标签:
ref: http://www.studytonight.com/java/multithreading-in-java
Multithreading
A program can be divided into a number of small processes. Each small process can be addressed as a single thread (a lightweight process). Multithreaded programs contain two or more threads that can run concurrently. This means that a single program can perform two or more tasks simultaneously. For example, one thread is writing content on a file at the same time another thread is performing spelling check.
In Java, thread means two different things:
1. an instance of Thread
2. a thread execution
An instance of Thread class is just an object, like any other object in java. But a thread of execution means an individual "lightweight" process that has its own call stack. In java each thread has its own call stack
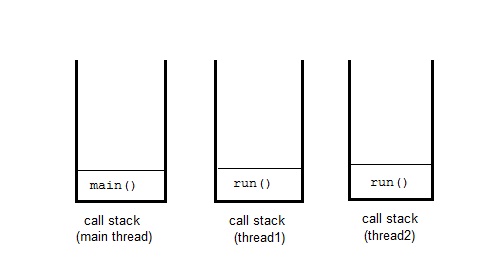
Even if you don‘t create any thread in your program, a thread called main thread is still created. Although the main thread is automatically created, you can control it by obtaining a reference to it by calling currentThread() method.
Two important things to know about main thread are,
class MainThread
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
t.setName("MainThread");
System.out.println("Name of thread is "+t);
}
}
Output : Name of thread is Thread[MainThread,5,main]
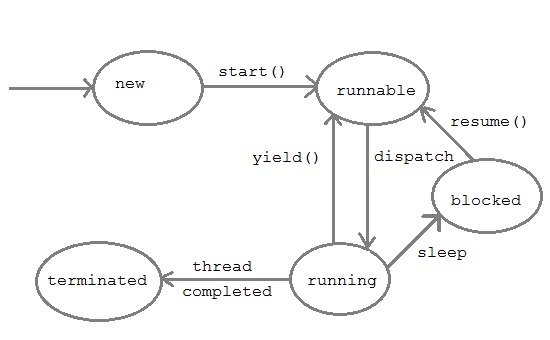
Every thread has a priority that helps the operating system determine the order in which threads are scheduled for execution. In java thread priority ranges between,
By default every thread is given a NORM-PRIORITY(5). The main thread always have NORM-PRIORITY.
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/morningdew/p/5618981.html