标签:
iOS开发多线程篇—线程的状态
一、简单介绍
线程的创建:
self.thread=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(test) object:nil];
说明:创建线程有多种方式,这里不做过多的介绍。

线程的开启:
[self.thread start];

线程的运行和阻塞:
(1)设置线程阻塞1,阻塞2秒
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2.0];
(2)第二种设置线程阻塞2,以当前时间为基准阻塞4秒
NSDate *date=[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:4.0];
[NSThread sleepUntilDate:date];
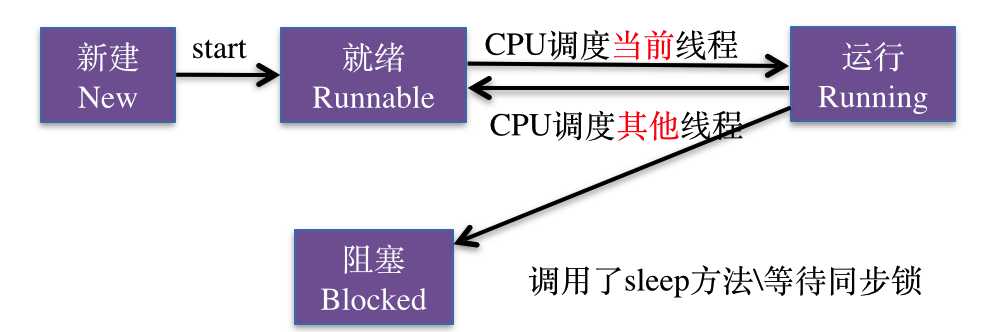
线程处理阻塞状态时在内存中的表现情况:(线程被移出可调度线程池,此时不可调度)

线程的死亡:
当线程的任务结束,发生异常,或者是强制退出这三种情况会导致线程的死亡。
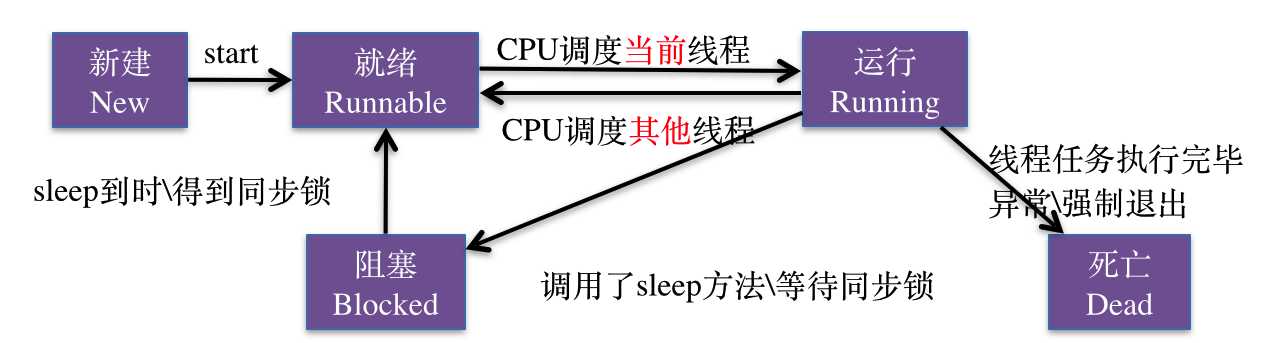
线程死亡后,线程对象从内存中移除。

二、代码示例
代码示例1:
1 //
2 // YYViewController.m
3 // 04-NSThread02-线程的状态
4 //
5 // Created by apple on 14-6-23.
6 // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved.
7 //
8
9 #import "YYViewController.h"
10
11 @interface YYViewController ()
12 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread;
13
14 @end
15
16 @implementation YYViewController
17
18 - (void)viewDidLoad
19 {
20 [super viewDidLoad];
21
22 //创建线程
23 self.thread=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(test) object:nil];
24 //设置线程的名称
25 [self.thread setName:@"线程A"];
26 }
27 //当手指按下的时候,开启线程
28 -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
29 {
30 //开启线程
31 [self.thread start];
32 }
33
34 -(void)test
35 {
36 //获取线程
37 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
38 NSLog(@"test---打印线程---%@",self.thread.name);
39 NSLog(@"test---线程开始---%@",current.name);
40
41 //设置线程阻塞1,阻塞2秒
42 NSLog(@"接下来,线程阻塞2秒");
43 [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2.0];
44
45 //第二种设置线程阻塞2,以当前时间为基准阻塞4秒
46 NSLog(@"接下来,线程阻塞4秒");
47 NSDate *date=[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:4.0];
48 [NSThread sleepUntilDate:date];
49 for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
50 NSLog(@"线程--%d--%@",i,current.name);
51
52 }
53 NSLog(@"test---线程结束---%@",current.name);
54 }
55
56 @end
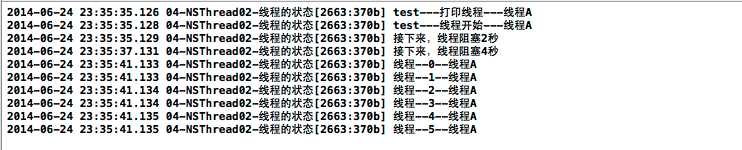
打印查看:

代码示例2(退出线程):
1 //
2 // YYViewController.m
3 // 04-NSThread02-线程的状态
4 //
5 // Created by apple on 14-6-23.
6 // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved.
7 //
8
9 #import "YYViewController.h"
10
11 @interface YYViewController ()
12 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread;
13
14 @end
15
16 @implementation YYViewController
17
18 - (void)viewDidLoad
19 {
20 [super viewDidLoad];
21
22 //创建线程
23 self.thread=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(test) object:nil];
24 //设置线程的名称
25 [self.thread setName:@"线程A"];
26 }
27 //当手指按下的时候,开启线程
28 -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
29 {
30 //开启线程
31 [self.thread start];
32 }
33
34 -(void)test
35 {
36 //获取线程
37 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
38 NSLog(@"test---打印线程---%@",self.thread.name);
39 NSLog(@"test---线程开始---%@",current.name);
40
41 //设置线程阻塞1,阻塞2秒
42 NSLog(@"接下来,线程阻塞2秒");
43 [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2.0];
44
45 //第二种设置线程阻塞2,以当前时间为基准阻塞4秒
46 NSLog(@"接下来,线程阻塞4秒");
47 NSDate *date=[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:4.0];
48 [NSThread sleepUntilDate:date];
49 for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
50 NSLog(@"线程--%d--%@",i,current.name);
51 if (5==i) {
52 //结束线程
53 [NSThread exit];
54 }
55
56 }
57 NSLog(@"test---线程结束---%@",current.name);
58 }
59
60 @end
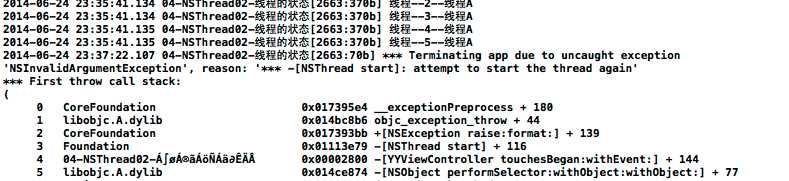
打印示例:
注意:人死不能复生,线程死了也不能复生(重新开启),如果在线程死亡之后,再次点击屏幕尝试重新开启线程,则程序会挂。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/LiLihongqiang/p/5608811.html