标签:style blog http color 使用 os strong io
Spring MVC 对HTTP请求的处理流程
通过之前的源码阅读,知道了ApplicationContext初始的过程,也知道了Spring
MVC环境的初始化过程,今天就来了解一下SpringMVC是如何处理HTTP请求的。
HTTP请求根据请求方式可以分为GET、POST、PUT、DELETE、OPTIONS、TRACE,最常用的还是GET和POST。
Spring对于这几种HTTP请求的处理都是使用了processRequest(req,rep);

@Override protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); } /** * Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}. * @see #doService */ @Override protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }
而在processRequest方法内部,可以看出处理请求的就是一个doService()。

/** * Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch} * for the actual dispatching. */ @Override protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request); logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘ processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + requestUri + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { logger.debug("Taking snapshot of request attributes before include"); attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } }
doDispatch:
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet‘s HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet‘s installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It‘s up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; int interceptorIndex = -1; try { ModelAndView mv; boolean errorView = false; try { // 检查是否是一个文件上传请求, 如果是一个文件上传请求,则将request转为Spring中封装的一个子类:DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest,封装后的类,就不能获取到非文件的表单字段了,需要了解这部分的代码设计才可以。 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. // 这里使用了适配器模式 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request); logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + requestUri + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // 和Struts2一样,也采用拦截器,来对HTTP请求做附加处理 // Apply preHandle methods of registered interceptors. HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = mappedHandler.getInterceptors(); if (interceptors != null) { for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; if (!interceptor.preHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())) { triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null); return; } interceptorIndex = i; } } // 调用你的action代码 // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); // 根据模型视图,来获取到视图名称 // Do we need view name translation? if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) { mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request)); } // 拦截器的后置处理 // Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors. if (interceptors != null) { for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; interceptor.postHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler(), mv); } } } catch (ModelAndViewDefiningException ex) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", ex); mv = ex.getModelAndView(); } catch (Exception ex) { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(processedRequest, response, handler, ex); errorView = (mv != null); } // 渲染页面 // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { render(mv, processedRequest, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘: assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); } } // Trigger after-completion for successful outcome. triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null); } catch (Exception ex) { // Trigger after-completion for thrown exception. triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex); throw ex; } catch (Error err) { ServletException ex = new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err); // Trigger after-completion for thrown exception. triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, ex); throw ex; } finally { // 清理文件上传请求的临时文件 // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (processedRequest != request) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } }
在上面的处理请求的过程中:
涉及了到拦截器、适配器模式。使用拦截器的好处就不多说了,前几篇博客中都有提及。这里但简单的说一下使用视陪器模式的好处。
上面的代码中,使用适配器的代码是:
// Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
传递了三个参数: request, response, 真正的handler。
HandlerAdapter ,根据这个名字,就知道他是用于适配Handler的。它有下面几个子类:
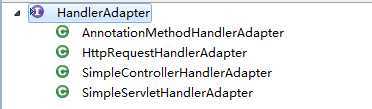
这几个子类,分别用于适配不同的Handler(我们写的请求处理代码)。
如果Handler是一个简单的Servlet(这是在web.xml配置自定义的Servlet时的方式),那么就使用SimpleServletHandlerAdapter
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((Servlet) handler).service(request, response); return null; }
如果Handler是一个简单的Controller的实例,就是用SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter来适配(在Spring2.5时,一般会采用这种方式):
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); }
如果使用了注解方式,就使用AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter,代码就不用粘了。
从上面的可以采用的几种处理HttpRequest的写法上来看,这几种Handler分别属于不同的类,也就是处理的接口是不同的。然而在DispatcherServlet中,只用了一个接口,采用了适配器模式,来屏蔽掉这种差异,在适配器的内部,进行接口的转换工作。
Spring源码阅读:Spring MVC 如何处理HTTP请求,布布扣,bubuko.com
Spring源码阅读:Spring MVC 如何处理HTTP请求
标签:style blog http color 使用 os strong io
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/f1194361820/p/3891315.html