标签:
学习Eigen人脸识别算法需要了解一下它用到的几个理论基础,现总结如下:
首先需要了解一下公式:
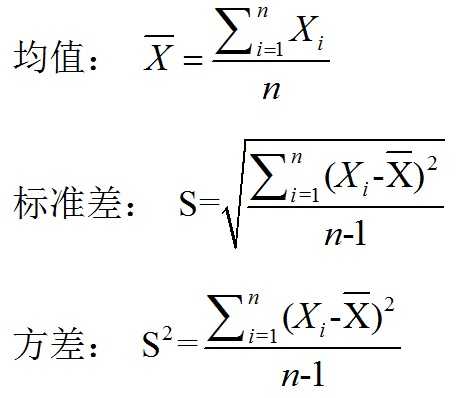
共公式可以看出:均值描述的是样本集合的平均值,而标准差描述的则是样本集合的各个样本点到均值的距离之平均。以一个国家国民收入为例,均值反映了平均收入,而均方差/方差则反映了贫富差距,如果两个国家国民收入均值相等,则标准差越大说明国家的国民收入越不均衡,贫富差距较大。以上公式都是用来描述一维数据量的,把方差公式推广到二维,则可得到协方差公式:
![]()
协方差表明了两个随机变量之间的相关性,值为正说明两者是正相关的,值为负说明两者是负相关的,值为零说明两者不相关,举一个简单的小例子,假设一个人用4个维度身高、体重、距离屋顶的高度、每天画画的时间来表示:身高取样X=[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9],体重取样Y=[11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19],距离屋顶的高度取样Z=[9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1],每天画画时间L=[1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1],则有cov(X,Y)=7.5,cov(X,Z)=-7.5,cov(X,L)=0,结果很明显X和Y协方差为正数两者正相关,X和Z协方差为负数两者负相关,X和L协方差为0,说明它们不相关。以上例子每一个随机变量都可以表示一个维度,我们计算了部分维度之间的协方差,计算所有维度之间的协方差并组织成矩阵的形式,就有了协方差矩阵的概念:Cnxn=[ci,j]=[cov(Dimi,Dimj)] i,j=1,2,…,n,Dimi表示第i个维度向量。以Matlab协方差矩阵为例,将X,Y,Z,L分别作为1,2,3,4个维度,则有c1,1=7.5,c1,2=7.5,c1,3=-7.5,c1,4=7.5……,所以协方差矩阵为:
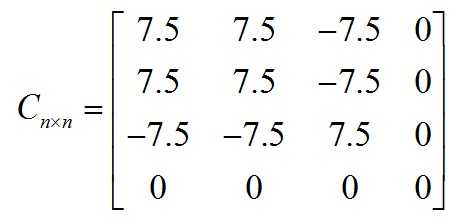
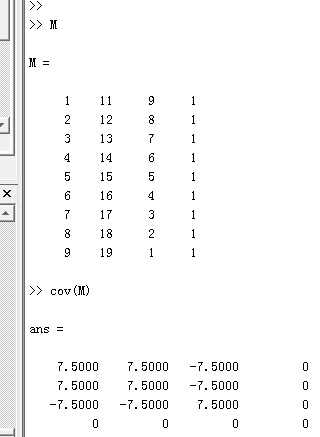
在Matlab中可以把矩阵的每行看做是4个随机变量的一组取样样本,每列看做是一个维度,则可以直接用con函数求得4个维度的协方差矩阵:
雅可比迭代法的基本思想是:通过一组平面旋转变换(相似正交变换)化对称矩阵A为对角矩阵,进而求出A的特征值与特征向量。由线性代数理论可知:若矩阵A是实对称矩阵,则一定存在正交矩阵U,使得UT*A*U=D,其中D对角矩阵,其主对角线元素λi是A的特征值,正交矩阵U的第i列是A对应特征值λi的特征向量。于是求对称矩阵A的特征值问题转化为寻找正交矩阵U,使得UT*A*U为对角矩阵,这个问题的困难在于如何构造U,为此我们先看一下平面上的旋转变换:
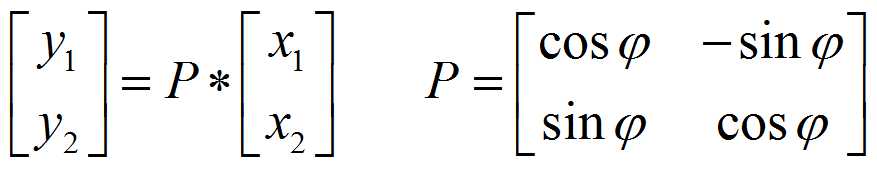
则有:
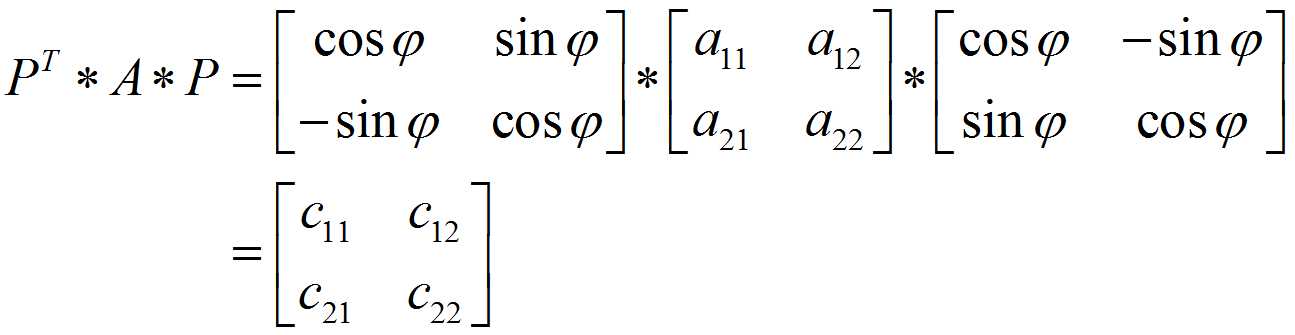
其中:
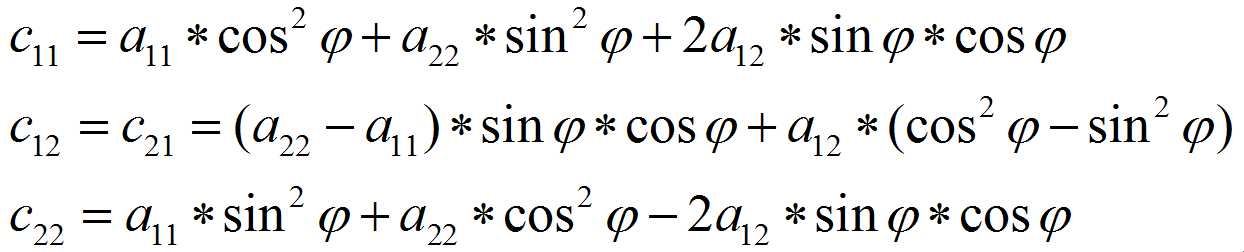

上述推导其实说明了一种构造正交矩阵P,并使得PT*A*P为对角矩阵的方法,可以将这种方法推广到nxn对角矩阵,首先引入n阶旋转矩阵(Givens矩阵)的概念:
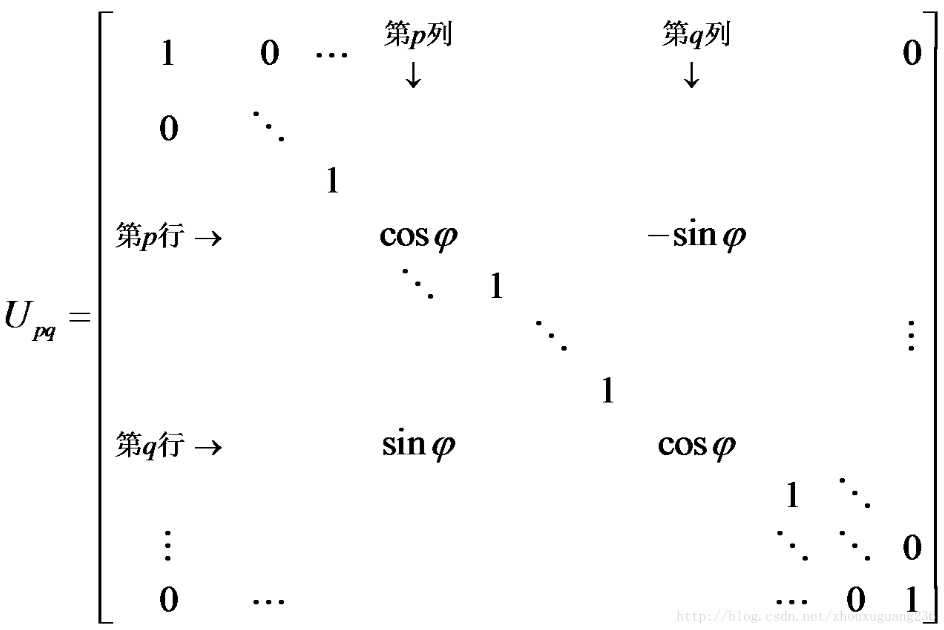
平面旋转矩阵有如下性质:
(1)Upq为正交矩阵,即UpqT*Upq=E
(2)UTAU=B仍为对称矩阵,且B与A有相同的特征值
Jacobi迭代法,在每一次迭代时都是进行一次(2)中的转换,这里p、q分别是前一次的迭代矩阵A的非主对角线上绝对值最大元素的行列号,变换后元素值可以由以下公式求出:
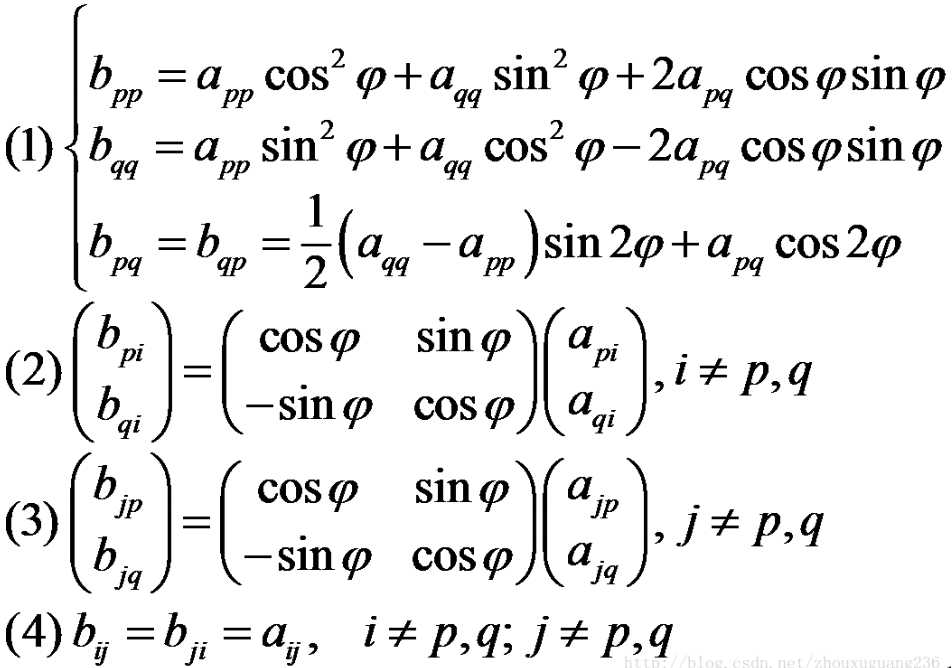
由公式可以看出转换后矩阵相比原矩阵只是在p,q行和列的元素发生了改变,旋转角的计算过程和2维时一样,其意义是使得apq和aqp值为零,这样每次迭代都使得非对角线上绝对值最大的元素变为零,所以整个迭代的过程就是使对角线外元素逐步逼近于零,这是对角线上的元素即为原对称矩阵的特征值λi。在进行Jacobi迭代时,假如i次迭代时旋转矩阵为Ui,每次迭代对单位矩阵I依次左乘Ui,最终迭代结束后可得矩阵D=Uk…U2U1I,这里k为迭代次数,则可以证明D的列向量即为特征值λi对应的特征向量,证明如下:
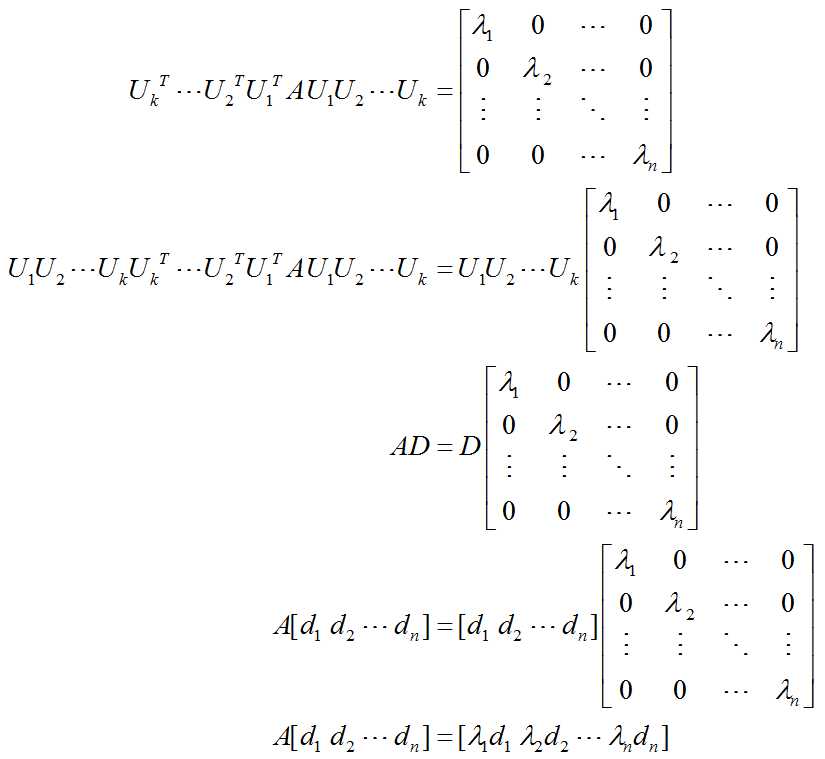
上述推导过程中di为矩阵D的i列表示的列向量,由最后的等式及特征值定义,可以得知λi是A的特征值,di为对应的特征向量。
(1)void reduce(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int dim, int rtype, int dtype=-1)
其英文注释:transforms 2D matrix to 1D row or column vector by taking sum, minimum, maximum or mean value over all the rows.
其英文注释不太准确,函数的作用其实是:将2维矩阵转换为1维行向量或列向量,如转换为行向量,则每列处的值为原矩阵对应列所有值的和,最小值,最大值,平均值;如转换为列向量,则每行处的值为原矩阵对应行所有值的和。该函数参数意义如下:
src: 原矩阵
dst: 目的向量
dim: 指明处理后向量是行向量还是列向量,0原矩阵被处理成行向量,否则原矩阵被处理成列向量
op: 取值为CV_REDUCE_SUM,CV_REDUCE_MAX,CV_REDUCE_MIN,CV_REDUCE_AVG之一
dtype: 目的向量类型
(2)void gemm(InputArray src1, InputArray src2, double alpha, InputArray src3, double gamma, OutputArray dst, int flags=0)
其英文注释:implements generalized matrix product algorithm GEMM from BLAS.
函数的作用:实现广义矩阵乘法,只对最后一个参数进行说明
flags: 取值为GEMM_1_T,GEMM_2_T,GEMM_3_T之1或者它们的组合,例如取值为GEMM_1_T则进行乘法之前对src1进行转置,所有函数作用可由以下公式来说明:
dst=alpha*op(src1)*op(src2)+gamma*op(src3),其中op(X)是X还是XT由flags确定。
(3)void mulTransposed( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, bool aTa, InputArray delta=noArray(), double scale=1, int dtype=-1 )
其英文注释:multiplies matrix by its transposition from the left or from the right.
函数的作用:矩阵左乘或右乘其转置矩阵,参数意思如下:
src: 原矩阵
dst: 目的矩阵
ata: 乘法顺序,true AT*A false A*AT
delta:在进行乘法前src先减去该数组
scale:乘法之后对结果进行scale倍缩放
dtype:目的矩阵类型
当ata为真时可用公式 dst=(src-delta)T*(src-delta)*scale 来说明函数的作用,该函数内部调用了函数(2)
(4)void calcCovarMatrix( InputArray samples, OutputArray covar, OutputArray mean, int flags, int ctype=CV_64F)
其英文注释:computes covariation matrix of a set of samples
函数作用:计算矩阵行向量或列向量的协方差矩阵,该函数中会调用函数(3)来实现相应功能
(5)bool eigen(InputArray src, OutputArray eigenvalues, OutputArray eigenvectors, int lowindex=-1, int highindex=-1)
其英文解释:finds eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric matrix
函数作用:求对称矩阵的特征值和特征向量,在该函数中会利用Jacobi方法来求对称矩阵的特征值和特征向量
特征脸EigenFace的思想是把人脸从像素空间变换到另一个空间,在另一个空间中做相似性计算,EigenFace选择的空间变换方法是PCA,就是大名鼎鼎的主成分分析。EigenFace方法利用PCA得到人脸分布的主成分,具体实现是对训练集中的所有人脸图像的协方差矩阵进行求特征值,特征值对应的特征向量就是所谓的“特征脸”,每个特征向量描述人脸的一种变化或者特征,所以每个人脸都可以表示为这些特征脸的线性组合。下面结合以AT&T人脸库(40个人每个人包含10个表情脸图像,共400个脸部图像,每个图像分辨率为92x112),取其中399个人脸为样本库,最后1个为待识别人脸,给出基于Eigen特征脸的人脸识别实现过程:
(1)将训练集中的每一个人脸图像数据都拉长成一行,并将他们组合在一起形成一个大矩阵A,则A的大小为399x10304,即399行10304列。
(2)将399个人脸每个人脸对应的维度数据相加,然后求平均值,得到平均值向量Mean1x10304,将矩阵A的每一行都减去平均值向量得到差值矩阵B。
(3)计算协方差矩阵C=B*BT,C的维度是399x399,再对C求特征值λi,及特征向量ei,0<=i<399。
(4)上一步骤中其实并不是真正的人脸取样集协方差矩阵,因为人脸取样的维度是10304,而协方差矩阵反应的是各个维度之前的相关性,所以人脸取样集真正的协方差矩阵是C‘=CT=BT*B,如果vi是C‘的第i个特征向量,可以证明λi同样是C‘的特征值,且vi=BT*ei(vi是10304行列向量),证明如下:
C*ei=λi*ei => B*BT*ei=λi*ei => BT*B*BT*ei=λi*BT*ei => C‘*vi=λi*vi
特征向量vi即为“特征脸”,所有特征向量组成特征向量矩阵V10304*399,则对于任意人脸向量α,将它与特征向量矩阵V相乘,将得到向量α在各个特征向量的投影,即α*V所得向量的每一个元素为α在对应“特征脸”的投影,在进行识别时,先求得待识别人脸向量在“特征脸”的投影向量,之后和每个样本脸的投影向量进行相似度比较,相似度最低者为最佳匹配。
代码取自Opencv2.4.9

1 void Eigenfaces::train(InputArrayOfArrays _src, InputArray _local_labels) { 2 if(_src.total() == 0) { 3 string error_message = format("Empty training data was given. You‘ll need more than one sample to learn a model."); 4 CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message); 5 } else if(_local_labels.getMat().type() != CV_32SC1) { 6 string error_message = format("Labels must be given as integer (CV_32SC1). Expected %d, but was %d.", CV_32SC1, _local_labels.type()); 7 CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message); 8 } 9 // make sure data has correct size 10 if(_src.total() > 1) { 11 for(int i = 1; i < static_cast<int>(_src.total()); i++) { 12 if(_src.getMat(i-1).total() != _src.getMat(i).total()) { 13 string error_message = format("In the Eigenfaces method all input samples (training images) must be of equal size! Expected %d pixels, but was %d pixels.", _src.getMat(i-1).total(), _src.getMat(i).total()); 14 CV_Error(CV_StsUnsupportedFormat, error_message); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 // get labels 19 Mat labels = _local_labels.getMat(); 20 // observations in row 21 Mat data = asRowMatrix(_src, CV_64FC1); 22 23 // number of samples 24 int n = data.rows; 25 // assert there are as much samples as labels 26 if(static_cast<int>(labels.total()) != n) { 27 string error_message = format("The number of samples (src) must equal the number of labels (labels)! len(src)=%d, len(labels)=%d.", n, labels.total()); 28 CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message); 29 } 30 // clear existing model data 31 _labels.release(); 32 _projections.clear(); 33 // clip number of components to be valid 34 if((_num_components <= 0) || (_num_components > n)) 35 _num_components = n; 36 37 // perform the PCA 38 PCA pca(data, Mat(), CV_PCA_DATA_AS_ROW, _num_components); 39 // copy the PCA results 40 _mean = pca.mean.reshape(1,1); // store the mean vector 41 _eigenvalues = pca.eigenvalues.clone(); // eigenvalues by row 42 transpose(pca.eigenvectors, _eigenvectors); // eigenvectors by column 43 // store labels for prediction 44 _labels = labels.clone(); 45 // save projections 46 for(int sampleIdx = 0; sampleIdx < data.rows; sampleIdx++) { 47 Mat p = subspaceProject(_eigenvectors, _mean, data.row(sampleIdx)); 48 _projections.push_back(p); 49 } 50 }
38行的PCA类中实现了求样本矩阵的协方差矩阵、求协方差矩阵特征向量等核心功能,47行_mean为人脸平均值向量,该行其实是求每一个人脸向量减去平均值向量在“特征脸”集上的投影向量。

1 PCA& PCA::operator()(InputArray _data, InputArray __mean, int flags, int maxComponents) 2 { 3 Mat data = _data.getMat(), _mean = __mean.getMat(); 4 int covar_flags = CV_COVAR_SCALE; 5 int i, len, in_count; 6 Size mean_sz; 7 8 CV_Assert( data.channels() == 1 ); 9 if( flags & CV_PCA_DATA_AS_COL ) 10 { 11 len = data.rows; 12 in_count = data.cols; 13 covar_flags |= CV_COVAR_COLS; 14 mean_sz = Size(1, len); 15 } 16 else 17 { 18 len = data.cols; 19 in_count = data.rows; 20 covar_flags |= CV_COVAR_ROWS; 21 mean_sz = Size(len, 1); 22 } 23 24 int count = std::min(len, in_count), out_count = count; 25 if( maxComponents > 0 ) 26 out_count = std::min(count, maxComponents); 27 28 // "scrambled" way to compute PCA (when cols(A)>rows(A)): 29 // B = A‘A; B*x=b*x; C = AA‘; C*y=c*y -> AA‘*y=c*y -> A‘A*(A‘*y)=c*(A‘*y) -> c = b, x=A‘*y 30 if( len <= in_count ) 31 covar_flags |= CV_COVAR_NORMAL; 32 33 int ctype = std::max(CV_32F, data.depth()); 34 mean.create( mean_sz, ctype ); 35 36 Mat covar( count, count, ctype ); 37 38 if( _mean.data ) 39 { 40 CV_Assert( _mean.size() == mean_sz ); 41 _mean.convertTo(mean, ctype); 42 covar_flags |= CV_COVAR_USE_AVG; 43 } 44 45 calcCovarMatrix( data, covar, mean, covar_flags, ctype ); 46 eigen( covar, eigenvalues, eigenvectors ); 47 48 if( !(covar_flags & CV_COVAR_NORMAL) ) 49 { 50 // CV_PCA_DATA_AS_ROW: cols(A)>rows(A). x=A‘*y -> x‘=y‘*A 51 // CV_PCA_DATA_AS_COL: rows(A)>cols(A). x=A‘‘*y -> x‘=y‘*A‘ 52 Mat tmp_data, tmp_mean = repeat(mean, data.rows/mean.rows, data.cols/mean.cols); 53 if( data.type() != ctype || tmp_mean.data == mean.data ) 54 { 55 data.convertTo( tmp_data, ctype ); 56 subtract( tmp_data, tmp_mean, tmp_data ); 57 } 58 else 59 { 60 subtract( data, tmp_mean, tmp_mean ); 61 tmp_data = tmp_mean; 62 } 63 64 Mat evects1(count, len, ctype); 65 gemm( eigenvectors, tmp_data, 1, Mat(), 0, evects1, 66 (flags & CV_PCA_DATA_AS_COL) ? CV_GEMM_B_T : 0); 67 eigenvectors = evects1; 68 69 // normalize eigenvectors 70 for( i = 0; i < out_count; i++ ) 71 { 72 Mat vec = eigenvectors.row(i); 73 normalize(vec, vec); 74 } 75 } 76 77 if( count > out_count ) 78 { 79 // use clone() to physically copy the data and thus deallocate the original matrices 80 eigenvalues = eigenvalues.rowRange(0,out_count).clone(); 81 eigenvectors = eigenvectors.rowRange(0,out_count).clone(); 82 } 83 return *this; 84 }
45行求样本矩阵的协方差矩阵,46行求协方差矩阵的特征值及特征向量。

1 void Eigenfaces::predict(InputArray _src, int &minClass, double &minDist) const { 2 // get data 3 Mat src = _src.getMat(); 4 // make sure the user is passing correct data 5 if(_projections.empty()) { 6 // throw error if no data (or simply return -1?) 7 string error_message = "This Eigenfaces model is not computed yet. Did you call Eigenfaces::train?"; 8 CV_Error(CV_StsError, error_message); 9 } else if(_eigenvectors.rows != static_cast<int>(src.total())) { 10 // check data alignment just for clearer exception messages 11 string error_message = format("Wrong input image size. Reason: Training and Test images must be of equal size! Expected an image with %d elements, but got %d.", _eigenvectors.rows, src.total()); 12 CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message); 13 } 14 // project into PCA subspace 15 Mat q = subspaceProject(_eigenvectors, _mean, src.reshape(1,1)); 16 minDist = DBL_MAX; 17 minClass = -1; 18 for(size_t sampleIdx = 0; sampleIdx < _projections.size(); sampleIdx++) { 19 double dist = norm(_projections[sampleIdx], q, NORM_L2); 20 if((dist < minDist) && (dist < _threshold)) { 21 minDist = dist; 22 minClass = _labels.at<int>((int)sampleIdx); 23 } 24 } 25 }
15行求待识别人脸向量减去人脸平均值向量在“特征脸”集上的投影向量X,19行求X与人脸样本投影向量的欧几里得距离(把此距离作为人脸相似度),20~23行取最小距离为识别结果。
最后给出Eigen人脸识别的示例代码,代码中仍使用AT&T人脸库,其下载地址见上一篇随笔。
1 #include "opencv2/core/core.hpp" 2 #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" 3 #include "opencv2/contrib/contrib.hpp" 4 5 #define CV_VERSION_ID CVAUX_STR(CV_MAJOR_VERSION) CVAUX_STR(CV_MINOR_VERSION) CVAUX_STR(CV_SUBMINOR_VERSION) 6 7 #ifdef _DEBUG 8 #define cvLIB(name) "opencv_" name CV_VERSION_ID "d" 9 #else 10 #define cvLIB(name) "opencv_" name CV_VERSION_ID 11 #endif 12 13 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("core") ) 14 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("imgproc") ) 15 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("highgui") ) 16 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("flann") ) 17 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("features2d") ) 18 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("calib3d") ) 19 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("gpu") ) 20 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("legacy") ) 21 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("ml") ) 22 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("objdetect") ) 23 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("ts") ) 24 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("video") ) 25 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("contrib") ) 26 #pragma comment( lib, cvLIB("nonfree") ) 27 28 #include <iostream> 29 #include <fstream> 30 #include <sstream> 31 32 using namespace cv; 33 using namespace std; 34 35 static Mat toGrayscale(InputArray _src) { 36 Mat src = _src.getMat(); 37 // only allow one channel 38 if(src.channels() != 1) { 39 CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "Only Matrices with one channel are supported"); 40 } 41 // create and return normalized image 42 Mat dst; 43 cv::normalize(_src, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); 44 return dst; 45 } 46 47 static void read_csv(const string& filename, vector<Mat>& images, vector<int>& labels, char separator = ‘;‘) { 48 std::ifstream file(filename.c_str(), ifstream::in); 49 if (!file) { 50 string error_message = "No valid input file was given, please check the given filename."; 51 CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message); 52 } 53 string line, path, classlabel; 54 while (getline(file, line)) { 55 stringstream liness(line); 56 getline(liness, path, separator); 57 getline(liness, classlabel); 58 if(!path.empty() && !classlabel.empty()) { 59 images.push_back(imread(path, 0)); 60 labels.push_back(atoi(classlabel.c_str())); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 65 int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { 66 // Check for valid command line arguments, print usage 67 // if no arguments were given. 68 if (argc != 2) { 69 cout << "usage: " << argv[0] << " <csv.ext>" << endl; 70 exit(1); 71 } 72 73 // Get the path to your CSV. 74 string fn_csv = string(argv[1]); 75 // These vectors hold the images and corresponding labels. 76 vector<Mat> images; 77 vector<int> labels; 78 // Read in the data. This can fail if no valid 79 // input filename is given. 80 try { 81 read_csv(fn_csv, images, labels); 82 } catch (cv::Exception& e) { 83 cerr << "Error opening file \"" << fn_csv << "\". Reason: " << e.msg << endl; 84 // nothing more we can do 85 exit(1); 86 } 87 // Quit if there are not enough images for this demo. 88 if(images.size() <= 1) { 89 string error_message = "This demo needs at least 2 images to work. Please add more images to your data set!"; 90 CV_Error(CV_StsError, error_message); 91 } 92 // Get the height from the first image. We‘ll need this 93 // later in code to reshape the images to their original 94 // size: 95 int height = images[0].rows; 96 // The following lines simply get the last images from 97 // your dataset and remove it from the vector. This is 98 // done, so that the training data (which we learn the 99 // cv::FaceRecognizer on) and the test data we test 100 // the model with, do not overlap. 101 Mat testSample = images[images.size() - 1]; 102 int testLabel = labels[labels.size() - 1]; 103 images.pop_back(); 104 labels.pop_back(); 105 // The following lines create an Eigenfaces model for 106 // face recognition and train it with the images and 107 // labels read from the given CSV file. 108 // This here is a full PCA, if you just want to keep 109 // 10 principal components (read Eigenfaces), then call 110 // the factory method like this: 111 // 112 // cv::createEigenFaceRecognizer(10); 113 // 114 // If you want to create a FaceRecognizer with a 115 // confidennce threshold, call it with: 116 // 117 // cv::createEigenFaceRecognizer(10, 123.0); 118 // 119 Ptr<FaceRecognizer> model = createEigenFaceRecognizer(); 120 model->train(images, labels); 121 // The following line predicts the label of a given 122 // test image: 123 int predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample); 124 // 125 // To get the confidence of a prediction call the model with: 126 // 127 // int predictedLabel = -1; 128 // double confidence = 0.0; 129 // model->predict(testSample, predictedLabel, confidence); 130 // 131 string result_message = format("Predicted class = %d / Actual class = %d.", predictedLabel, testLabel); 132 cout << result_message << endl; 133 // Sometimes you‘ll need to get/set internal model data, 134 // which isn‘t exposed by the public cv::FaceRecognizer. 135 // Since each cv::FaceRecognizer is derived from a 136 // cv::Algorithm, you can query the data. 137 // 138 // First we‘ll use it to set the threshold of the FaceRecognizer 139 // to 0.0 without retraining the model. This can be useful if 140 // you are evaluating the model: 141 // 142 model->set("threshold", 0.0); 143 // Now the threshold of this model is set to 0.0. A prediction 144 // now returns -1, as it‘s impossible to have a distance below 145 // it 146 predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample); 147 cout << "Predicted class = " << predictedLabel << endl; 148 // Here is how to get the eigenvalues of this Eigenfaces model: 149 Mat eigenvalues = model->getMat("eigenvalues"); 150 // And we can do the same to display the Eigenvectors (read Eigenfaces): 151 Mat W = model->getMat("eigenvectors"); 152 // From this we will display the (at most) first 10 Eigenfaces: 153 for (int i = 0; i < min(10, W.cols); i++) { 154 string msg = format("Eigenvalue #%d = %.5f", i, eigenvalues.at<double>(i)); 155 cout << msg << endl; 156 // get eigenvector #i 157 Mat ev = W.col(i).clone(); 158 // Reshape to original size & normalize to [0...255] for imshow. 159 Mat grayscale = toGrayscale(ev.reshape(1, height)); 160 // Show the image & apply a Jet colormap for better sensing. 161 Mat cgrayscale; 162 applyColorMap(grayscale, cgrayscale, COLORMAP_JET); 163 imshow(format("%d", i), cgrayscale); 164 } 165 waitKey(0); 166 167 return 0; 168 }
程序运行结果及用伪彩色图像显示的前10个特征脸,如图所示:
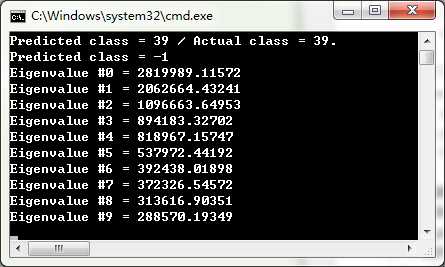
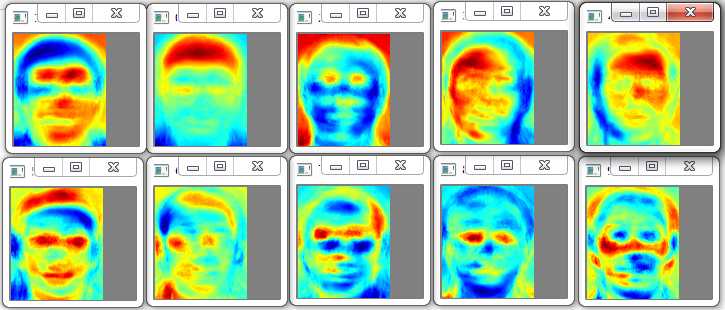
本博客参考了以下资料,一并致谢!
http://www.cnblogs.com/guoming0000/archive/2012/09/27/2706019.html
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/45276053
http://blog.csdn.net/zhouxuguang236/article/details/40212143
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/6023207e168884868762d644.html
《数值分析简明教程》 王兵团 张作泉 赵平福 编著
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoweiwei/p/Eigen.html