标签:
width height 模板方法 读写width/height
[‘width‘, ‘height‘].forEach(function(dimension){ //将width,hegiht转成Width,Height,用于document获取 var dimensionProperty = dimension.replace(/./, function(m){ return m[0].toUpperCase() }) $.fn[dimension] = function(value){ var offset, el = this[0] //读时,是window 用innerWidth,innerHeight获取 if (value === undefined) return isWindow(el) ? el[‘inner‘ + dimensionProperty] : //是document,用scrollWidth,scrollHeight获取 isDocument(el) ? el.documentElement[‘scroll‘ + dimensionProperty] : (offset = this.offset()) && offset[dimension] //TODO:否则用 offsetWidth offsetHeight //写 else return this.each(function(idx){ el = $(this) //设值,支持value为函数 el.css(dimension, funcArg(this, value, idx, el[dimension]())) }) } })
/./ 是匹配除换行(\n)以外所有的字符,不加/g,只会匹配一个字符,这里匹配的是h或w
var name = "height".replace(/./,function(m){ console.log(m); return m[0].toUpperCase()});
console.log(name);
h
Height
<div id="high" style="width: 150px;height: 41px;float: left;border: 2px solid red;margin: 10px;padding: 10px;background-color: blue;" id="test">
<div style="height:100%;"></div>
</div>
$("#high").height()
65
$("#high")[0].offsetHeight
65
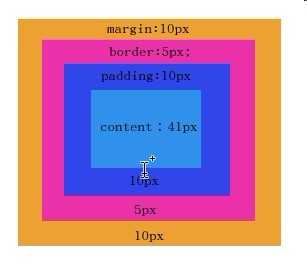
$("#high").height()即offsetHeight包含content,padding,border在内,style=“height:41px” 指的是content为41px;因为默认样式为:box-sizing:content-box,如果指定box-sizing:border-box;则sthle=“height:41px",指的是offsetHeight为41px;
offsetHeight:指的是元素视口高度。
scrollHeight:指的是元素内部的实际高度,因此document求高度要用到它。
innerHeight: 只读属性,声明了窗口的文档显示区的高度和宽度,以像素计。这里的宽度和高度不包括菜单栏、工具栏以及滚动条等的高度。
document.documentElement.clientHeight:与window.innerHeight的效果一样
outerHeight: 只读属性,声明了窗口的高度,包含工具栏。
详细信息请点击:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuteng/articles/1894578.html
注意: 这里的height()可以接受函数作为参数
Generate the "after","prepend","before","append","insertAfter","insertBefore","appendTo", and "prependTo" methods adjacencyOperators = [ ‘after‘, ‘prepend‘, ‘before‘, ‘append‘ ],
adjacencyOperators = [ ‘after‘, ‘prepend‘, ‘before‘, ‘append‘ ],
adjacencyOperators.forEach(function(operator, operatorIndex) { var inside = operatorIndex % 2 //=> prepend, append 有余数 注意forEach遍历出的索引从0开始 $.fn[operator] = function(){ // arguments can be nodes, arrays of nodes, Zepto objects and HTML strings //nodes HTML字符串生成的DOM集 var argType, nodes = $.map(arguments, function(arg) { argType = type(arg) //传参非 object、array、null,就直接调用zepto.fragment生成DOM return argType == "object" || argType == "array" || arg == null ? arg : zepto.fragment(arg) }), //如果$长度>1,需要克隆里面的元素 parent, copyByClone = this.length > 1 if (nodes.length < 1) return this //为0,不需要操作,直接返回 //遍历源$,执行插入 _指代此参数无效或不用 return this.each(function(_, target){ parent = inside ? target : target.parentNode //prepend, append取父元素 // convert all methods to a "before" operation //用insertBefore模拟实现 target = operatorIndex == 0 ? target.nextSibling : //after,target等于下一个兄弟元素,然后将DOM通过insertBefore插入到target前 operatorIndex == 1 ? target.firstChild : //prepend target为parent的第一个元素,然后将DOM通过insertBefore插入到target前 operatorIndex == 2 ? target : // before 直接将将DOM通过insertBefore插入到target前 null // append 直接调用$(target).append //父元素是否在document中 var parentInDocument = $.contains(document.documentElement, parent) //遍历待插入的元素 nodes.forEach(function(node){ //克隆 if (copyByClone) node = node.cloneNode(true) //定位元素不存在,,没法执行插入操作,直接删除,返回 else if (!parent) return $(node).remove() //插入节点后,如果被插入的节点是SCRIPT,则执行里面的内容并将window设为上下文 //插入元素 parent.insertBefore(node, target) //如果父元素在document里,修正script标签。原因是script标签通过innerHTML加入DOM不执行。需要在全局环境下执行它 if (parentInDocument) traverseNode(node, function(el){ if (el.nodeName != null && el.nodeName.toUpperCase() === ‘SCRIPT‘ && (!el.type || el.type === ‘text/javascript‘) && !el.src) window[‘eval‘].call(window, el.innerHTML) }) }) }) } // after => insertAfter // prepend => prependTo // before => insertBefore // append => appendTo /** * 插入方法转换 * @param html * @returns {*} */ $.fn[inside ? operator+‘To‘ : ‘insert‘+(operatorIndex ? ‘Before‘ : ‘After‘)] = function(html){ $(html)[operator](this) return
this } })
因为 ’after‘,’prepend‘,’before‘,’append‘ 都可用insertBefore来实现,所以这四个函数的内容格式是一样的,这里就可以用工厂模式来循环生产这四个函数。
这里大致流程如下:
// 可传递多个参数包括字符串和对象
$.fn[operator] = function () {
// arguments.map 针对arguments里面的数组进行处理,将里面的字符串项转化为对象
// this.forEach 循环对每一个调用者target做对应操作
// 因最后要做parent.insertBefore操作,所以这里要根据operator 确认与target有关的parent
// 因用insertBefore来模拟实现,这里要选择对应的参照节点并统一赋值给target
// 执行 parent.insertBefore(node, target);
// 如果node为script,则还必须将里面的脚本内容用window.eval()来执行
}
这里有几个小技巧说一下:
1:inside = operatorIndex % 2 ,parent = inside?target:target.parentNode如果对一个数组中的特定项进行不同的操作,可以对索引取余数,因为在js里面0代表false,正数代表true
2:target.nextSibling 表示取节点的下一个兄弟节点,这里经过测试,如果target在页面上为最后一个节点,则target.nextSibling 依然会返回一个虚拟节点,如下例子
$("#high")[0].nextSibling
结果:
#text
baseURI: "file:///home/zhutao/Documents/lib/zepto/test/defer.html"
childNodes: NodeList[0]
data: "↵"
firstChild: null
lastChild: null
length: 1
nextElementSibling: null
nextSibling: null
nodeName: "#text"
nodeType: 3
nodeValue: "↵"
ownerDocument: document
parentElement: div#first.test
parentNode: div#first.test
previousElementSibling: div#high
previousSibling: div#high
textContent: "↵"
wholeText: "↵"
__proto__: CharacterData
3:node.cloneNode(deep),deep为true,则将子节点也clone进去,否则不会clone子节点,这跟clone对象是一个道理,例子如下:
$("#clone")[0].cloneNode(true);
<div id=?"clone" data-test=?"测试" style=?"height:?50px;?width:? 50px;?border:?1px solid red;?overflow:? hidden">
?<div data-index=?"1111">?clone测试?</div>
?</div>?
$("#clone")[0].cloneNode();
<div id=?"clone" data-test=?"测试" style=?"height:?50px;?width:? 50px;?border:?1px solid red;?overflow:? hidden">?</div>?
4:window.eval() 与 eval()的区别:window.eval() = window.eval.call(window,script); eval() = window.eval.call(this,script); ,eval()常在闭包函数使用 这里的this指的是闭包的环境变量。如下例子 :
var x = 5; function fn(){ var x = ‘jack‘; window.eval(‘x=10;‘); } fn(); console.log(x); // -->5 10 undefined var x = 5; function fn(){ var x = ‘jack‘; eval(‘x=10;‘); } fn(); console.log(x); // -->5 5 undefined
(例子来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/snandy/archive/2011/03/16/1986055.html)
zepto源码研究 - zepto.js - 6(模板方法)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhutao/p/5671746.html