标签:
&1 思想和时间复杂度
&2 算法
#1. 在待排数列中(n个数)选择一个基准数(理论上可以任意);
#2. 剩下的 n-1 个数与基准数对比,比基准数小的放左边,反之在右边;(也有人称为划分操作)
#3. 一轮循环结束,此时基准数是位于它的最终位置;
#4. 重复步骤#1~#3,直到最后一个基准数左边和右边的元素个数为0或1,则排序完成。
&3 举例

&4 c++程序实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void QuickSort(vector<int > &A, int p, int q);
int Partition(vector<int> &a, int p, int q);
void swapv(int &a, int &b);
int main(){
vector<int> seti = { 13, 19, 9, 5, 12, 8, 7, 4, 21, 2, 6, 11 };
int len = seti.size();
QuickSort(seti,0,len-1);
cout << "The sorted array is: \n";
for (vector<int>::iterator iter = seti.begin(); iter != seti.end(); iter++)
cout << *iter << "\t";
cout << endl;
system("Pause");
return 0;
}
void QuickSort(vector<int > &A,int p,int q){
if (p < q){
int pos = Partition(A, p, q);
QuickSort(A, p, pos - 1);
QuickSort(A, pos + 1, q);
}
}
int Partition(vector<int> &a,int p, int q){
int val = a[p];
int j = q + 1;
for (int i = q; i > p-1; i--){
if (a[i]>val){
j = j - 1;
if (i != j)
swapv(a[j],a[i]);
}
}
if (p != j - 1)
swapv(a[p],a[j-1]);
return j - 1;
}
void swapv(int &a,int &b){
a = a + b;
b = a - b;
a = a - b;
}
&5 程序实现结果截图
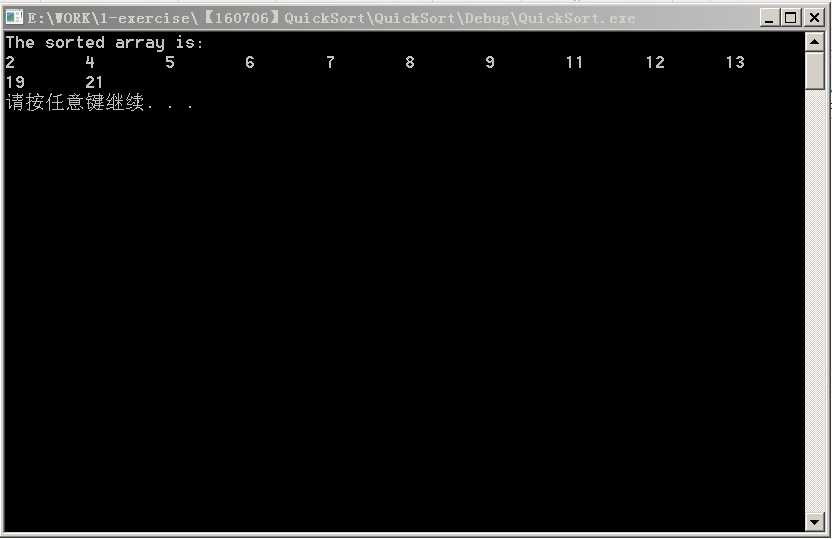
如果对代码优化,亲有更好的想法,咱可以一起学习讨论哦!
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sophia-hxw/p/5357824.html