标签:
1.RelativeLayout
在RelativeLayout中,组件可以根据父级边界进行定位,除了这样的定位,也可以相对其他控件进行定位。特点是,可以随意拖动空间,拖到哪里就停到哪里。
代码中添加子对象:
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.RelativeLayout; import android.widget.TextView; public class Main2Activity extends AppCompatActivity { private RelativeLayout root; private TextView tv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); root = new RelativeLayout(this); //初始化一个relativelayout setContentView(root);//使该activity加载这个布局 tv = new TextView(this); tv.setText("安卓入门进阶"); RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);//创建布局参数对象 lp.leftMargin = 200;//调整textView的位置 lp.topMargin = 500; root.addView(tv,lp);//将textView添加到layout中 } }
2.FramLayout
framlayout特点为无论拖进去多少个控件对象,都可以重叠。并且只有九个位置可以放置。它的特点与功能在relativeLayout中都可以实现,但是framlayout更加轻量级,并且使用方便简洁。
举个例子,在一个framlayout中重叠放置两张图片,点击图片互相切换。
java源码:
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.FrameLayout; import android.widget.ImageView; public class Main2Activity extends AppCompatActivity { private FrameLayout root; private ImageView iva; private ImageView ivb; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2); root = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.root); //根据id获取到父容器framlayout iva = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iva);//获取组件 ivb = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.ivb); root.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { //点击执行图片的切换 if(iva.getVisibility()==View.VISIBLE){ showB(); }else{ showA(); } } }); } private void showA() { //显示A图片的方法 iva.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); ivb.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); } private void showB() { //显示B图片的方法 iva.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); ivb.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } }
xml源码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:id="@+id/root" tools:context="com.example.lzc.myapplication.Main2Activity"> <ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:src="@drawable/img1" android:id="@+id/iva"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:src="@drawable/img1" android:id="@+id/ivb"/> </FrameLayout>
3.LinearLayout
linerlayout是安卓中的线性布局。使其子对象水平方向或者垂直方向一字排开。其中的属性android:orientation可以控制排列的方向。android:orientation="vertical"为垂直排列。android:orientation="horizontal"为水平排列。在线性布局中有一个重要的属性为比重。也就是layout_weight,它规定了分割父级容器的比例。
如果两个控件,控件A有layout_weight,控件B没有,那么B的宽度就是它本身的宽度,剩下的空间全部给A。
例子布局:
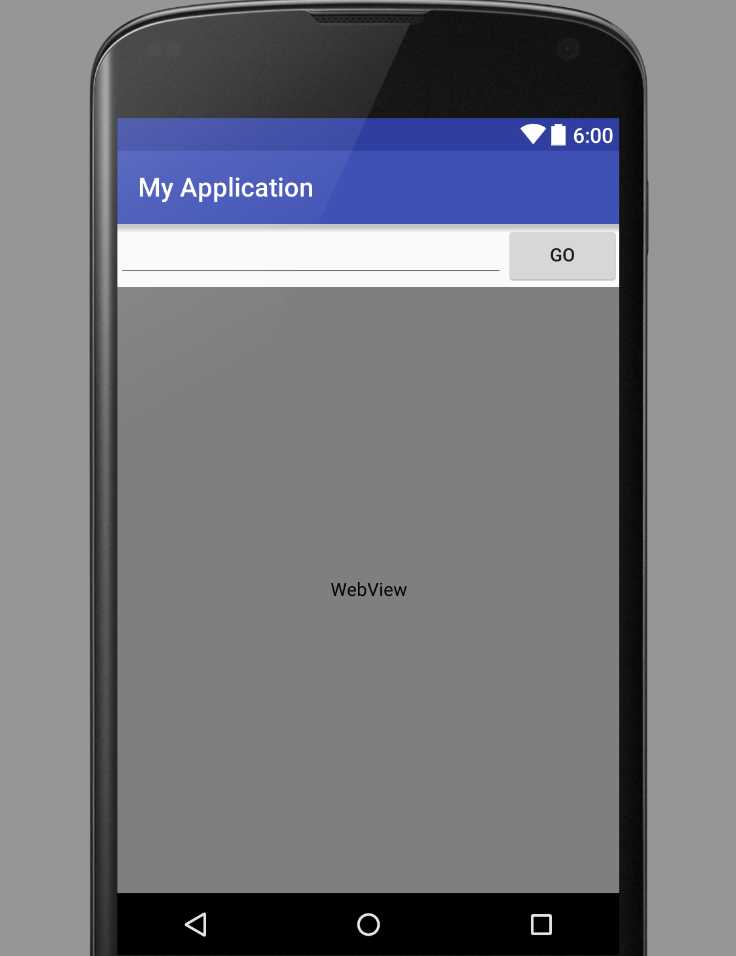
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="go"/> </LinearLayout> <WebView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1"></WebView> </LinearLayout>
效果图:
进阶篇-用户界面:3.android中的基本布局-layout
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/androidNot/p/5625502.html