标签:
Express是一个基于Node.js实现的Web框架,其响应HTTP请求的response对象中有两个用于URL跳转方法res.location()和res.redirect(),使用它们可以实现URL的301或302重定向。
res.location(path)
下面列举了几种,设置http响应头Location的方法
res.location(‘/foo/bar‘); res.location(‘http://example.com‘); res.location(‘back‘);
路径值back具有特殊的意义,这个涉及到请求头Referer中指定的URL,如果Referer头没有指定,将会设置为‘/‘。
Express通过Location头将指定的URL字符串传递给浏览器,它并不会对指定的字符串进行验证(除‘back‘外)。而浏览器则负责将当前URL重定义到响应头Location中指定的URL。
其中参数:
status:{Number},表示要设置的HTTP状态码path:{String},要设置到Location头中的URL使用指定的http状态码,重定向到指定的URL,如果不指定http状态码,使用默认的状态码”302“:”Found“,
res.redirect(‘/foo/bar‘); res.redirect(‘http://example.com‘); res.redirect(301, ‘http://example.com‘); res.redirect(‘../login‘);
重定向可以是一个完整的URL,这样会重定向到一个不同的站点上。
res.redirect(‘http://google.com‘);
重定向也可以相对于所在主机的根目录,例如,如果你的程序运行在:http://example.com/admin/post/new上下面的代码将会重定向到如下地址:http://example.com/admin
res.redirect(‘/admin‘);
重定向也可以相对于当前的URL,例如:从http://example.com/blog/admin/这个地址(注意反斜杠),下面的代码将会重定向到地址:http://example.com/blog/admin/post/new
res.redirect(‘post/new‘)
在从地址: http://example.com/blog/admin重定向到 post/new,如果没有反斜杠的话将会重定向到:http://example.com/blog/post/new
如果你感觉上面的行为很迷惑,想想文件目录和文件的路径,这会让你更好理解。
相对路径的重定向也是允许的,如果你的地址是: http://example.com/admin/post/new,下面的代码将会重定向到http//example.com/admin/post这个地址:
res.redirect(‘..‘);
back重定向,重定向到请求的referer,当没有referer请求头的情况下,默认为‘/’
res.redirect(‘back‘);
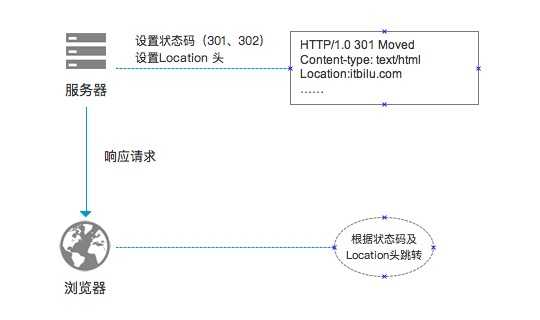
进行URL重定向时,服务器只在响应信息的HTTP头信息中设置了HTTP状态码和Location头信息。
当状态码为301或302时(301-永久重定向、302-临时重定向),表示资源位置发生了改变,需要进行重定向。
Location头信息表示了资源的改变的位置,即:要跳重定向的URL。
location()与redirect()的比较Express的response对象,是对Node.js原生对象ServerResponse的扩展。location()方法只会设置Location头,而redirect()方法除了会设置Location头外还可自动或手头设置HTTP状态码。理论上讲两者可以实现重定向。
location()方法实现过程大致如下:
res.location = function(url){ var req = this.req; // "back" 是 referrer的别名 if (‘back‘ == url) url = req.get(‘Referrer‘) || ‘/‘; // 设置Lcation this.setHeader(‘Location‘, url); return this; };
从以上代码可以看出,location()方法本质上是调用了ServerResponse对象的setHeader()方法,但并没有设置状态码。通过location()设置头信息后,其后的代码还会执行。
使用location()方法实现URL的重定向,还要手动设置HTTP状态码:
res.location(‘http://itbilu.com‘);
res.statusCode = 301;
如果需要立即返回响应信息,还要调用end()方法:
res.location(‘http://itbilu.com‘); res.statusCode = 301; res.end(‘响应的内容‘); // 或 res.location(‘http://itbilu.com‘); res.sent(302);
redirect()方法实现过程大致如下:
res.redirect = function(url){ var head = ‘HEAD‘ == this.req.method; var status = 302; var body; // 一些处理 …… // 通过 location 方法设置头信息 this.location(url); // 另一些处理 …… // 设置状态并返回响应 this.statusCode = status; this.set(‘Content-Length‘, Buffer.byteLength(body)); this.end(head ? null : body); };
从以上代码可以看出,redirect()方法是对location()方法的扩展。通过location()设置Loction头后,设置HTTP状态码,最后通过ServerResponse对象的end()方法返回响应信息。调用redirect()方法后,其后的代码都不会被执行
在使用的过程中,redirect()方法大多能重定向成功,而location()方法则不太确定,有时可以成功有时不能成功。这与我们的用法有关。
上面讲过,URL重定向是在浏览器端完成的,而URL重定向与HTTP状态码和Location头有关。浏览器首先会判断状态码,只有当状态码是:301或302时,才会根据Location头中的URL进行跳转。
所以,使用location()设置头信息,而不设置状态码或状态码不是301或302,并不会发生重定向:
res.location(‘http://itbilu.com‘);
res.sent(200);
而使用redirect()设置的状态码不是301或302也不会发生跳转:
res.redirect(200, ‘http://itbilu.com‘);
参考:
1、http://itbilu.com
2、http://www.expressjs.com.cn/4x/api.html#res.location
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/duhuo/p/5609127.html