标签:des style blog http color java 使用 os
昨天回忆了我在学习JDBC时自己设计的JDBCTemplate(写在上一篇博客中),在使用Spring过程中,有时会用到Spring给我们提供的JdbcTemplate,这里看看Spring是如何实现这个组件的。
在使用Spring JDBC是你要做的工作很少:

从上面的图上可以看出来,使用Spring JDBC,你只需要做四个工作:
1)定义连接参数:也就是定义url,driver,user,password这个几个参数,一般我们会用一个jdbc.properties文件来配置。
2)指定要执行那个sql语句:项目中要用到什么样的SQL语句,Spring是肯定不知道的,只能我们自己设置的。
3)使用PreparedStatement时需要参数,传递哪些参数肯定也是需要我们自己设置的。
4)迭代结果集的过程需要做那些事情,肯定也是需要我们自己写的。
之前我定义的JDBCTemplate需要做的工作有:
1)配置连接参数
2)指定sql语句
3)传递参数
4)处理结果集
综合来看,两者功能是类似的,但是我定义的那个处理能力是有限,例如处理存储过程的方式并没有一个特定的模板。而在Spring中定义的,是一个可用性很好的组件。根据名称就知道它也是使用了模板方法模式,那么它是如何实现的呢?又提供了哪些模板呢?
先来复习一下,如何使用Spring JDBC组件。
在Dao层是这样使用JdbcTemplate的:
@Repository public class JdbcCorporateEventDao implements CorporateEventDao { private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Autowired public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) { this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource); } // JDBC-backed implementations of the methods on the CorporateEventDao follow... }
与上面的使用关联的Spring Bean Definition是:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <!-- Scans within the base package of the application for @Components to configure as beans --> <context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.docs.test" /> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/> </beans>
在Java代码中只需要指定相应的DataSource,就可以获取到JdbcTemplate对象了。
JdbcTemplate作为Spring JDBC组件的核心类,很有必要来看看它是如何实现的。

/** * <b>This is the central class in the JDBC core package.</b> * It simplifies the use of JDBC and helps to avoid common errors. * It executes core JDBC workflow, leaving application code to provide SQL * and extract results. This class executes SQL queries or updates, initiating * iteration over ResultSets and catching JDBC exceptions and translating * them to the generic, more informative exception hierarchy defined in the * <code>org.springframework.dao</code> package. * * <p>Code using this class need only implement callback interfaces, giving * them a clearly defined contract. The {@link PreparedStatementCreator} callback * interface creates a prepared statement given a Connection, providing SQL and * any necessary parameters. The {@link ResultSetExtractor} interface extracts * values from a ResultSet. See also {@link PreparedStatementSetter} and * {@link RowMapper} for two popular alternative callback interfaces. * * <p>Can be used within a service implementation via direct instantiation * with a DataSource reference, or get prepared in an application context * and given to services as bean reference. Note: The DataSource should * always be configured as a bean in the application context, in the first case * given to the service directly, in the second case to the prepared template. * * <p>Because this class is parameterizable by the callback interfaces and * the {@link org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLExceptionTranslator} * interface, there should be no need to subclass it. * * <p>All SQL operations performed by this class are logged at debug level, * using "org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" as log category. */
1)这个类是Spring JDBC core包的主要类。通过上面的说明,可以对JdbcTemplate有个初步的了解:
2)这个类简化了JDBC的使用,有利于避免一些常见的错误。
3)它能够执行JDBC的流程,并且能够将SQL的提供和结果的处理分离。(其实就是说由用户来提供SQL语句,和结果处理)
4)它能够执行SQL的executeQuery,executeUpdate (这两个是Statement、PreparedStatement的方法),能够初始化ResultSet的迭代器。
5)能够帮助我们捕获异常
6)使用这个类编码时,只需要实现相应的callback接口就行了。
常用的接口有:PreparedStatementCreator、ResultSetExtractor、PreparedStatementSetter、RowMapper
7)可以通过在appliction contex中配置DataSource来直接获取JdbcTemplate对象。
8)如果想要使用log4j等来记录日志信息,需要设置:
log4j.logger.org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate=debug
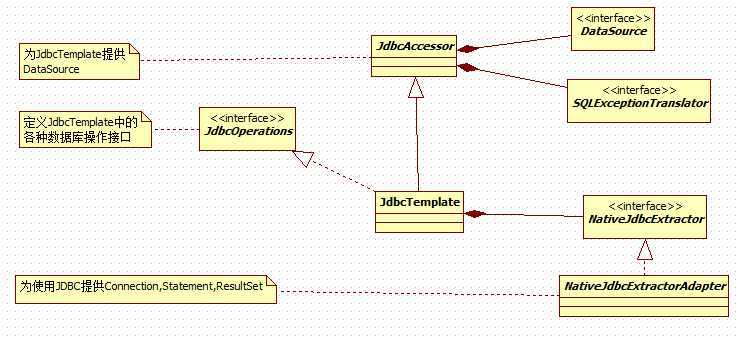
通过上面的类图,就可以了解到:
1)JdbcTemplate通过继承JdbcAccessor,可以从Spring IOC中获取到DataSource.
DataSource是用户在Bean定义文件中配置的。
2)JdbcOperations为JdbcTemplate提供了一些标准的操作接口。接口中的方法都为用户操作数据库提供了极大的便利。
3)JdbcTemplate使用NativeJdbcExtractor用于从各种不同的JDBC厂商或者数据库连接池获取Connection、Statem、ResultSet等,这个类在JdbcTemplate提供的模板方法内部使用。
通过对JdbcTemplate提供的那些方便的方法的浏览,发现了这些方法共同特点是都是用来execute方法。再查看execute方法,发现了JdbcTemplate根据JDBC中的Statement的分类,提供了三种execute:
Statement语句模板: public <T> T execute(StatementCallback<T> action) CallableStatement语句模板: public <T> T execute(CallableStatementCreator csc, CallableStatementCallback<T> action) PreparedStatement语句模板: public <T> T execute(PreparedStatementCreator psc, PreparedStatementCallback<T> action) // 附加一种,这种很少用到 public <T> T execute(ConnectionCallback<T> action)
根据这几个模板就可以看出来,它也是采用了使用Callback的TemplateMethod模式。接下来,分别了解他们是如何实现的:

public <T> T execute(StatementCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException { Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); // 获取到Connection Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(getDataSource()); Statement stmt = null; try { Connection conToUse = con; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null && this.nativeJdbcExtractor.isNativeConnectionNecessaryForNativeStatements()) { conToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeConnection(con); } // 根据connection创建 Statement stmt = conToUse.createStatement(); applyStatementSettings(stmt); Statement stmtToUse = stmt; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { stmtToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeStatement(stmt); } // 在Callback函数中执行SQL语句,并返回结果 T result = action.doInStatement(stmtToUse); // 异常处理 handleWarnings(stmt); return result; } catch (SQLException ex) { // Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock // in the case when the exception translator hasn‘t been initialized yet. // 关闭、释放连接 JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt); stmt = null; DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); con = null; throw getExceptionTranslator().translate("StatementCallback", getSql(action), ex); } finally { JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt); DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); } }
看来这三步的操作要在StatementCallback中来完成了。这个模板方法中对使用JDBC的流程都走了一遍。连接的获取、打开、关闭、方法的调用、异常的处理都设计到了,没有完善的有:SQL的设定、执行,结果的处理。
在JdbcTemplate中找一个使用了这个模板的例子:

public void execute(final String sql) throws DataAccessException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Executing SQL statement [" + sql + "]"); } class ExecuteStatementCallback implements StatementCallback<Object>, SqlProvider { public Object doInStatement(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { stmt.execute(sql); return null; } public String getSql() { return sql; } } execute(new ExecuteStatementCallback()); }
从这个方法可以看出来,SQL语句确实由我们提供,这个模板是在执行SQL操作时才指定SQL语句。这个使用没有对结果的处理
再看查询的例子:

public <T> T query(final String sql, final ResultSetExtractor<T> rse) throws DataAccessException { Assert.notNull(sql, "SQL must not be null"); Assert.notNull(rse, "ResultSetExtractor must not be null"); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Executing SQL query [" + sql + "]"); } class QueryStatementCallback implements StatementCallback<T>, SqlProvider { public T doInStatement(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { ResultSet rs = null; try { rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); ResultSet rsToUse = rs; if (nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { rsToUse = nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeResultSet(rs); } return rse.extractData(rsToUse); } finally { JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(rs); } } public String getSql() { return sql; } } return execute(new QueryStatementCallback()); }
这个例子,就是包括自定义结果处理的模板使用。如果我们使用这个方法,处理ResultSet时,还得自己写结果集迭代器。JdbcTemplate中还提供了一种更简洁的方式:

public void query(String sql, RowCallbackHandler rch) throws DataAccessException { query(sql, new RowCallbackHandlerResultSetExtractor(rch)); } // 这个类可以帮我们使用迭代器获取结果集中的每一行 private static class RowCallbackHandlerResultSetExtractor implements ResultSetExtractor<Object> { private final RowCallbackHandler rch; public RowCallbackHandlerResultSetExtractor(RowCallbackHandler rch) { this.rch = rch; } public Object extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { while (rs.next()) { this.rch.processRow(rs); } return null; } }
PreparedStatement语句模板

public <T> T execute(PreparedStatementCreator psc, PreparedStatementCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException { Assert.notNull(psc, "PreparedStatementCreator must not be null"); Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String sql = getSql(psc); logger.debug("Executing prepared SQL statement" + (sql != null ? " [" + sql + "]" : "")); } // 获取Connection Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(getDataSource()); PreparedStatement ps = null; try { Connection conToUse = con; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null && this.nativeJdbcExtractor.isNativeConnectionNecessaryForNativePreparedStatements()) { conToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeConnection(con); } // 创建PreparedStatement ps = psc.createPreparedStatement(conToUse); applyStatementSettings(ps); PreparedStatement psToUse = ps; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { psToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativePreparedStatement(ps); } // 执行SQL,获取结果 T result = action.doInPreparedStatement(psToUse); handleWarnings(ps); return result; } catch (SQLException ex) { // Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock // in the case when the exception translator hasn‘t been initialized yet. if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) { ((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters(); } String sql = getSql(psc); psc = null; JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps); ps = null; DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); con = null; throw getExceptionTranslator().translate("PreparedStatementCallback", sql, ex); } finally { if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) { ((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters(); } JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps); DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); } }
在使用PreparedStatement可能会用到的类有:
PreparedStatementCreator:用于指定SQL语句
PreparedStatementSetter:用于给SQL语句中的参数赋值
指定SQL: private static class SimplePreparedStatementCreator implements PreparedStatementCreator, SqlProvider { private final String sql; public SimplePreparedStatementCreator(String sql) { Assert.notNull(sql, "SQL must not be null"); this.sql = sql; } public PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection con) throws SQLException { return con.prepareStatement(this.sql); } public String getSql() { return this.sql; } }
设置参数,也是通过遍历参数数组的方式:
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
if (this.args != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.args.length; i++) {
Object arg = this.args[i];
doSetValue(ps, i + 1, arg);
}
}
}
这两个操作都是在内部类中实现的。

public <T> T execute(CallableStatementCreator csc, CallableStatementCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException { Assert.notNull(csc, "CallableStatementCreator must not be null"); Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String sql = getSql(csc); logger.debug("Calling stored procedure" + (sql != null ? " [" + sql + "]" : "")); } Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(getDataSource()); CallableStatement cs = null; try { Connection conToUse = con; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { conToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeConnection(con); } cs = csc.createCallableStatement(conToUse); applyStatementSettings(cs); CallableStatement csToUse = cs; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { csToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeCallableStatement(cs); } T result = action.doInCallableStatement(csToUse); handleWarnings(cs); return result; } catch (SQLException ex) { // Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock // in the case when the exception translator hasn‘t been initialized yet. if (csc instanceof ParameterDisposer) { ((ParameterDisposer) csc).cleanupParameters(); } String sql = getSql(csc); csc = null; JdbcUtils.closeStatement(cs); cs = null; DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); con = null; throw getExceptionTranslator().translate("CallableStatementCallback", sql, ex); } finally { if (csc instanceof ParameterDisposer) { ((ParameterDisposer) csc).cleanupParameters(); } JdbcUtils.closeStatement(cs); DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); } }
这个看起来和前两个有什么不同吗?
接下来看看JdbcTemplate中的其他方法:
他们都是在这几个模板方法的基础上对回调接口给出的部分实现而已。
Spring源码阅读:Spring JDBC 组件的设计与实现,布布扣,bubuko.com
Spring源码阅读:Spring JDBC 组件的设计与实现
标签:des style blog http color java 使用 os
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/f1194361820/p/3894316.html