标签:
Given a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
For example:
Given the following binary tree,
1 <--- / 2 3 <--- \ 5 4 <---
You should return [1, 3, 4].
Credits:
Special thanks to @amrsaqr for adding this problem and creating all test cases.
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 public class Solution { 11 public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) { 12 List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 13 addright(ans,0,root); 14 return ans; 15 } 16 17 public void addright(List<Integer> ans, int high, TreeNode root){ 18 if(root == null) return; 19 if(ans.size() == high) ans.add(root.val);// 每一层加入一个元素 20 addright(ans,high+1,root.right); 21 addright(ans,high+1,root.left); 22 } 23 }
该题可以用递归解决,每次加入元素从最右边开始,每层加入一个。左子树能加入的情况就是high 高度大于右子树的情况。
如:
1
/ \
2 5
/
4
中元素4所处的情况。虽然代码上看是递归,实际上程序执行时间是O(n)复杂度。
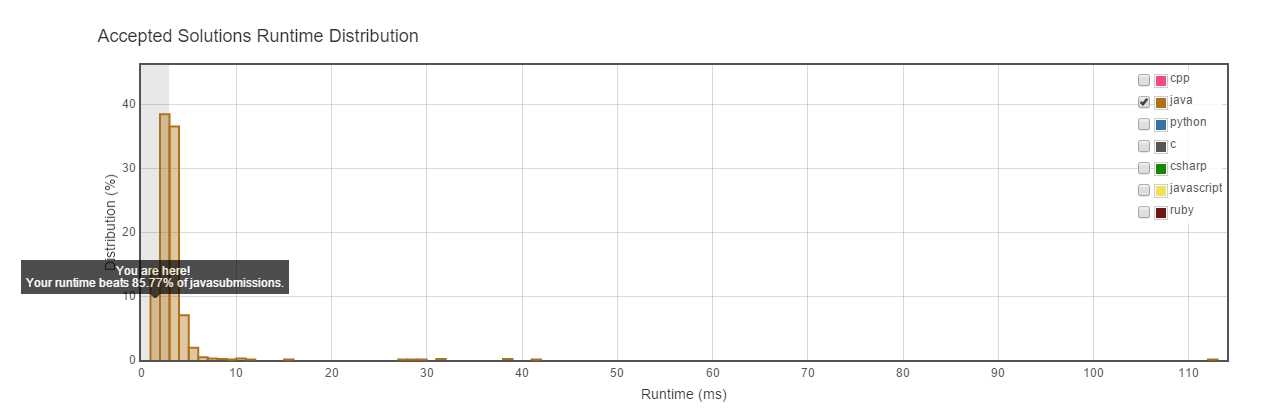
解法2:
该题也可以使用按照层序遍历的方式,每层把最右节点的值加入list即可。
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 public class Solution { 11 public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) { 12 List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 13 if(root == null) return ans; 14 Deque<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); 15 int current = 1,next = 0;//使用current 和next来标记当前层后下一层的元素个数 16 TreeNode node; 17 q.addLast(root); 18 while(q.size() > 0){ 19 node = q.removeFirst(); 20 current--; 21 if(node.left != null){ 22 q.addLast(node.left); 23 next++; 24 } 25 if(node.right != null){ 26 q.addLast(node.right); 27 next++; 28 } 29 if(current == 0){ 30 ans.add(node.val);//每次加入该层最右元素 31 current = next; 32 next = 0; 33 } 34 } 35 return ans; 36 } 37 38 }
实际运行时间:
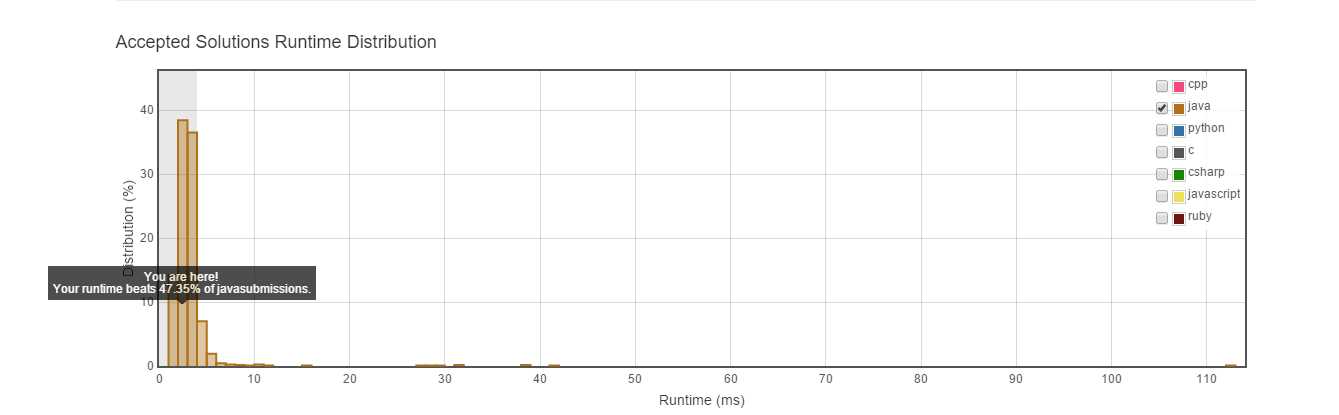
不如解法一。
199. Binary Tree Right Side View java solutions
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/guoguolan/p/5620335.html