标签:
前文使用包passport实现了一个简单的用户名、密码认证。本文改用oauth2来实现更加安全的认证。
代码在这里。
用户认证,只使用用户名、密码还是非常基础的认证方式。现在RESTful API认证最多使用的是oauth2。使用oauth2就需要使用https,并hash处理client secret、auth code以及access token。
oauth2需要使用包oauth2orize:
npm install --save oauth2orize首先看看oauth2的认证时序图:
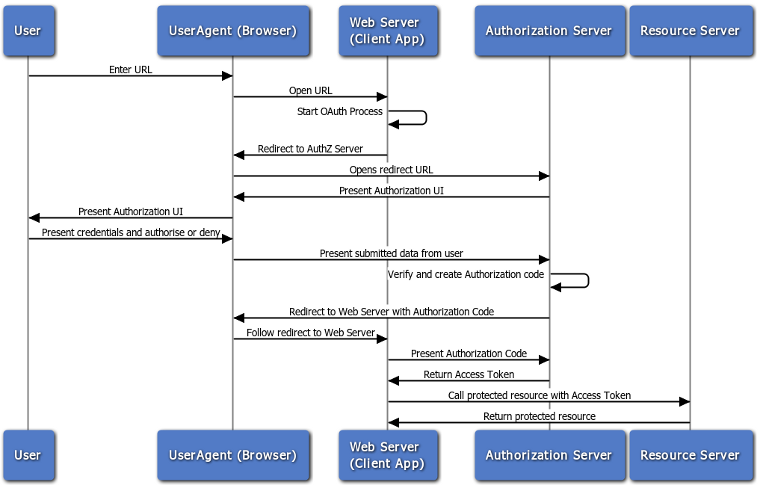
仔细看图发现我们现在的代码并不足以支撑oauth2认证。我们还需要一个UI界面供用户输入用户名、密码产生authorization code和access token。
目前为止,还没有使用过任何的界面。我们现在添加一个简单的页面。用户可以允许活拒绝application client访问他们账户的请求。
Express可以使用的界面模板是很多的:jade、handlebars、ejs等。我们使用ejs。安装ejs:
npm install --save ejs在server.js中设置Express,让Express可以解析ejs模板:
var ejs = require(‘ejs‘);
...
// 创建一个express的server
var app = express();
app.set(‘view engine‘, ‘ejs‘);
...在目录petshop/server/下添加一个文件夹views。在目录中添加文件dialog.ejs。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Beer Locker</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hi <%= user.username %>!</p>
<p><b><%= client.name %></b> is requesting <b>full access</b> to your account.</p>
<p>Do you approve?</p>
<form action="/api/oauth2/authorize" method="post">
<input name="transaction_id" type="hidden" value="<%= transactionID %>">
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Allow" id="allow">
<input type="submit" value="Deny" name="cancel" id="deny">
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>oauth2orize需要用到session。只有这样才能完成认证过程。首先安装session依赖包express-session。
npm install --save express-session接下来是如何使用这个包。更新server.js文件:
var session = require(‘express-session‘);
...
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: true
}));
app.use(session({
secret: ‘a4f8071f-4447-c873-8ee2‘,
saveUninitialized: true,
resave: true
}));
...首先,我们需要添加一个新的model和一个controller,然后再创建一个application client方便以后使用。一个application client会请求一个用户的账户。比如,有这么一个服务可以替你管理你的宠物。在狗粮不够的时候通知你。
var mongoose = require(‘mongoose‘);
var clientSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {type: String, unique: true, required: true},
id: {type: String, required: true},
secret: {type: String, required: true},
userId: {type: String, required: true}
});
module.exports = mongoose.model(‘client‘, clientSchema);name就是用来区分不同的application client的。id和secret会在后面的oauth2认证过程中使用。这两个字段的值应该一直都保证是加密的,不过在本文中没有做加密处理。产品环境必须加密。最后的userId用来表明哪个用户拥有这个application client。接下来创建client对应的controller。
var Client = require(‘../models/client‘);
var postClients = function(req, res) {
var client = new Client();
client.name = req.body.name;
client.id = req.body.id;
client.secret = req.body.secret;
client.userId = req.user._id;
client.save(function(err) {
if (err) {
res.json({message: ‘error‘, data: err});
return;
}
res.json({message: ‘done‘, data: client});
});
};
var getClients = function(req, res) {
Client.find({userId: req.user._id}, function(err, clients) {
if (err) {
res.json({messag: ‘error‘, data: err});
return;
}
res.json({message: ‘done‘, data: clients});
});
};
module.exports = {postClients: postClients,
getClients: getClients
};这两个方法可以用来添加新的client和获取某用户的全部的client。
修改server.js:
var clientController = require(‘./controllers/client‘);
...
// 处理 /clients
router.route(‘/clients‘)
.post(authController.isAuthenticated, clientController.postClients)
.get(authController.isAuthenticated, clientController.getClients);
...下面使用Postman来创建一个application client。
前文中,我们已经可以使用用户名和密码来验证用户了。下面就来验证application client。
在controllers里打开auth.js。更新这个文件, 添加一个新的认证strategy:
passport.use(‘client-basic‘, new BasicStrategy(
function(username, password, done) {
Client.findOne({id: username}, function(err, client) {
if (err) {
return done(err);
}
if (!client || client.secret !== password) {
return done(null, false);
}
return done(null, client);
});
}
));
module.exports.isClientAuthenticated = passport.authenticate(‘client-basic‘, {session: false});
我们新增了一个BasicStrategy,之所以可以这样就是应为我们给这个strategy指定了一个名称client-basic。
这个strategy的功能是用给定的clientId来查找一个client,并检查password(client的secret)是否正确。
我们还需要创建一个model来存放authorization code。这个authorizention code用来来获取access token。
现在我们在models目录下创建一个code.js文件。代码如下:
var mongoose = require(‘mongoose‘);
var Schema = mongoose.Schema;
var codeSchema = new Schema({
value: {type: String, required: true},
redirectUri: {type: String, required: true},
userId: {type: String, required: true},
clientId: {type: String, required: true}
});
module.exports = mongoose.model(‘code‘, codeSchema);很简单对吧。value是用来存放authorization code的。redirectUri用来存放跳转的uri,稍后会详细介绍。clientId和userId用来存放哪个用户和哪个application client拥有这个authorization code。为了安全考虑,你可以hash了authorization code。
这里也需要我们来创建一个model来存放access token。在models目录下添加一个token.js文件:
var mongoose = require(‘mongoose‘);
var Schema = mongoose.Schema;
var tokenSchema = new Schema({
value: {type: String, required: true},
userId: {type: String, required: true},
clientId: {type: String, required: true}
});
module.exports = mongoose.model(‘token‘, tokenSchema);用户访问api的时候使用的token就是value字段的值。userId和clientId就是用来表明哪个用户和application client拥有这个token。产品环境下最好把token做hash处理,绝对不要想我们的例子一样使用明文。
我们之前已经添加了第二个BasicStrategy,这样就可以验证client发出的请求。现在我们在新建一个BearerStrategy,这样我们就可以验证用户使用oauth的token发出的请求了。
首先安装依赖包passport-http-bearer。
npm install passport-http-bearer --save更新controllers/auth.js文件。在这个文件中require passport-http-bearer包和Token model。
var passport = require(‘passport‘),
BasicStrategy = require(‘passport-http‘).BasicStrategy,
BearerStrategy = require(‘passport-http-bearer‘).Strategy,
User = require(‘../models/user‘),
Client = require(‘../models/client‘),
Token = require(‘../models/token‘);
passport.use(new BearerStrategy(
function(accessToken, done) {
Token.findOne({value: accessToken}, function (err, token) {
if (err) {
return done(err);
}
if (!token) {
return done(null, false);
}
User.findOne({_id: token.userId}, function (err, user) {
if (err) {
return done(err);
}
if (!user) {
return done(null, false);
}
done(null, user, {scope: ‘*‘});
});
});
}
));
...
module.exports.isBearerAuthenticated = passport.authenticate(‘bearer‘, {session: false});新的strategy允许我们接受application client发出的请求,并使用发送过来的token验证这些请求。
现在正式进入oauth2的开发阶段。首先安装oauth2orize包:
npm install --save oauth2orize 接下来在controllers里创建一个oauth2.js文件。接下来在这个写代码。
var oauth2orize = require(‘oauth2orize‘),
User = require(‘../models/user‘),
Client = require(‘../models/client‘),
Token = require(‘../models/token‘),
Code = require(‘../models/code‘);// 创建一个OAuth 2.0 server
var server = oauth2orize.createServer();server.serializeClient(function(client, callback) {
return callback(null, client._id);
});
server.deserializeClient(function(id, callback) {
Client.findOne({_id: id}, function (err, client) {
if (err) {
return callback(err);
}
return callback(null, client);
});
});server.grant(oauth2orize.grant.code(function(client, redirectUri, user, ares, callback) {
var code = new Code({
value: uid(16),
clientId: client._id,
redirectUri: redirectUri,
useId: user._id
});
code.save(function(err) {
if (err) {
return callback(err);
}
callback(null, code.value);
});
}));使用oauth2.0,用户可以指定application client可以访问哪些被保护的资源。其过程概括起来就是用户授权client application,之后client再用用户许可换取access token。
server.exchange(oauth2orize.exchange.code(function(client, code, redirectUri, callback) {
Code.findOne({value: code}, function (err, authCode) {
if (err) {return callback(err);}
if (authCode === undefined) {return callback(null, false);}
if (client._id.toString() !== authCode.clientId) {return callback(null, false);}
if (redirectUri !== authCode.redirectUri) {return callback(null, false);}
authCode.remove(function (err) {
if (err) {return callback(err);}
var token = new token({
value: uid(256),
clientId: authCode.clientId,
userId: authCode.userId
});
token.save(function (err) {
if (err) {
return callback(err);
}
callback(null, token);
});
});
});
}));上面的代码就完成了authorization code交换access token的过程。首先检查是否存在一个authorization code,如果存在则开始以后的验证过程。在前面的步骤全部通过的时候,删除已存在的authorization code,这样就不能再次使用。并创建一个新的access token。这个token和application client以及用户绑定在一起。最后存入MongoDB。
module.exports.authorization = [
server.authorization(function(clientId, redirectUri, callback) {
Client.findOne({id: clientId}, function(err, client) {
if (err) {return callback(err);}
return callback(null, client, redirectUri);
});
}),
function(req, res) {
res.render(‘dialog‘, {transationID: req.oauth2.transactionID, user: req.user, client: req.oauth2.client});
}
];这个终端初始化了一个新的授权事务。这个事务里首先找到访问用户账户的client,然后渲染我们前面创建的dialog视图。
module.exports.decision = [server.decision()];无论用户同意或拒绝授权,都有server.decision()来处理。之后调用server.grant()方法。这个方法我们在前面已经创建好。
module.exports.token = [
server.token(),
server.errorHandler()
];这段代码用来处理用户授权application client之后的请求。
function uid(len) {
var buf = [],
chars = ‘ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789‘,
charlen = chars.length;
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++){
buf.push(chars[getRandomInt(0, charlen - 1)]);
}
return buf.join(‘‘);
}
function getRandomInt(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}现在我们可以给oauth2添加路由了。现在来更新server.js代码,给这些终端添加必要的路由。
var oauth2Controller = require(‘./controllers/oauth2‘);
...
router.route(‘/oauth2/authorize‘)
.post(authController.isAuthenticated, oauth2Controller.authorization)
.get(authController.isAuthenticated, oauth2Controller.decision);
router.route(‘/oauth2/token‘)
.post(authController.isClientAuthenticated, oauth2Controller.token);在这一步,oauth2 server需要的全部“工具”都有了。最后一步,需要我们更新一下需要授权的终端(endpoint)。现在我们使用BasicStrategy来认证的,这主要需要用户名和密码。我们现在要换用BearerStrategy来使用access token认证。
把文件controllers/auth.js中module.exports.isAuthenticated语句修改为可以使用basic或者bearer策略。
module.exports.isAuthenticated = passport.authenticate([‘basic‘, ‘bearer‘], {session: false});这已修改,认证就会使用用户名、密码和access token两个了。
代码好多。赶紧试试效果。在浏览器中输入url:http://localhost:3090/api/oauth2/authorize?client_id=my_id&response_type=code&redirect_uri=http://localhost:3090。注意:client_id的值是我前面用postman添加的一个,你需要改成你自己的client_id。
如果你选择了allow(同意),那么就会显示下面的界面:
oauth2orize是一个很强的库,开发一个oauth2 server简单了很多。
基于Node的PetShop,oauth2认证RESTful API
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/future_challenger/article/details/51799959