonce_count, nonce, time.ctime()) b = s.encode("ascii") + _randombytes(8) dig = hashlib.sha1(b).hexdigest() return dig[:16] def get_authorization(self, req, chal): try: realm = chal[‘realm‘] nonce = chal[‘nonce‘] qop = chal.get(‘qop‘) algorithm = chal.get(‘algorithm‘, ‘MD5‘) # mod_digest doesn‘t send an opaque, even though it isn‘t # supposed to be optional opaque = chal.get(‘opaque‘, None) except KeyError: return None H, KD = self.get_algorithm_impls(algorithm) if H is None: return None user, pw = self.passwd.find_user_password(realm, req.full_url) if user is None: return None # XXX not implemented yet if req.data is not None: entdig = self.get_entity_digest(req.data, chal) else: entdig = None A1 = "%s:%s:%s" % (user, realm, pw) A2 = "%s:%s" % (req.get_method(), # XXX selector: what about proxies and full urls req.selector) if qop == ‘auth‘: if nonce == self.last_nonce: self.nonce_count += 1 else: self.nonce_count = 1 self.last_nonce = nonce ncvalue = ‘%08x‘ % self.nonce_count cnonce = self.get_cnonce(nonce) noncebit = "%s:%s:%s:%s:%s" % (nonce, ncvalue, cnonce, qop, H(A2)) respdig = KD(H(A1), noncebit) elif qop is None: respdig = KD(H(A1), "%s:%s" % (nonce, H(A2))) else: # XXX handle auth-int. raise URLError("qop ‘%s‘ is not supported." % qop) # XXX should the partial digests be encoded too? base = ‘username="%s", realm="%s", nonce="%s", uri="%s", ‘ ‘response="%s"‘ % (user, realm, nonce, req.selector, respdig) if opaque: base += ‘, opaque="%s"‘ % opaque if entdig: base += ‘, digest="%s"‘ % entdig base += ‘, algorithm="%s"‘ % algorithm if qop: base += ‘, qop=auth, nc=%s, cnonce="%s"‘ % (ncvalue, cnonce) return base def get_algorithm_impls(self, algorithm): # lambdas assume digest modules are imported at the top level if algorithm == ‘MD5‘: H = lambda x: hashlib.md5(x.encode("ascii")).hexdigest() elif algorithm == ‘SHA‘: H = lambda x: hashlib.sha1(x.encode("ascii")).hexdigest() # XXX MD5-sess KD = lambda s, d: H("%s:%s" % (s, d)) return H, KD def get_entity_digest(self, data, chal): # XXX not implemented yet return None class HTTPDigestAuthHandler(BaseHandler, AbstractDigestAuthHandler): """An authentication protocol defined by RFC 2069 Digest authentication improves on basic authentication because it does not transmit passwords in the clear. """ auth_header = ‘Authorization‘ handler_order = 490 # before Basic auth def http_error_401(self, req, fp, code, msg, headers): host = urlparse(req.full_url)[1] retry = self.http_error_auth_reqed(‘www-authenticate‘, host, req, headers) self.reset_retry_count() return retry class ProxyDigestAuthHandler(BaseHandler, AbstractDigestAuthHandler): auth_header = ‘Proxy-Authorization‘ handler_order = 490 # before Basic auth def http_error_407(self, req, fp, code, msg, headers): host = req.host retry = self.http_error_auth_reqed(‘proxy-authenticate‘, host, req, headers) self.reset_retry_count() return retry class AbstractHTTPHandler(BaseHandler): def __init__(self, debuglevel=0): self._debuglevel = debuglevel def set_http_debuglevel(self, level): self._debuglevel = level def do_request_(self, request): host = request.host if not host: raise URLError(‘no host given‘) if request.data is not None: # POST data = request.data if isinstance(data, str): msg = "POST data should be bytes or an iterable of bytes. " "It cannot be of type str." raise TypeError(msg) if not request.has_header(‘Content-type‘): request.add_unredirected_header( ‘Content-type‘, ‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded‘) if not request.has_header(‘Content-length‘): try: mv = memoryview(data) except TypeError: if isinstance(data, collections.Iterable): raise ValueError("Content-Length should be specified " "for iterable data of type %r %r" % (type(data), data)) else: request.add_unredirected_header( ‘Content-length‘, ‘%d‘ % (len(mv) * mv.itemsize)) sel_host = host if request.has_proxy(): scheme, sel = splittype(request.selector) sel_host, sel_path = splithost(sel) if not request.has_header(‘Host‘): request.add_unredirected_header(‘Host‘, sel_host) for name, value in self.parent.addheaders: name = name.capitalize() if not request.has_header(name): request.add_unredirected_header(name, value) return request def do_open(self, http_class, req, **http_conn_args): """Return an HTTPResponse object for the request, using http_class. http_class must implement the HTTPConnection API from http.client. """ host = req.host if not host: raise URLError(‘no host given‘) # will parse host:port h = http_class(host, timeout=req.timeout, **http_conn_args) headers = dict(req.unredirected_hdrs) headers.update(dict((k, v) for k, v in req.headers.items() if k not in headers)) # TODO(jhylton): Should this be redesigned to handle # persistent connections? # We want to make an HTTP/1.1 request, but the addinfourl # class isn‘t prepared to deal with a persistent connection. # It will try to read all remaining data from the socket, # which will block while the server waits for the next request. # So make sure the connection gets closed after the (only) # request. headers["Connection"] = "close" headers = dict((name.title(), val) for name, val in headers.items()) if req._tunnel_host: tunnel_headers = {} proxy_auth_hdr = "Proxy-Authorization" if proxy_auth_hdr in headers: tunnel_headers[proxy_auth_hdr] = headers[proxy_auth_hdr] # Proxy-Authorization should not be sent to origin # server. del headers[proxy_auth_hdr] h.set_tunnel(req._tunnel_host, headers=tunnel_headers) try: try: h.request(req.get_method(), req.selector, req.data, headers) except OSError as err: # timeout error raise URLError(err) r = h.getresponse() except: h.close() raise # If the server does not send us a ‘Connection: close‘ header, # HTTPConnection assumes the socket should be left open. Manually # mark the socket to be closed when this response object goes away. if h.sock: h.sock.close() h.sock = None r.url = req.get_full_url() # This line replaces the .msg attribute of the HTTPResponse # with .headers, because urllib clients expect the response to # have the reason in .msg. It would be good to mark this # attribute is deprecated and get then to use info() or # .headers. r.msg = r.reason return r class HTTPHandler(AbstractHTTPHandler): def http_open(self, req): return self.do_open(http.client.HTTPConnection, req) http_request = AbstractHTTPHandler.do_request_ if hasattr(http.client, ‘HTTPSConnection‘): class HTTPSHandler(AbstractHTTPHandler): def __init__(self, debuglevel=0, context=None, check_hostname=None): AbstractHTTPHandler.__init__(self, debuglevel) self._context = context self._check_hostname = check_hostname def https_open(self, req): return self.do_open(http.client.HTTPSConnection, req, context=self._context, check_hostname=self._check_hostname) https_request = AbstractHTTPHandler.do_request_ __all__.append(‘HTTPSHandler‘) class HTTPCookieProcessor(BaseHandler): def __init__(self, cookiejar=None): import http.cookiejar if cookiejar is None: cookiejar = http.cookiejar.CookieJar() self.cookiejar = cookiejar def http_request(self, request): self.cookiejar.add_cookie_header(request) return request def http_response(self, request, response): self.cookiejar.extract_cookies(response, request) return response https_request = http_request https_response = http_response class UnknownHandler(BaseHandler): def unknown_open(self, req): type = req.type raise URLError(‘unknown url type: %s‘ % type) def parse_keqv_list(l): """Parse list of key=value strings where keys are not duplicated.""" parsed = {} for elt in l: k, v = elt.split(‘=‘, 1) if v[0] == ‘"‘ and v[-1] == ‘"‘: v = v[1:-1] parsed[k] = v return parsed def parse_http_list(s): """Parse lists as described by RFC 2068 Section 2. In particular, parse comma-separated lists where the elements of the list may include quoted-strings. A quoted-string could contain a comma. A non-quoted string could have quotes in the middle. Neither commas nor quotes count if they are escaped. Only double-quotes count, not single-quotes. """ res = [] part = ‘‘ escape = quote = False for cur in s: if escape: part += cur escape = False continue if quote: if cur == ‘\\‘: escape = True continue elif cur == ‘"‘: quote = False part += cur continue if cur == ‘,‘: res.append(part) part = ‘‘ continue if cur == ‘"‘: quote = True part += cur # append last part if part: res.append(part) return [part.strip() for part in res] class FileHandler(BaseHandler): # Use local file or FTP depending on form of URL def file_open(self, req): url = req.selector if url[:2] == ‘//‘ and url[2:3] != ‘/‘ and (req.host and req.host != ‘localhost‘): if not req.host in self.get_names(): raise URLError("file:// scheme is supported only on localhost") else: return self.open_local_file(req) # names for the localhost names = None def get_names(self): if FileHandler.names is None: try: FileHandler.names = tuple( socket.gethostbyname_ex(‘localhost‘)[2] + socket.gethostbyname_ex(socket.gethostname())[2]) except socket.gaierror: FileHandler.names = (socket.gethostbyname(‘localhost‘),) return FileHandler.names # not entirely sure what the rules are here def open_local_file(self, req): import email.utils import mimetypes host = req.host filename = req.selector localfile = url2pathname(filename) try: stats = os.stat(localfile) size = stats.st_size modified = email.utils.formatdate(stats.st_mtime, usegmt=True) mtype = mimetypes.guess_type(filename)[0] headers = email.message_from_string( ‘Content-type: %s\nContent-length: %d\nLast-modified: %s\n‘ % (mtype or ‘text/plain‘, size, modified)) if host: host, port = splitport(host) if not host or (not port and _safe_gethostbyname(host) in self.get_names()): if host: origurl = ‘file://‘ + host + filename else: origurl = ‘file://‘ + filename return addinfourl(open(localfile, ‘rb‘), headers, origurl) except OSError as exp: # users shouldn‘t expect OSErrors coming from urlopen() raise URLError(exp) raise URLError(‘file not on local host‘) def _safe_gethostbyname(host): try: return socket.gethostbyname(host) except socket.gaierror: return None class FTPHandler(BaseHandler): def ftp_open(self, req): import ftplib import mimetypes host = req.host if not host: raise URLError(‘ftp error: no host given‘) host, port = splitport(host) if port is None: port = ftplib.FTP_PORT else: port = int(port) # username/password handling user, host = splituser(host) if user: user, passwd = splitpasswd(user) else: passwd = None host = unquote(host) user = user or ‘‘ passwd = passwd or ‘‘ try: host = socket.gethostbyname(host) except OSError as msg: raise URLError(msg) path, attrs = splitattr(req.selector) dirs = path.split(‘/‘) dirs = list(map(unquote, dirs)) dirs, file = dirs[:-1], dirs[-1] if dirs and not dirs[0]: dirs = dirs[1:] try: fw = self.connect_ftp(user, passwd, host, port, dirs, req.timeout) type = file and ‘I‘ or ‘D‘ for attr in attrs: attr, value = splitvalue(attr) if attr.lower() == ‘type‘ and value in (‘a‘, ‘A‘, ‘i‘, ‘I‘, ‘d‘, ‘D‘): type = value.upper() fp, retrlen = fw.retrfile(file, type) headers = "" mtype = mimetypes.guess_type(req.full_url)[0] if mtype: headers += "Content-type: %s\n" % mtype if retrlen is not None and retrlen >= 0: headers += "Content-length: %d\n" % retrlen headers = email.message_from_string(headers) return addinfourl(fp, headers, req.full_url) except ftplib.all_errors as exp: exc = URLError(‘ftp error: %r‘ % exp) raise exc.with_traceback(sys.exc_info()[2]) def connect_ftp(self, user, passwd, host, port, dirs, timeout): return ftpwrapper(user, passwd, host, port, dirs, timeout, persistent=False) class CacheFTPHandler(FTPHandler): # XXX would be nice to have pluggable cache strategies # XXX this stuff is definitely not thread safe def __init__(self): self.cache = {} self.timeout = {} self.soonest = 0 self.delay = 60 self.max_conns = 16 def setTimeout(self, t): self.delay = t def setMaxConns(self, m): self.max_conns = m def connect_ftp(self, user, passwd, host, port, dirs, timeout): key = user, host, port, ‘/‘.join(dirs), timeout if key in self.cache: self.timeout[key] = time.time() + self.delay else: self.cache[key] = ftpwrapper(user, passwd, host, port, dirs, timeout) self.timeout[key] = time.time() + self.delay self.check_cache() return self.cache[key] def check_cache(self): # first check for old ones t = time.time() if self.soonest <= t: for k, v in list(self.timeout.items()): if v < t: self.cache[k].close() del self.cache[k] del self.timeout[k] self.soonest = min(list(self.timeout.values())) # then check the size if len(self.cache) == self.max_conns: for k, v in list(self.timeout.items()): if v == self.soonest: del self.cache[k] del self.timeout[k] break self.soonest = min(list(self.timeout.values())) def clear_cache(self): for conn in self.cache.values(): conn.close() self.cache.clear() self.timeout.clear() class DataHandler(BaseHandler): def data_open(self, req): # data URLs as specified in RFC 2397. # # ignores POSTed data # # syntax: # dataurl := "data:" [ mediatype ] [ ";base64" ] "," data # mediatype := [ type "/" subtype ] *( ";" parameter ) # data := *urlchar # parameter := attribute "=" value url = req.full_url scheme, data = url.split(":",1) mediatype, data = data.split(",",1) # even base64 encoded data URLs might be quoted so unquote in any case: data = unquote_to_bytes(data) if mediatype.endswith(";base64"): data = base64.decodebytes(data) mediatype = mediatype[:-7] if not mediatype: mediatype = "text/plain;charset=US-ASCII" headers = email.message_from_string("Content-type: %s\nContent-length: %d\n" % (mediatype, len(data))) return addinfourl(io.BytesIO(data), headers, url) # Code move from the old urllib module MAXFTPCACHE = 10 # Trim the ftp cache beyond this size # Helper for non-unix systems if os.name == ‘nt‘: from nturl2path import url2pathname, pathname2url else: def url2pathname(pathname): """OS-specific conversion from a relative URL of the ‘file‘ scheme to a file system path; not recommended for general use.""" return unquote(pathname) def pathname2url(pathname): """OS-specific conversion from a file system path to a relative URL of the ‘file‘ scheme; not recommended for general use.""" return quote(pathname) # This really consists of two pieces: # (1) a class which handles opening of all sorts of URLs # (plus assorted utilities etc.) # (2) a set of functions for parsing URLs # XXX Should these be separated out into different modules? ftpcache = {} class URLopener: """Class to open URLs. This is a class rather than just a subroutine because we may need more than one set of global protocol-specific options. Note -- this is a base class for those who don‘t want the automatic handling of errors type 302 (relocated) and 401 (authorization needed).""" __tempfiles = None version = "Python-urllib/%s" % __version__ # Constructor def __init__(self, proxies=None, **x509): msg = "%(class)s style of invoking requests is deprecated. " "Use newer urlopen functions/methods" % {‘class‘: self.__class__.__name__} warnings.warn(msg, DeprecationWarning, stacklevel=3) if proxies is None: proxies = getproxies() assert hasattr(proxies, ‘keys‘), "proxies must be a mapping" self.proxies = proxies self.key_file = x509.get(‘key_file‘) self.cert_file = x509.get(‘cert_file‘) self.addheaders = [(‘User-Agent‘, self.version)] self.__tempfiles = [] self.__unlink = os.unlink # See cleanup() self.tempcache = None # Undocumented feature: if you assign {} to tempcache, # it is used to cache files retrieved with # self.retrieve(). This is not enabled by default # since it does not work for changing documents (and I # haven‘t got the logic to check expiration headers # yet). self.ftpcache = ftpcache # Undocumented feature: you can use a different # ftp cache by assigning to the .ftpcache member; # in case you want logically independent URL openers # XXX This is not threadsafe. Bah. def __del__(self): self.close() def close(self): self.cleanup() def cleanup(self): # This code sometimes runs when the rest of this module # has already been deleted, so it can‘t use any globals # or import anything. if self.__tempfiles: for file in self.__tempfiles: try: self.__unlink(file) except OSError: pass del self.__tempfiles[:] if self.tempcache: self.tempcache.clear() def addheader(self, *args): """Add a header to be used by the HTTP interface only e.g. u.addheader(‘Accept‘, ‘sound/basic‘)""" self.addheaders.append(args) # External interface def open(self, fullurl, data=None): """Use URLopener().open(file) instead of open(file, ‘r‘).""" fullurl = unwrap(to_bytes(fullurl)) fullurl = quote(fullurl, safe="%/:=&?~#+!$,;‘@()*[]|") if self.tempcache and fullurl in self.tempcache: filename, headers = self.tempcache[fullurl] fp = open(filename, ‘rb‘) return addinfourl(fp, headers, fullurl) urltype, url = splittype(fullurl) if not urltype: urltype = ‘file‘ if urltype in self.proxies: proxy = self.proxies[urltype] urltype, proxyhost = splittype(proxy) host, selector = splithost(proxyhost) url = (host, fullurl) # Signal special case to open_*() else: proxy = None name = ‘open_‘ + urltype self.type = urltype name = name.replace(‘-‘, ‘_‘) if not hasattr(self, name): if proxy: return self.open_unknown_proxy(proxy, fullurl, data) else: return self.open_unknown(fullurl, data) try: if data is None: return getattr(self, name)(url) else: return getattr(self, name)(url, data) except (HTTPError, URLError): raise except OSError as msg: raise OSError(‘socket error‘, msg).with_traceback(sys.exc_info()[2]) def open_unknown(self, fullurl, data=None): """Overridable interface to open unknown URL type.""" type, url = splittype(fullurl) raise OSError(‘url error‘, ‘unknown url type‘, type) def open_unknown_proxy(self, proxy, fullurl, data=None): """Overridable interface to open unknown URL type.""" type, url = splittype(fullurl) raise OSError(‘url error‘, ‘invalid proxy for %s‘ % type, proxy) # External interface def retrieve(self, url, filename=None, reporthook=None, data=None): """retrieve(url) returns (filename, headers) for a local object or (tempfilename, headers) for a remote object.""" url = unwrap(to_bytes(url)) if self.tempcache and url in self.tempcache: return self.tempcache[url] type, url1 = splittype(url) if filename is None and (not type or type == ‘file‘): try: fp = self.open_local_file(url1) hdrs = fp.info() fp.close() return url2pathname(splithost(url1)[1]), hdrs except OSError as msg: pass fp = self.open(url, data) try: headers = fp.info() if filename: tfp = open(filename, ‘wb‘) else: import tempfile garbage, path = splittype(url) garbage, path = splithost(path or "") path, garbage = splitquery(path or "") path, garbage = splitattr(path or "") suffix = os.path.splitext(path)[1] (fd, filename) = tempfile.mkstemp(suffix) self.__tempfiles.append(filename) tfp = os.fdopen(fd, ‘wb‘) try: result = filename, headers if self.tempcache is not None: self.tempcache[url] = result bs = 1024*8 size = -1 read = 0 blocknum = 0 if "content-length" in headers: size = int(headers["Content-Length"]) if reporthook: reporthook(blocknum, bs, size) while 1: block = fp.read(bs) if not block: break read += len(block) tfp.write(block) blocknum += 1 if reporthook: reporthook(blocknum, bs, size) finally: tfp.close() finally: fp.close() # raise exception if actual size does not match content-length header if size >= 0 and read < size: raise ContentTooShortError( "retrieval incomplete: got only %i out of %i bytes" % (read, size), result) return result # Each method named open_<type> knows how to open that type of URL def _open_generic_http(self, connection_factory, url, data): """Make an HTTP connection using connection_class. This is an internal method that should be called from open_http() or open_https(). Arguments: - connection_factory should take a host name and return an HTTPConnection instance. - url is the url to retrieval or a host, relative-path pair. - data is payload for a POST request or None. """ user_passwd = None proxy_passwd= None if isinstance(url, str): host, selector = splithost(url) if host: user_passwd, host = splituser(host) host = unquote(host) realhost = host else: host, selector = url # check whether the proxy contains authorization information proxy_passwd, host = splituser(host) # now we proceed with the url we want to obtain urltype, rest = splittype(selector) url = rest user_passwd = None if urltype.lower() != ‘http‘: realhost = None else: realhost, rest = splithost(rest) if realhost: user_passwd, realhost = splituser(realhost) if user_passwd: selector = "%s://%s%s" % (urltype, realhost, rest) if proxy_bypass(realhost): host = realhost if not host: raise OSError(‘http error‘, ‘no host given‘) if proxy_passwd: proxy_passwd = unquote(proxy_passwd) proxy_auth = base64.b64encode(proxy_passwd.encode()).decode(‘ascii‘) else: proxy_auth = None if user_passwd: user_passwd = unquote(user_passwd) auth = base64.b64encode(user_passwd.encode()).decode(‘ascii‘) else: auth = None http_conn = connection_factory(host) headers = {} if proxy_auth: headers["Proxy-Authorization"] = "Basic %s" % proxy_auth if auth: headers["Authorization"] = "Basic %s" % auth if realhost: headers["Host"] = realhost # Add Connection:close as we don‘t support persistent connections yet. # This helps in closing the socket and avoiding ResourceWarning headers["Connection"] = "close" for header, value in self.addheaders: headers[header] = value if data is not None: headers["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" http_conn.request("POST", selector, data, headers) else: http_conn.request("GET", selector, headers=headers) try: response = http_conn.getresponse() except http.client.BadStatusLine: # something went wrong with the HTTP status line raise URLError("http protocol error: bad status line") # According to RFC 2616, "2xx" code indicates that the client‘s # request was successfully received, understood, and accepted. if 200 <= response.status < 300: return addinfourl(response, response.msg, "http:" + url, response.status) else: return self.http_error( url, response.fp, response.status, response.reason, response.msg, data) def open_http(self, url, data=None): """Use HTTP protocol.""" return self._open_generic_http(http.client.HTTPConnection, url, data) def http_error(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data=None): """Handle http errors. Derived class can override this, or provide specific handlers named http_error_DDD where DDD is the 3-digit error code.""" # First check if there‘s a specific handler for this error name = ‘http_error_%d‘ % errcode if hasattr(self, name): method = getattr(self, name) if data is None: result = method(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) else: result = method(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data) if result: return result return self.http_error_default(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) def http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers): """Default error handler: close the connection and raise OSError.""" fp.close() raise HTTPError(url, errcode, errmsg, headers, None) if _have_ssl: def _https_connection(self, host): return http.client.HTTPSConnection(host, key_file=self.key_file, cert_file=self.cert_file) def open_https(self, url, data=None): """Use HTTPS protocol.""" return self._open_generic_http(self._https_connection, url, data) def open_file(self, url): """Use local file or FTP depending on form of URL.""" if not isinstance(url, str): raise URLError(‘file error: proxy support for file protocol currently not implemented‘) if url[:2] == ‘//‘ and url[2:3] != ‘/‘ and url[2:12].lower() != ‘localhost/‘: raise ValueError("file:// scheme is supported only on localhost") else: return self.open_local_file(url) def open_local_file(self, url): """Use local file.""" import email.utils import mimetypes host, file = splithost(url) localname = url2pathname(file) try: stats = os.stat(localname) except OSError as e: raise URLError(e.strerror, e.filename) size = stats.st_size modified = email.utils.formatdate(stats.st_mtime, usegmt=True) mtype = mimetypes.guess_type(url)[0] headers = email.message_from_string( ‘Content-Type: %s\nContent-Length: %d\nLast-modified: %s\n‘ % (mtype or ‘text/plain‘, size, modified)) if not host: urlfile = file if file[:1] == ‘/‘: urlfile = ‘file://‘ + file return addinfourl(open(localname, ‘rb‘), headers, urlfile) host, port = splitport(host) if (not port and socket.gethostbyname(host) in ((localhost(),) + thishost())): urlfile = file if file[:1] == ‘/‘: urlfile = ‘file://‘ + file elif file[:2] == ‘./‘: raise ValueError("local file url may start with / or file:. Unknown url of type: %s" % url) return addinfourl(open(localname, ‘rb‘), headers, urlfile) raise URLError(‘local file error: not on local host‘) def open_ftp(self, url): """Use FTP protocol.""" if not isinstance(url, str): raise URLError(‘ftp error: proxy support for ftp protocol currently not implemented‘) import mimetypes host, path = splithost(url) if not host: raise URLError(‘ftp error: no host given‘) host, port = splitport(host) user, host = splituser(host) if user: user, passwd = splitpasswd(user) else: passwd = None host = unquote(host) user = unquote(user or ‘‘) passwd = unquote(passwd or ‘‘) host = socket.gethostbyname(host) if not port: import ftplib port = ftplib.FTP_PORT else: port = int(port) path, attrs = splitattr(path) path = unquote(path) dirs = path.split(‘/‘) dirs, file = dirs[:-1], dirs[-1] if dirs and not dirs[0]: dirs = dirs[1:] if dirs and not dirs[0]: dirs[0] = ‘/‘ key = user, host, port, ‘/‘.join(dirs) # XXX thread unsafe! if len(self.ftpcache) > MAXFTPCACHE: # Prune the cache, rather arbitrarily for k in list(self.ftpcache): if k != key: v = self.ftpcache[k] del self.ftpcache[k] v.close() try: if key not in self.ftpcache: self.ftpcache[key] = ftpwrapper(user, passwd, host, port, dirs) if not file: type = ‘D‘ else: type = ‘I‘ for attr in attrs: attr, value = splitvalue(attr) if attr.lower() == ‘type‘ and value in (‘a‘, ‘A‘, ‘i‘, ‘I‘, ‘d‘, ‘D‘): type = value.upper() (fp, retrlen) = self.ftpcache[key].retrfile(file, type) mtype = mimetypes.guess_type("ftp:" + url)[0] headers = "" if mtype: headers += "Content-Type: %s\n" % mtype if retrlen is not None and retrlen >= 0: headers += "Content-Length: %d\n" % retrlen headers = email.message_from_string(headers) return addinfourl(fp, headers, "ftp:" + url) except ftperrors() as exp: raise URLError(‘ftp error %r‘ % exp).with_traceback(sys.exc_info()[2]) def open_data(self, url, data=None): """Use "data" URL.""" if not isinstance(url, str): raise URLError(‘data error: proxy support for data protocol currently not implemented‘) # ignore POSTed data # # syntax of data URLs: # dataurl := "data:" [ mediatype ] [ ";base64" ] "," data # mediatype := [ type "/" subtype ] *( ";" parameter ) # data := *urlchar # parameter := attribute "=" value try: [type, data] = url.split(‘,‘, 1) except ValueError: raise OSError(‘data error‘, ‘bad data URL‘) if not type: type = ‘text/plain;charset=US-ASCII‘ semi = type.rfind(‘;‘) if semi >= 0 and ‘=‘ not in type[semi:]: encoding = type[semi+1:] type = type[:semi] else: encoding = ‘‘ msg = [] msg.append(‘Date: %s‘%time.strftime(‘%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT‘, time.gmtime(time.time()))) msg.append(‘Content-type: %s‘ % type) if encoding == ‘base64‘: # XXX is this encoding/decoding ok? data = base64.decodebytes(data.encode(‘ascii‘)).decode(‘latin-1‘) else: data = unquote(data) msg.append(‘Content-Length: %d‘ % len(data)) msg.append(‘‘) msg.append(data) msg = ‘\n‘.join(msg) headers = email.message_from_string(msg) f = io.StringIO(msg) #f.fileno = None # needed for addinfourl return addinfourl(f, headers, url) class FancyURLopener(URLopener): """Derived class with handlers for errors we can handle (perhaps).""" def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): URLopener.__init__(self, *args, **kwargs) self.auth_cache = {} self.tries = 0 self.maxtries = 10 def http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers): """Default error handling -- don‘t raise an exception.""" return addinfourl(fp, headers, "http:" + url, errcode) def http_error_302(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data=None): """Error 302 -- relocated (temporarily).""" self.tries += 1 if self.maxtries and self.tries >= self.maxtries: if hasattr(self, "http_error_500"): meth = self.http_error_500 else: meth = self.http_error_default self.tries = 0 return meth(url, fp, 500, "Internal Server Error: Redirect Recursion", headers) result = self.redirect_internal(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data) self.tries = 0 return result def redirect_internal(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data): if ‘location‘ in headers: newurl = headers[‘location‘] elif ‘uri‘ in headers: newurl = headers[‘uri‘] else: return fp.close() # In case the server sent a relative URL, join with original: newurl = urljoin(self.type + ":" + url, newurl) urlparts = urlparse(newurl) # For security reasons, we don‘t allow redirection to anything other # than http, https and ftp. # We are using newer HTTPError with older redirect_internal method # This older method will get deprecated in 3.3 if urlparts.scheme not in (‘http‘, ‘https‘, ‘ftp‘, ‘‘): raise HTTPError(newurl, errcode, errmsg + " Redirection to url ‘%s‘ is not allowed." % newurl, headers, fp) return self.open(newurl) def http_error_301(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data=None): """Error 301 -- also relocated (permanently).""" return self.http_error_302(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data) def http_error_303(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data=None): """Error 303 -- also relocated (essentially identical to 302).""" return self.http_error_302(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data) def http_error_307(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data=None): """Error 307 -- relocated, but turn POST into error.""" if data is None: return self.http_error_302(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data) else: return self.http_error_default(url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) def http_error_401(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data=None, retry=False): """Error 401 -- authentication required. This function supports Basic authentication only.""" if ‘www-authenticate‘ not in headers: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) stuff = headers[‘www-authenticate‘] match = re.match(‘[ \t]*([^ \t]+)[ \t]+realm="([^"]*)"‘, stuff) if not match: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) scheme, realm = match.groups() if scheme.lower() != ‘basic‘: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) if not retry: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) name = ‘retry_‘ + self.type + ‘_basic_auth‘ if data is None: return getattr(self,name)(url, realm) else: return getattr(self,name)(url, realm, data) def http_error_407(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers, data=None, retry=False): """Error 407 -- proxy authentication required. This function supports Basic authentication only.""" if ‘proxy-authenticate‘ not in headers: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) stuff = headers[‘proxy-authenticate‘] match = re.match(‘[ \t]*([^ \t]+)[ \t]+realm="([^"]*)"‘, stuff) if not match: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) scheme, realm = match.groups() if scheme.lower() != ‘basic‘: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) if not retry: URLopener.http_error_default(self, url, fp, errcode, errmsg, headers) name = ‘retry_proxy_‘ + self.type + ‘_basic_auth‘ if data is None: return getattr(self,name)(url, realm) else: return getattr(self,name)(url, realm, data) def retry_proxy_http_basic_auth(self, url, realm, data=None): host, selector = splithost(url) newurl = ‘http://‘ + host + selector proxy = self.proxies[‘http‘] urltype, proxyhost = splittype(proxy) proxyhost, proxyselector = splithost(proxyhost) i = proxyhost.find(‘@‘) + 1 proxyhost = proxyhost[i:] user, passwd = self.get_user_passwd(proxyhost, realm, i) if not (user or passwd): return None proxyhost = "%s:%s@%s" % (quote(user, safe=‘‘), quote(passwd, safe=‘‘), proxyhost) self.proxies[‘http‘] = ‘http://‘ + proxyhost + proxyselector if data is None: return self.open(newurl) else: return self.open(newurl, data) def retry_proxy_https_basic_auth(self, url, realm, data=None): host, selector = splithost(url) newurl = ‘https://‘ + host + selector proxy = self.proxies[‘https‘] urltype, proxyhost = splittype(proxy) proxyhost, proxyselector = splithost(proxyhost) i = proxyhost.find(‘@‘) + 1 proxyhost = proxyhost[i:] user, passwd = self.get_user_passwd(proxyhost, realm, i) if not (user or passwd): return None proxyhost = "%s:%s@%s" % (quote(user, safe=‘‘), quote(passwd, safe=‘‘), proxyhost) self.proxies[‘https‘] = ‘https://‘ + proxyhost + proxyselector if data is None: return self.open(newurl) else: return self.open(newurl, data) def retry_http_basic_auth(self, url, realm, data=None): host, selector = splithost(url) i = host.find(‘@‘) + 1 host = host[i:] user, passwd = self.get_user_passwd(host, realm, i) if not (user or passwd): return None host = "%s:%s@%s" % (quote(user, safe=‘‘), quote(passwd, safe=‘‘), host) newurl = ‘http://‘ + host + selector if data is None: return self.open(newurl) else: return self.open(newurl, data) def retry_https_basic_auth(self, url, realm, data=None): host, selector = splithost(url) i = host.find(‘@‘) + 1 host = host[i:] user, passwd = self.get_user_passwd(host, realm, i) if not (user or passwd): return None host = "%s:%s@%s" % (quote(user, safe=‘‘), quote(passwd, safe=‘‘), host) newurl = ‘https://‘ + host + selector if data is None: return self.open(newurl) else: return self.open(newurl, data) def get_user_passwd(self, host, realm, clear_cache=0): key = realm + ‘@‘ + host.lower() if key in self.auth_cache: if clear_cache: del self.auth_cache[key] else: return self.auth_cache[key] user, passwd = self.prompt_user_passwd(host, realm) if user or passwd: self.auth_cache[key] = (user, passwd) return user, passwd def prompt_user_passwd(self, host, realm): """Override this in a GUI environment!""" import getpass try: user = input("Enter username for %s at %s: " % (realm, host)) passwd = getpass.getpass("Enter password for %s in %s at %s: " % (user, realm, host)) return user, passwd except KeyboardInterrupt: print() return None, None # Utility functions _localhost = None def localhost(): """Return the IP address of the magic hostname ‘localhost‘.""" global _localhost if _localhost is None: _localhost = socket.gethostbyname(‘localhost‘) return _localhost _thishost = None def thishost(): """Return the IP addresses of the current host.""" global _thishost if _thishost is None: try: _thishost = tuple(socket.gethostbyname_ex(socket.gethostname())[2]) except socket.gaierror: _thishost = tuple(socket.gethostbyname_ex(‘localhost‘)[2]) return _thishost _ftperrors = None def ftperrors(): """Return the set of errors raised by the FTP class.""" global _ftperrors if _ftperrors is None: import ftplib _ftperrors = ftplib.all_errors return _ftperrors _noheaders = None def noheaders(): """Return an empty email Message object.""" global _noheaders if _noheaders is None: _noheaders = email.message_from_string("") return _noheaders # Utility classes class ftpwrapper: """Class used by open_ftp() for cache of open FTP connections.""" def __init__(self, user, passwd, host, port, dirs, timeout=None, persistent=True): self.user = user self.passwd = passwd self.host = host self.port = port self.dirs = dirs self.timeout = timeout self.refcount = 0 self.keepalive = persistent try: self.init() except: self.close() raise def init(self): import ftplib self.busy = 0 self.ftp = ftplib.FTP() self.ftp.connect(self.host, self.port, self.timeout) self.ftp.login(self.user, self.passwd) _target = ‘/‘.join(self.dirs) self.ftp.cwd(_target) def retrfile(self, file, type): import ftplib self.endtransfer() if type in (‘d‘, ‘D‘): cmd = ‘TYPE A‘; isdir = 1 else: cmd = ‘TYPE ‘ + type; isdir = 0 try: self.ftp.voidcmd(cmd) except ftplib.all_errors: self.init() self.ftp.voidcmd(cmd) conn = None if file and not isdir: # Try to retrieve as a file try: cmd = ‘RETR ‘ + file conn, retrlen = self.ftp.ntransfercmd(cmd) except ftplib.error_perm as reason: if str(reason)[:3] != ‘550‘: raise URLError(‘ftp error: %r‘ % reason).with_traceback( sys.exc_info()[2]) if not conn: # Set transfer mode to ASCII! self.ftp.voidcmd(‘TYPE A‘) # Try a directory listing. Verify that directory exists. if file: pwd = self.ftp.pwd() try: try: self.ftp.cwd(file) except ftplib.error_perm as reason: raise URLError(‘ftp error: %r‘ % reason) from reason finally: self.ftp.cwd(pwd) cmd = ‘LIST ‘ + file else: cmd = ‘LIST‘ conn, retrlen = self.ftp.ntransfercmd(cmd) self.busy = 1 ftpobj = addclosehook(conn.makefile(‘rb‘), self.file_close) self.refcount += 1 conn.close() # Pass back both a suitably decorated object and a retrieval length return (ftpobj, retrlen) def endtransfer(self): self.busy = 0 def close(self): self.keepalive = False if self.refcount <= 0: self.real_close() def file_close(self): self.endtransfer() self.refcount -= 1 if self.refcount <= 0 and not self.keepalive: self.real_close() def real_close(self): self.endtransfer() try: self.ftp.close() except ftperrors(): pass # Proxy handling def getproxies_environment(): """Return a dictionary of scheme -> proxy server URL mappings. Scan the environment for variables named <scheme>_proxy; this seems to be the standard convention. If you need a different way, you can pass a proxies dictionary to the [Fancy]URLopener constructor. """ proxies = {} for name, value in os.environ.items(): name = name.lower() if value and name[-6:] == ‘_proxy‘: proxies[name[:-6]] = value return proxies def proxy_bypass_environment(host): """Test if proxies should not be used for a particular host. Checks the environment for a variable named no_proxy, which should be a list of DNS suffixes separated by commas, or ‘*‘ for all hosts. """ no_proxy = os.environ.get(‘no_proxy‘, ‘‘) or os.environ.get(‘NO_PROXY‘, ‘‘) # ‘*‘ is special case for always bypass if no_proxy == ‘*‘: return 1 # strip port off host hostonly, port = splitport(host) # check if the host ends with any of the DNS suffixes no_proxy_list = [proxy.strip() for proxy in no_proxy.split(‘,‘)] for name in no_proxy_list: if name and (hostonly.endswith(name) or host.endswith(name)): return 1 # otherwise, don‘t bypass return 0 # This code tests an OSX specific data structure but is testable on all # platforms def _proxy_bypass_macosx_sysconf(host, proxy_settings): """ Return True iff this host shouldn‘t be accessed using a proxy This function uses the MacOSX framework SystemConfiguration to fetch the proxy information. proxy_settings come from _scproxy._get_proxy_settings or get mocked ie: { ‘exclude_simple‘: bool, ‘exceptions‘: [‘foo.bar‘, ‘*.bar.com‘, ‘127.0.0.1‘, ‘10.1‘, ‘10.0/16‘] } """ from fnmatch import fnmatch hostonly, port = splitport(host) def ip2num(ipAddr): parts = ipAddr.split(‘.‘) parts = list(map(int, parts)) if len(parts) != 4: parts = (parts + [0, 0, 0, 0])[:4] return (parts[0] << 24) | (parts[1] << 16) | (parts[2] << 8) | parts[3] # Check for simple host names: if ‘.‘ not in host: if proxy_settings[‘exclude_simple‘]: return True hostIP = None for value in proxy_settings.get(‘exceptions‘, ()): # Items in the list are strings like these: *.local, 169.254/16 if not value: continue m = re.match(r"(\d+(?:\.\d+)*)(/\d+)?", value) if m is not None: if hostIP is None: try: hostIP = socket.gethostbyname(hostonly) hostIP = ip2num(hostIP) except OSError: continue base = ip2num(m.group(1)) mask = m.group(2) if mask is None: mask = 8 * (m.group(1).count(‘.‘) + 1) else: mask = int(mask[1:]) mask = 32 - mask if (hostIP >> mask) == (base >> mask): return True elif fnmatch(host, value): return True return False if sys.platform == ‘darwin‘: from _scproxy import _get_proxy_settings, _get_proxies def proxy_bypass_macosx_sysconf(host): proxy_settings = _get_proxy_settings() return _proxy_bypass_macosx_sysconf(host, proxy_settings) def getproxies_macosx_sysconf(): """Return a dictionary of scheme -> proxy server URL mappings. This function uses the MacOSX framework SystemConfiguration to fetch the proxy information. """ return _get_proxies() def proxy_bypass(host): if getproxies_environment(): return proxy_bypass_environment(host) else: return proxy_bypass_macosx_sysconf(host) def getproxies(): return getproxies_environment() or getproxies_macosx_sysconf() elif os.name == ‘nt‘: def getproxies_registry(): """Return a dictionary of scheme -> proxy server URL mappings. Win32 uses the registry to store proxies. """ proxies = {} try: import winreg except ImportError: # Std module, so should be around - but you never know! return proxies try: internetSettings = winreg.OpenKey(winreg.HKEY_CURRENT_USER, r‘Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings‘) proxyEnable = winreg.QueryValueEx(internetSettings, ‘ProxyEnable‘)[0] if proxyEnable: # Returned as Unicode but problems if not converted to ASCII proxyServer = str(winreg.QueryValueEx(internetSettings, ‘ProxyServer‘)[0]) if ‘=‘ in proxyServer: # Per-protocol settings for p in proxyServer.split(‘;‘): protocol, address = p.split(‘=‘, 1) # See if address has a type:// prefix if not re.match(‘^([^/:]+)://‘, address): address = ‘%s://%s‘ % (protocol, address) proxies[protocol] = address else: # Use one setting for all protocols if proxyServer[:5] == ‘http:‘: proxies[‘http‘] = proxyServer else: proxies[‘http‘] = ‘http://%s‘ % proxyServer proxies[‘https‘] = ‘https://%s‘ % proxyServer proxies[‘ftp‘] = ‘ftp://%s‘ % proxyServer internetSettings.Close() except (OSError, ValueError, TypeError): # Either registry key not found etc, or the value in an # unexpected format. # proxies already set up to be empty so nothing to do pass return proxies def getproxies(): """Return a dictionary of scheme -> proxy server URL mappings. Returns settings gathered from the environment, if specified, or the registry. """ return getproxies_environment() or getproxies_registry() def proxy_bypass_registry(host): try: import winreg except ImportError: # Std modules, so should be around - but you never know! return 0 try: internetSettings = winreg.OpenKey(winreg.HKEY_CURRENT_USER, r‘Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings‘) proxyEnable = winreg.QueryValueEx(internetSettings, ‘ProxyEnable‘)[0] proxyOverride = str(winreg.QueryValueEx(internetSettings, ‘ProxyOverride‘)[0]) # ^^^^ Returned as Unicode but problems if not converted to ASCII except OSError: return 0 if not proxyEnable or not proxyOverride: return 0 # try to make a host list from name and IP address. rawHost, port = splitport(host) host = [rawHost] try: addr = socket.gethostbyname(rawHost) if addr != rawHost: host.append(addr) except OSError: pass try: fqdn = socket.getfqdn(rawHost) if fqdn != rawHost: host.append(fqdn) except OSError: pass # make a check value list from the registry entry: replace the # ‘<local>‘ string by the localhost entry and the corresponding # canonical entry. proxyOverride = proxyOverride.split(‘;‘) # now check if we match one of the registry values. for test in proxyOverride: if test == ‘<local>‘: if ‘.‘ not in rawHost: return 1 test = test.replace(".", r"\.") # mask dots test = test.replace("*", r".*") # change glob sequence test = test.replace("?", r".") # change glob char for val in host: if re.match(test, val, re.I): return 1 return 0 def proxy_bypass(host): """Return a dictionary of scheme -> proxy server URL mappings. Returns settings gathered from the environment, if specified, or the registry. """ if getproxies_environment(): return proxy_bypass_environment(host) else: return proxy_bypass_registry(host) else: # By default use environment variables getproxies = getproxies_environment proxy_bypass = proxy_bypass_environment

""" robotparser.py Copyright (C) 2000 Bastian Kleineidam You can choose between two licenses when using this package: 1) GNU GPLv2 2) PSF license for Python 2.2 The robots.txt Exclusion Protocol is implemented as specified in http://www.robotstxt.org/norobots-rfc.txt """ import urllib.parse, urllib.request __all__ = ["RobotFileParser"] class RobotFileParser: """ This class provides a set of methods to read, parse and answer questions about a single robots.txt file. """ def __init__(self, url=‘‘): self.entries = [] self.default_entry = None self.disallow_all = False self.allow_all = False self.set_url(url) self.last_checked = 0 def mtime(self): """Returns the time the robots.txt file was last fetched. This is useful for long-running web spiders that need to check for new robots.txt files periodically. """ return self.last_checked def modified(self): """Sets the time the robots.txt file was last fetched to the current time. """ import time self.last_checked = time.time() def set_url(self, url): """Sets the URL referring to a robots.txt file.""" self.url = url self.host, self.path = urllib.parse.urlparse(url)[1:3] def read(self): """Reads the robots.txt URL and feeds it to the parser.""" try: f = urllib.request.urlopen(self.url) except urllib.error.HTTPError as err: if err.code in (401, 403): self.disallow_all = True elif err.code >= 400 and err.code < 500: self.allow_all = True else: raw = f.read() self.parse(raw.decode("utf-8").splitlines()) def _add_entry(self, entry): if "*" in entry.useragents: # the default entry is considered last if self.default_entry is None: # the first default entry wins self.default_entry = entry else: self.entries.append(entry) def parse(self, lines): """Parse the input lines from a robots.txt file. We allow that a user-agent: line is not preceded by one or more blank lines. """ # states: # 0: start state # 1: saw user-agent line # 2: saw an allow or disallow line state = 0 entry = Entry() self.modified() for line in lines: if not line: if state == 1: entry = Entry() state = 0 elif state == 2: self._add_entry(entry) entry = Entry() state = 0 # remove optional comment and strip line i = line.find(‘#‘) if i >= 0: line = line[:i] line = line.strip() if not line: continue line = line.split(‘:‘, 1) if len(line) == 2: line[0] = line[0].strip().lower() line[1] = urllib.parse.unquote(line[1].strip()) if line[0] == "user-agent": if state == 2: self._add_entry(entry) entry = Entry() entry.useragents.append(line[1]) state = 1 elif line[0] == "disallow": if state != 0: entry.rulelines.append(RuleLine(line[1], False)) state = 2 elif line[0] == "allow": if state != 0: entry.rulelines.append(RuleLine(line[1], True)) state = 2 if state == 2: self._add_entry(entry) def can_fetch(self, useragent, url): """using the parsed robots.txt decide if useragent can fetch url""" if self.disallow_all: return False if self.allow_all: return True # Until the robots.txt file has been read or found not # to exist, we must assume that no url is allowable. # This prevents false positives when a user erronenously # calls can_fetch() before calling read(). if not self.last_checked: return False # search for given user agent matches # the first match counts parsed_url = urllib.parse.urlparse(urllib.parse.unquote(url)) url = urllib.parse.urlunparse((‘‘,‘‘,parsed_url.path, parsed_url.params,parsed_url.query, parsed_url.fragment)) url = urllib.parse.quote(url) if not url: url = "/" for entry in self.entries: if entry.applies_to(useragent): return entry.allowance(url) # try the default entry last if self.default_entry: return self.default_entry.allowance(url) # agent not found ==> access granted return True def __str__(self): return ‘‘.join([str(entry) + "\n" for entry in self.entries]) class RuleLine: """A rule line is a single "Allow:" (allowance==True) or "Disallow:" (allowance==False) followed by a path.""" def __init__(self, path, allowance): if path == ‘‘ and not allowance: # an empty value means allow all allowance = True path = urllib.parse.urlunparse(urllib.parse.urlparse(path)) self.path = urllib.parse.quote(path) self.allowance = allowance def applies_to(self, filename): return self.path == "*" or filename.startswith(self.path) def __str__(self): return ("Allow" if self.allowance else "Disallow") + ": " + self.path class Entry: """An entry has one or more user-agents and zero or more rulelines""" def __init__(self): self.useragents = [] self.rulelines = [] def __str__(self): ret = [] for agent in self.useragents: ret.extend(["User-agent: ", agent, "\n"]) for line in self.rulelines: ret.extend([str(line), "\n"]) return ‘‘.join(ret) def applies_to(self, useragent): """check if this entry applies to the specified agent""" # split the name token and make it lower case useragent = useragent.split("/")[0].lower() for agent in self.useragents: if agent == ‘*‘: # we have the catch-all agent return True agent = agent.lower() if agent in useragent: return True return False def allowance(self, filename): """Preconditions: - our agent applies to this entry - filename is URL decoded""" for line in self.rulelines: if line.applies_to(filename): return line.allowance return True

"""Response classes used by urllib. The base class, addbase, defines a minimal file-like interface, including read() and readline(). The typical response object is an addinfourl instance, which defines an info() method that returns headers and a geturl() method that returns the url. """ import tempfile __all__ = [‘addbase‘, ‘addclosehook‘, ‘addinfo‘, ‘addinfourl‘] class addbase(tempfile._TemporaryFileWrapper): """Base class for addinfo and addclosehook. Is a good idea for garbage collection.""" # XXX Add a method to expose the timeout on the underlying socket? def __init__(self, fp): super(addbase, self).__init__(fp, ‘<urllib response>‘, delete=False) # Keep reference around as this was part of the original API. self.fp = fp def __repr__(self): return ‘<%s at %r whose fp = %r>‘ % (self.__class__.__name__, id(self), self.file) def __enter__(self): if self.fp.closed: raise ValueError("I/O operation on closed file") return self def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback): self.close() class addclosehook(addbase): """Class to add a close hook to an open file.""" def __init__(self, fp, closehook, *hookargs): super(addclosehook, self).__init__(fp) self.closehook = closehook self.hookargs = hookargs def close(self): try: closehook = self.closehook hookargs = self.hookargs if closehook: self.closehook = None self.hookargs = None closehook(*hookargs) finally: super(addclosehook, self).close() class addinfo(addbase): """class to add an info() method to an open file.""" def __init__(self, fp, headers): super(addinfo, self).__init__(fp) self.headers = headers def info(self): return self.headers class addinfourl(addinfo): """class to add info() and geturl() methods to an open file.""" def __init__(self, fp, headers, url, code=None): super(addinfourl, self).__init__(fp, headers) self.url = url self.code = code def getcode(self): return self.code def geturl(self): return self.url
二、入门练习
1、用Python抓取指定页面
1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 4 import urllib.request 5 6 url = "https://www.baidu.com" 7 data = urllib.request.urlopen(url).read() 8 data = data.decode(‘UTF-8‘) 9 with open(‘baidu.html‘, ‘wb‘) as f: 10 f.write(str.encode(data))
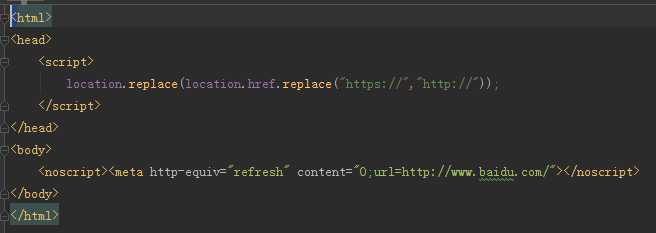
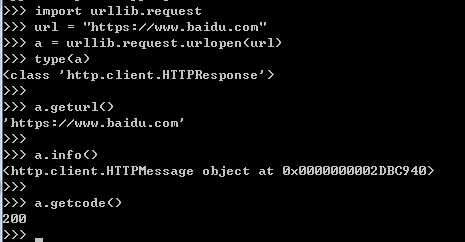
2、用Python简单处理URL
1 import urllib 2 import urllib.request 3 4 data = {} 5 data[‘word‘] = ‘课表‘ 6 7 url_values = urllib.parse.urlencode(data) 8 url = "http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/4731930.html" 9 full_url = url+url_values 10 11 data = urllib.request.urlopen(full_url).read() 12 data = data.decode(‘UTF-8‘) 13 with open(‘kebiao.html‘, ‘wb‘) as f: 14 f.write(str.encode(data))
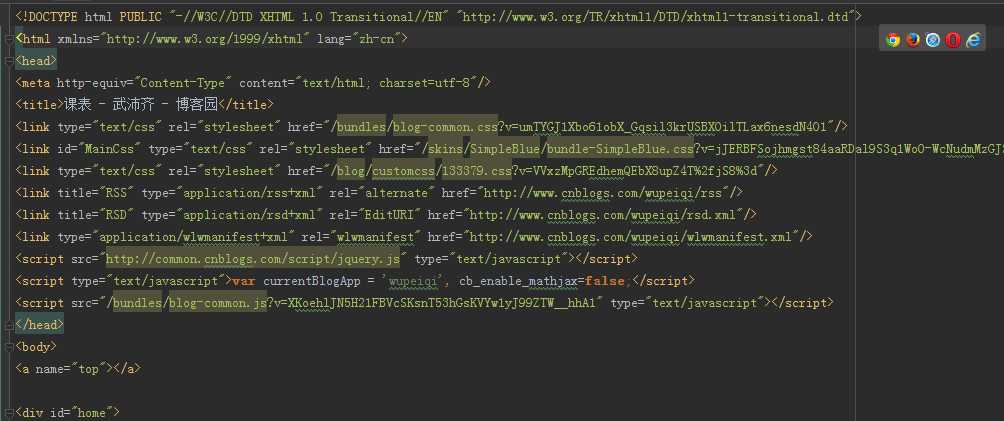
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Rambotien/p/5500628.html