标签:
Swift提供三种原始的集合类型:数组、集合、字典,这三种类型在使用时key和value的类型都是确定的,意味着只有类型对应的元素才能保存到相应的集合中。
一旦将集合类型声明为常量,其大小和内容都不能再变化。
数组用于存储有序的同一类型的数据元素。
(1)数组的简写
数组类型的全写为: Array<Element>,其中,Element是元素的类型。
可以简写为:[Element].
(2)创建空的数组
1 var someInts = [Int]() 2 print("someInts is of type [Int] with \(someInts.count) items.") 3 // prints "someInts is of type [Int] with 0 items."
如果数组的类型已知,可用[]将其赋值为空数组。
1 someInts.append(3) 2 // someInts now contains 1 value of type Int 3 someInts = [] 4 // someInts is now an empty array, but is still of type [Int]
(3)用默认的值来创建数组
1 var threeDoubles = Array(repeating: 0.0, count: 3) 2 // threeDoubles is of type [Double], and equals [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
以下是V2.1的对应方法:
1 var threeDoubles = [Double](count: 3, repeatedValue: 0.0)
2 // threeDoubles is of type [Double], and equals [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
(4)通过两个数组相加,创建一个数组
1 var anotherThreeDoubles = Array(repeating: 2.5, count: 3)
2 // anotherThreeDoubles is of type [Double], and equals [2.5, 2.5, 2.5] 3 4 var sixDoubles = threeDoubles + anotherThreeDoubles 5 // sixDoubles is inferred as [Double], and equals [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5]
(5)通过字面值创建一个数组
1 var shoppingList: [String] = ["Eggs", "Milk"] 2 // shoppingList has been initialized with two initial items
由于有了类型推断,不必声明数组的类型,如下,Swift会将shoppingList推断为[String]类型:
1 var shoppingList = ["Eggs", "Milk"]
(6)访问和修改数组
count属性得到数组的长度:
print("The shopping list contains \(shoppingList.count) items.") // prints "The shopping list contains 2 items."
isEmpty属性判断数组是否为空:
1 if shoppingList.isEmpty { 2 print("The shopping list is empty.") 3 } else { 4 print("The shopping list is not empty.") 5 } 6 // prints "The shopping list is not empty."
append(_:)方法,在后面插入字符串:
1 shoppingList.append("Flour") 2 // shoppingList now contains 3 items, and someone is making pancakes
也可以直接用+=运算符:
1 shoppingList += ["Baking Powder"] 2 // shoppingList now contains 4 items 3 shoppingList += ["Chocolate Spread", "Cheese", "Butter"] 4 // shoppingList now contains 7 items
通过下标,访问数组中的元素:
1 var firstItem = shoppingList[0] 2 // firstItem is equal to "Eggs"
通过下标,改变数组中的元素:
1 shoppingList[0] = "Six eggs" 2 // the first item in the list is now equal to "Six eggs" rather than "Eggs"
可以使用范围运算符改变一定范围下边内的数组元素, 如下,将"Chocolate Spread", "Cheese", :"Butter"替换为"Bananas" 和"Apples":
1 shoppingList[4...6] = ["Bananas", "Apples"] 2 // shoppingList now contains 6 items
注意:不能用下标在数组末尾添加新的元素.
插入元素:
1shoppingList.insert("Maple Syrup", at: 0)
2 // shoppingList now contains 7 items 3 // "Maple Syrup" is now the first item in the list
移除元素:
1let mapleSyrup = shoppingList.remove(at: 0)
2 // the item that was at index 0 has just been removed 3 // shoppingList now contains 6 items, and no Maple Syrup 4 // the mapleSyrup constant is now equal to the removed "Maple Syrup" string
如果移除最后一个元素,请使用removeLast()方法:
1 let apples = shoppingList.removeLast() 2 // the last item in the array has just been removed 3 // shoppingList now contains 5 items, and no apples 4 // the apples constant is now equal to the removed "Apples" string
(7)遍历数组
1 for item in shoppingList { 2 print(item) 3 } 4 // Six eggs 5 // Milk 6 // Flour 7 // Baking Powder 8 // Bananas
如果既需要值,又需要下标,则使用 enumerate()方法:
1 for (index, value) in shoppingList.enumerate() { 2 print("Item \(index + 1): \(value)") 3 } 4 // Item 1: Six eggs 5 // Item 2: Milk 6 // Item 3: Flour 7 // Item 4: Baking Powder 8 // Item 5: Bananas
集合用于存储值各不相同的同一类型的元素。
(1)元素的Hash值
要能够被存储在集合中,数据类型一定要hashable,也就是说该类型需提供一定方法来计算它的Hash值。Hash值是一种整型的数据,对于相等的所有对象而言,其Hash值是相同的。
如果a == b,则a.hashValue == b.hashValue。
Swift的基本类型 String, Int, Double, 和Bool,默认都是hashable,可以用作Set的value类型或者Dictionary的key类型。没有关联值的枚举中的值也是默认hashable。
注意:你可以把自定义的类型用作Set的value类型或者Dictionary的key类型,只要它们实现Hashable协议。要实现Hashable协议,则该类型需要有一个gettable的名为hashValue的Int属性。该属性在不同程序或者同一程序的不同执行情况下不一定要返回相同的值。由于Hashable协议遵守了Equatable协议,所以也必须实现相等比较运算符(==),== 的实现必须遵循以下要求:
a == a (Reflexivity)
a == b implies b == a (Symmetry)
a == b && b == c implies a == c (Transitivity)
(2)Set的声明
Set<Element>,其中,Element是元素的类型。
(3)创建并初始化一个空的Set
1 var letters = Set<Character>() 2 print("letters is of type Set<Character> with \(letters.count) items.") 3 // prints "letters is of type Set<Character> with 0 items."
此外,如果Set已经明确类型,则可以用[]将Set赋为空:
1 letters.insert("a") 2 // letters now contains 1 value of type Character 3 letters = [] 4 // letters is now an empty set, but is still of type Set<Character>
(4)用数组字面量来声明一个Set
1 var favoriteGenres: Set<String> = ["Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop"] 2 // favoriteGenres has been initialized with three initial items
Set类型不能只由数组字面量来推断出,所以Set关键字必须显示地声明。由于数组的元素类型是可以推断出来的,Set的value类型可以不用显示声明。
1 var favoriteGenres: Set = ["Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop"]
(5)访问和修改Set
访问元素数量:
1 print("I have \(favoriteGenres.count) favorite music genres.") 2 // prints "I have 3 favorite music genres."
Set是否为空:
1 if favoriteGenres.isEmpty { 2 print("As far as music goes, I‘m not picky.") 3 } else { 4 print("I have particular music preferences.") 5 } 6 // prints "I have particular music preferences."
添加元素:
1 favoriteGenres.insert("Jazz") 2 // favoriteGenres now contains 4 items
移除元素:
1 if let removedGenre = favoriteGenres.remove("Rock") { 2 print("\(removedGenre)? I‘m over it.") 3 } else { 4 print("I never much cared for that.") 5 } 6 // prints "Rock? I‘m over it."
是否包含某个元素:
1 if favoriteGenres.contains("Funk") { 2 print("I get up on the good foot.") 3 } else { 4 print("It‘s too funky in here.") 5 } 6 // prints "It‘s too funky in here."
(6)遍历Set
1 for genre in favoriteGenres { 2 print("\(genre)") 3 } 4 // Classical 5 // Jazz 6 // Hip hop
以某种指定顺序遍历Set(用<进行排序):
1 for genre in favoriteGenres.sorted() {// for genre in favoriteGenres.sort() V2.1 2 print("\(genre)") 3 } 4 // Classical 5 // Hip hop 6 // Jazz
(7)Set运算
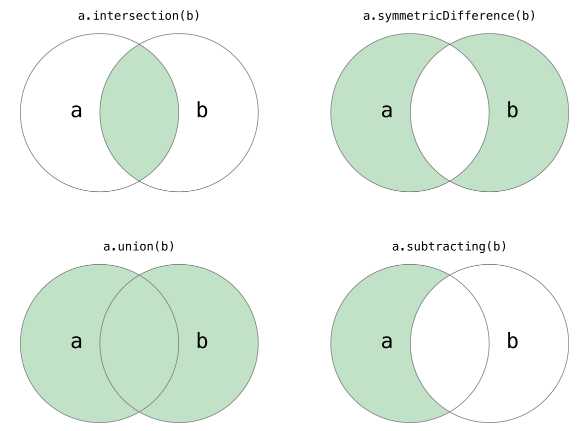
并集、异或、交集、差集
1 let oddDigits: Set = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] 2 let evenDigits: Set = [0, 2, 4, 6, 8] 3 let singleDigitPrimeNumbers: Set = [2, 3, 5, 7] 4 5 oddDigits.union(evenDigits).sort() 6 // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 7 oddDigits.intersection(evenDigits).sort() 8 // [] 9 oddDigits.subtracting(singleDigitPrimeNumbers).sort() 10 // [1, 9] 11 oddDigits.symmetricDifference(singleDigitPrimeNumbers).sort() 12 // [1, 2, 9]
(8)Set之间的关系
== 判断两个Set的元素是否完全相同。
isSubsetOf(_:) 判断Set中的所有元素是否包含在另一Set中。
isSupersetOf(_:) 判断Set是否包含另一Set的所有元素。
isStrictSubsetOf(_:) 或者 isStrictSupersetOf(_:) 判断set是否是另一Set的超集或子集,并且并不相等。
isDisjointWith(_:) 判断两个Set是否有交集。
1 let houseAnimals: Set = ["??", "??"] 2 let farmAnimals: Set = ["??", "??", "??", "??", "??"] 3 let cityAnimals: Set = ["??", "??"] 4 houseAnimals.isSubset(of: farmAnimals) 5 // true 6 farmAnimals.isSuperset(of: houseAnimals) 7 // true 8 farmAnimals.isDisjoint(with: cityAnimals) 9 // true
字典存储键值对,键的类型是一致的,值的类型是一致的。与数组不同,字典中的元素没有次序,只能用键来查询值。
(1)字典的简写
全写:Dictionary<Key, Value>,Key为键类型,Value为值类型。
Key必须满足Hashable协议。
简写:[Key: Value]
(2)创建空数组
1 var namesOfIntegers = [Int: String]() 2 // namesOfIntegers is an empty [Int: String] dictionary
[:]将已声明的字典赋值为空:
1 namesOfIntegers[16] = "sixteen" 2 // namesOfIntegers now contains 1 key-value pair 3 namesOfIntegers = [:] 4 // namesOfIntegers is once again an empty dictionary of type [Int: String]
(3)用字面量创建字典
1 var airports: [String: String] = ["YYZ": "Toronto Pearson", "DUB": "Dublin"]
从字面量可以推断出Key和Value的类型,则两者不必显示声明:
1 var airports = ["YYZ": "Toronto Pearson", "DUB": "Dublin"]
(4)访问和修改字典
元素数目:
1 print("The airports dictionary contains \(airports.count) items.") 2 // prints "The airports dictionary contains 2 items."
是否为空:
1 if airports.isEmpty { 2 print("The airports dictionary is empty.") 3 } else { 4 print("The airports dictionary is not empty.") 5 } 6 // prints "The airports dictionary is not empty."
添加新元素:
1 airports["LHR"] = "London" 2 // the airports dictionary now contains 3 items
改变某个元素:
1 airports["LHR"] = "London Heathrow" 2 // the value for "LHR" has been changed to "London Heathrow"
也可以用updateValue(_:forKey:)方法代替下标方法来更新某个元素的值。如果元素不存在,则该方法会创建这个元素。不同于下标方法,updateValue(_:forKey:)如果是更新元素的值,它会返回旧的元素值,这可以用来判断该元素是更新还是创建的。
updateValue(_:forKey:)返回的是元素值的可选型,如果更新,则该可选值有值,如果是新建的,则该可选值等于nil。
1 if let oldValue = airports.updateValue("Dublin Airport", forKey: "DUB") { 2 print("The old value for DUB was \(oldValue).") 3 } 4 // prints "The old value for DUB was Dublin."
可以用下标的方法取出某个key对应的值,如果key不存在,则返回nil:
1 if let airportName = airports["DUB"] { 2 print("The name of the airport is \(airportName).") 3 } else { 4 print("That airport is not in the airports dictionary.") 5 } 6 // prints "The name of the airport is Dublin Airport."
用下标方法移除某个键值对:
1 airports["APL"] = "Apple International" 2 // "Apple International" is not the real airport for APL, so delete it 3 airports["APL"] = nil 4 // APL has now been removed from the dictionary
也可以用removeValue(forKey:)方法来移除元素:(removeValueForKey(_:) V2.1)
1 if let removedValue = airports.removeValue(forKey:" DUB") {
2 print("The removed airport‘s name is \(removedValue).")
3 } else {
4 print("The airports dictionary does not contain a value for DUB.")
5 }
6 // prints "The removed airport‘s name is Dublin Airport."
(5)遍历字典
1 for (airportCode, airportName) in airports { 2 print("\(airportCode): \(airportName)") 3 } 4 // YYZ: Toronto Pearson 5 // LHR: London Heathrow
只取出key或value:
1 for airportCode in airports.keys { 2 print("Airport code: \(airportCode)") 3 } 4 // Airport code: YYZ 5 // Airport code: LHR 6 7 for airportName in airports.values { 8 print("Airport name: \(airportName)") 9 } 10 // Airport name: Toronto Pearson 11 // Airport name: London Heathrow
把key和value取作数组:
1 let airportCodes = [String](airports.keys) 2 // airportCodes is ["YYZ", "LHR"] 3 4 let airportNames = [String](airports.values) 5 // airportNames is ["Toronto Pearson", "London Heathrow"]
Swift中的字典是没有次序的,如果要以某种次序遍历key或value,可以用keys或values属性的sorted()方法对其排序。(sort() V2.1)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/tt2015-sz/p/4861601.html