标签:
2016-06-29
1 字符串处理
求子串。 helloworld
String str="helloworld";
//5<= n <9
//str=str.substring(5,10);
str=str.substring(0,5);
package com.java1995; /** * 求子串 * @author Administrator * */ public class TestString { public static void main(String[] args){ String str="helloworld"; // 5<= n < 9 //str=str.substring(5,10); str=str.substring(0,5); System.out.println(str); } }
测试字符串是否相等。equals
Object equals:比较内存地址
String equals:比较内容
API 1.6
1,寄存器
2,栈
3,堆 * new
4,静态存储区
5,常量存储区 * final static String常量池
6,其他存储位置
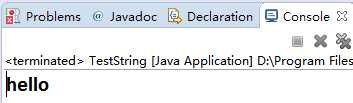
package com.java1995; /** * 判断字符串是否相等 * @author Administrator * */ public class TestString2 { public static void main(String[] args){ String s1="hello";//声明一个String类型的变量 String s2="hello";//声明另一个内容相同的String类型变量 String s3="hello"+"world"; //比较内容 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //比较内存地址 true System.out.println(s1 == s2); //比较内容 System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); //比较内存地址 System.out.println(s1 == s3); // 运行结果 true true false false } }
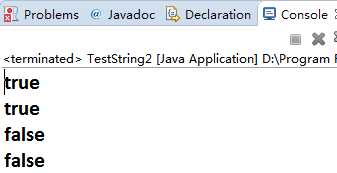
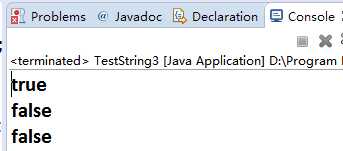
package com.java1995; /** * String常量池、堆内存 * @author Administrator * */ public class TestString3 { public static void main(String[] args){ //维护在常量池里面 String a="hello"; String b="hello"; //new出来的所有对象都是在堆内存 //只要是new出来的,都是新对象 String c= new String("hello"); String d= new String("hello"); System.out.println(a==b);//true System.out.println(a==c);//false System.out.println(c==d);//false } }
字符串编辑
字符串的内容不会变,改变的是引用
String a="hello";
a=a+"world";
System.out.println(a);
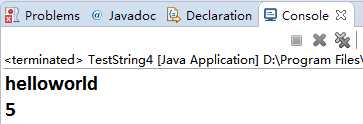
package com.java1995; /** * 字符串编辑 * @author Administrator * */ public class TestString4 { public static void main(String[] args){ String a="hello"; a=a+"world"; int count=a.indexOf("world"); System.out.println(a); System.out.println(count); } }
2 字符串其他常用操作
【参考资料】
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/cenliang/p/5626435.html