标签:
最近有写一个电子订单商务网站,使用JAVA8,SPRING,ANGULARJS对项目使用的技术和大家分享。
第一次写博客,哪有不对需要改正的请联系改正。
因为是项目是我给别人做的无法提供源码见谅,我尽最大努力让大家能看懂。
首先从项目的构建开始,我采用的gradle构建项目,使用的版本是2.4。
开发环境用的IDEA 14,项目数据库使用的是SQL SERVER。
Spring Boot 技术文档:http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle
你可以在这里查看所有Boot的配置与技术开发,对于英文不好的建议大致了解,我后面会慢慢写出来,慢慢了解,把我所知道的。
先看下Gradle Spring Boot 配置,采用的版本是最新1.2.3
buildscript {
ext {
springBootVersion = "1.2.3.RELEASE"
}
repositories {
mavenLocal()
jcenter()
maven { url "http://repo.spring.io/snapshot" }
maven { url "http://repo.spring.io/milestone" }
maven { url "http://repo.spring.io/plugins-release"}
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
classpath("org.springframework:springloaded:${springBootVersion}")
classpath("org.springframework.build.gradle:propdeps-plugin:0.0.6")
}
}
apply plugin: "java"
apply plugin: "spring-boot"
这是一个gradle 基本的build.gradle配置文件。详细你可以到gradle官网去了解使用它,跟它相同功能的有maven工具。Spring是支持这两个插件构建的。
它在build.gradle文件代码如下
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
testCompile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test")
}
我们来看dependencies里面的内容,compile是gradle里面一个绑定资源方法,它可以把我们需要的资源包以及依赖去加载项目里面。如果你使用IDEA14它会自动帮你配置,引用类,一切都是那么简单。
首先我们增加spring 的spring-boot-starter-web组件到项目里面。
Spring boot 是一个高集成化对spring管理工具,它可以将spring的组件协调处理,让你花更少的时间去配置spring.
首先我们在项目根目录包src/main/java/com/demo/下创建一个Application.java类,应该是这样的:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication 这是spring boot 入口。
我们写一个实体Bean,src/main/java/com/demo/ Greeting.java 如下:
package com.demo;
public class Greeting {
private final long id;
private final String content;
public Greeting(long id, String content) {
this.id = id;
this.content = content;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}
接下来我们写一个简单的控制器controller,src/main/java/com/demo/GreetingController.java 如下:
package com.demo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
@RestController
public class GreetingController {
private static final String template = "Hello, %s!";
private final AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
@RequestMapping("/greeting")
public Greeting greeting(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "World") String name) {
return new Greeting(counter.incrementAndGet(),
String.format(template, name));
}
}
@RestController表示这个控制器是rest的控制器,那么它返回的不是我们常见的VIEW对象,它会自动把对象JSON,这是spring 默认的,后面会介绍如何返回其他类型(XML,excel,FILE)
到这里我们已经写了一个简单的spring boot应用了。
在IDEA里面我们可以直接点击Application类右键直接运行,但是这样做我们不推荐,因为这样运行你只是运行了本地的目录配置,没有用到spring boot的。
我们使用gradle 构建所以我们更推荐你使用gradle 去运行你的项目。在IDEA 里面右边你会找到gradle 的显示窗口。就像刚一开始我们把spring boot 组件已经应用,gradle 配置文件build.gradle里面了。
apply plugin: ‘java‘ apply plugin: ‘idea‘ apply plugin: ‘spring-boot‘
所以我们应该可以在gradle的tasks里面找到application的程序组件。它们通常是这样的:
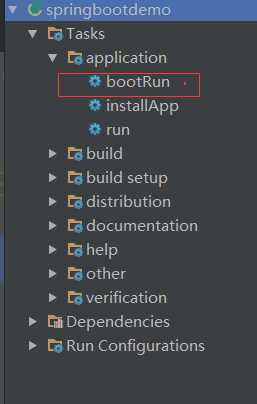
而我们点击bootRun 去运行它。
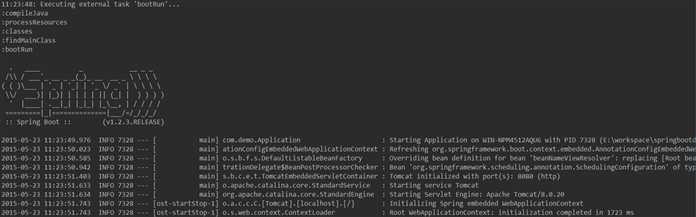
接下来我们在浏览器访问
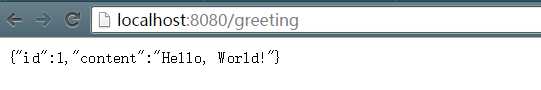
应该是这样的。表示我们简单的spring boot运行成功了。
http://www.cnblogs.com/jasonbob/p/4524385.html#undefined
Spring Boot 是由 Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新 Spring 应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。
本文主要是记录使用 Spring Boot 和 Gradle 创建项目的过程,其中会包括 Spring Boot 的安装及使用方法,希望通过这篇文章能够快速搭建一个项目。
你可以通过 Spring Initializr 来创建一个空的项目,也可以手动创建,这里我使用的是手动创建 gradle 项目。
参考 使用Gradle构建项目 创建一个 ng-spring-boot 项目,执行的命令如下:
$ mkdir ng-spring-boot && cd ng-spring-boot
$ gradle init
ng-spring-boot 目录结构如下:
? ng-spring-boot tree
.
├── build.gradle
├── gradle
│ └── wrapper
│ ├── gradle-wrapper.jar
│ └── gradle-wrapper.properties
├── gradlew
├── gradlew.bat
└── settings.gradle
2 directories, 6 files
然后修改 build.gradle 文件:
buildscript {
ext {
springBootVersion = ‘1.2.2.RELEASE‘
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
}
}
apply plugin: ‘java‘
apply plugin: ‘eclipse‘
apply plugin: ‘idea‘
apply plugin: ‘spring-boot‘
jar {
baseName = ‘ng-spring-boot‘
version = ‘0.0.1-SNAPSHOT‘
}
sourceCompatibility = 1.7
targetCompatibility = 1.7
repositories {
mavenCentral()
maven { url "https://repo.spring.io/libs-release" }
}
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa")
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator")
runtime("org.hsqldb:hsqldb")
testCompile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test")
}
eclipse {
classpath {
containers.remove(‘org.eclipse.jdt.launching.JRE_CONTAINER‘)
containers ‘org.eclipse.jdt.launching.JRE_CONTAINER/org.eclipse.jdt.internal.debug.ui.launcher.StandardVMType/JavaSE-1.7‘
}
}
task wrapper(type: Wrapper) {
gradleVersion = ‘2.3‘
}
使用 spring-boot-gradle-plugin 插件可以提供一些创建可执行 jar 和从源码运行项目的任务,它还提供了 ResolutionStrategy 以方便依赖中不用写版本号。
首先,新建一个符合 Maven 规范的目录结构:
$ mkdir -p src/main/java/com/javachen
创建一个 Sping boot 启动类:
package com.javachen;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
main 方法使用了 SpringApplication 工具类。这将告诉Spring去读取 Application 的元信息,并在Spring的应用上下文作为一个组件被管理。
@Configuration 注解告诉 spring 该类定义了 application context 的 bean 的一些配置。
@ComponentScan 注解告诉 Spring 遍历带有 @Component 注解的类。这将保证 Spring 能找到并注册 GreetingController,因为它被 @RestController 标记,这也是 @Component 的一种。
@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解会基于你的类加载路径的内容切换合理的默认行为。比如,因为应用要依赖内嵌版本的 tomcat,所以一个tomcat服务器会被启动并代替你进行合理的配置。再比如,因为应用要依赖 Spring 的 MVC 框架,一个 Spring MVC 的 DispatcherServlet 将被配置并注册,并且不再需要 web.xml 文件。
你还可以添加 @EnableWebMvc 注解配置 Spring Mvc。
上面三个注解还可以用 @SpringBootApplication 代替:
package com.javachen.examples.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication // same as @Configuration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
你也可以修改该类的 main 方法,获取 ApplicationContext:
package com.javachen;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
System.out.println("Let‘s inspect the beans provided by Spring Boot:");
String[] beanNames = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Arrays.sort(beanNames);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
System.out.println(beanName);
}
}
}
创建一个实体类 src/main/java/com/javachen/model/Item.java:
package com.javachen.model;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class Item {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
@Column
private boolean checked;
@Column
private String description;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public boolean isChecked() {
return checked;
}
public void setChecked(boolean checked) {
this.checked = checked;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
创建一个 Restfull 的控制类,该类主要提供增删改查的方法:
package com.javachen.controller;
import com.javachen.model.Item;
import com.javachen.repository.ItemRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.dao.EmptyResultDataAccessException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.persistence.EntityNotFoundException;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/items")
public class ItemController {
@Autowired
private ItemRepository repo;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<Item> findItems() {
return repo.findAll();
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Item addItem(@RequestBody Item item) {
item.setId(null);
return repo.saveAndFlush(item);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public Item updateItem(@RequestBody Item updatedItem, @PathVariable Integer id) {
Item item = repo.getOne(id);
item.setChecked(updatedItem.isChecked());
item.setDescription(updatedItem.getDescription());
return repo.saveAndFlush(item);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT)
public void deleteItem(@PathVariable Integer id) {
repo.delete(id);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(value = { EmptyResultDataAccessException.class, EntityNotFoundException.class })
public void handleNotFound() { }
}
Greeting 对象会被转换成 JSON 字符串,这得益于 Spring 的 HTTP 消息转换支持,你不必人工处理。由于 Jackson2 在 classpath 里,Spring的 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 会自动完成这一工作。
这段代码使用 Spring4 新的注解:@RestController,表明该类的每个方法返回对象而不是视图。它实际就是 @Controller 和 @ResponseBody 混合使用的简写方法。
使用 JAP 来持久化数据:
package com.javachen.repository;
import com.javachen.model.Item;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import java.util.List;
public interface ItemRepository extends JpaRepository<Item, Integer> {
@Query("SELECT i FROM Item i WHERE i.checked=true")
List<Item> findChecked();
}
Spring Boot 可以自动配置嵌入式的数据库,包括 H2、HSQL 和 Derby,你不需要配置数据库链接的 url,只需要添加相关的依赖即可。另外,你还需要依赖 spring-jdbc,在本例中,我们是引入了对 spring-boot-starter-data-jpa 的依赖。如果你想使用其他类型的数据库,则需要配置 spring.datasource.* 属性,一个示例是在 application.properties 中配置如下属性:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/test
spring.datasource.username=dbuser
spring.datasource.password=dbpass
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
创建 src/main/resources/application.properties 文件,修改 JPA 相关配置,如:
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
注意:
SpringApplication 会在以下路径查找 application.properties 并加载该文件:
- /config 目录下
- 当前目录
- classpath 中 /config 包下
- classpath 根路径下
可以在项目根路径直接运行下面命令:
$ export JAVA_OPTS=-Xmx1024m -XX:MaxPermSize=128M -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom
$ ./gradlew bootRun
也可以先 build 生成一个 jar 文件,然后执行该 jar 文件:
$ ./gradlew build && java -jar build/libs/ng-spring-boot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
启动过程中你会看到如下内容,这部分内容是在 Application 类中打印出来的:
Let‘s inspect the beans provided by Spring Boot:
application
beanNameHandlerMapping
defaultServletHandlerMapping
dispatcherServlet
embeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
handlerExceptionResolver
helloController
httpRequestHandlerAdapter
messageSource
mvcContentNegotiationManager
mvcConversionService
mvcValidator
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration$DispatcherServletConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration$EmbeddedTomcat
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.properties.ServerProperties
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.enhancedConfigurationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.importAwareProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
propertySourcesBinder
propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
requestMappingHandlerAdapter
requestMappingHandlerMapping
resourceHandlerMapping
simpleControllerHandlerAdapter
tomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory
viewControllerHandlerMapping
你也可以启动远程调试:
$ ./gradlew build
$ java -Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:server=y,transport=dt_socket,address=8000,suspend=n -jar build/libs/spring-boot-examples-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
接下来,打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/items,你会看到页面输出一个空的数组。然后,你可以使用浏览器的 Restfull 插件来添加、删除、修改数据。
这里主要使用 Bower 来管理前端依赖,包括 angular 和 bootstrap。
配置 Bower ,需要在项目根目录下创建 .bowerrc 和 bower.json 两个文件。
.bowerrc 文件制定下载的依赖存放路径:
{
"directory": "src/main/resources/static/bower_components",
"json": "bower.json"
}bower.json 文件定义依赖关系:
{
"name": "ng-spring-boot",
"dependencies": {
"angular": "~1.3.0",
"angular-resource": "~1.3.0",
"bootstrap-css-only": "~3.2.0"
}
}如果你没有安装 Bower,则运行下面命令进行安装:
npm install -g bower
安装之后下载依赖:
bower install
运行成功之后,查看 src/main/resources/static/bower_components 目录结构:
src/main/resources/static/bower_components
├── angular
├── angular-resource
└── bootstrap-css-only
注意:
前端页面和 js 存放到 src/main/resources/static/ 目录下,是因为 Spring Boot 会自动在 /static 或者 /public 或者 /resources 或者 /META-INF/resources 加载静态页面。
创建 src/main/resources/static 目录存放静态页面 index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./bower_components/bootstrap-css-only/css/bootstrap.min.css" />
</head>
<body ng-app="myApp">
<div class="container" ng-controller="AppController">
<div class="page-header">
<h1>A checklist</h1>
</div>
<div class="alert alert-info" role="alert" ng-hide="items && items.length > 0">
There are no items yet.
</div>
<form class="form-horizontal" role="form" ng-submit="addItem(newItem)">
<div class="form-group" ng-repeat="item in items">
<div class="checkbox col-xs-9">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" ng-model="item.checked" ng-change="updateItem(item)"/>
</label>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-3">
<button class="pull-right btn btn-danger" type="button" title="Delete"
ng-click="deleteItem(item)">
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-trash"></span>
</button>
</div>
</div>
<hr />
<div class="input-group">
<input type="text" class="form-control" ng-model="newItem" placeholder="Enter the description..." />
<span class="input-group-btn">
<button class="btn btn-default" type="submit" ng-disabled="!newItem" title="Add">
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus"></span>
</button>
</span>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./bower_components/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./bower_components/angular-resource/angular-resource.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./bower_components/lodash/dist/lodash.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./app/app.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./app/controllers.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./app/services.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
这里使用闭包的方式来初始化 AngularJS,代码见 src/main/resources/static/app/app.js :
(function(angular) {
angular.module("myApp.controllers", []);
angular.module("myApp.services", []);
angular.module("myApp", ["ngResource", "myApp.controllers", "myApp.services"]);
}(angular));
代码见 src/main/resources/static/app/services.js :
(function(angular) {
var ItemFactory = function($resource) {
return $resource(‘/items/:id‘, {
id: ‘@id‘
}, {
update: {
method: "PUT"
},
remove: {
method: "DELETE"
}
});
};
ItemFactory.$inject = [‘$resource‘];
angular.module("myApp.services").factory("Item", ItemFactory);
}(angular));
代码见 src/main/resources/static/app/controllers.js :
(function(angular) {
var AppController = function($scope, Item) {
Item.query(function(response) {
$scope.items = response ? response : [];
});
$scope.addItem = function(description) {
new Item({
description: description,
checked: false
}).$save(function(item) {
$scope.items.push(item);
});
$scope.newItem = "";
};
$scope.updateItem = function(item) {
item.$update();
};
$scope.deleteItem = function(item) {
item.$remove(function() {
$scope.items.splice($scope.items.indexOf(item), 1);
});
};
};
AppController.$inject = [‘$scope‘, ‘Item‘];
angular.module("myApp.controllers").controller("AppController", AppController);
}(angular));
再一次打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost:8080/ 进行测试。

本文主要是记录快速使用 Spring Boot 和 Gradle 创建 AngularJS 项目的过程。,希望能对你有所帮助。
文中相关的源码在 ng-spring-boot,你可以下载该项目,然后编译、运行代码。
该项目也可以使用 maven 编译、运行:
$ mvn clean package
$ java -jar target/ng-spring-boot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
或者直接运行:
$ mvn spring-boot:run
http://www.cnblogs.com/mingjian/p/4680845.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/5631763.html