标签:
前面两篇文章学习到了,服务端验证,和客户端的验证,但大家有没有发现,这两种验证各自都有弊端,服务器端的验证,验证的逻辑和代码的逻辑混合在一起了,如果代码量很大的话,以后维护扩展起来,就不是很方便。而客户端的验证,必须要启用客户端验证,也就是在配置文件中配置相应的节点,并且还要引入Jquery插件。如果人为的在浏览器上,禁用了js脚本,那么客户端验证就不起作用了,所以在这里,我将继续学习另外一个验证,也就是Fluent Validation。
Fluent Validation是一个开源的.NET类库,它使用Fluent接口和lambda表达式,来为实体做验证。Fluent Validation是专门为实体做验证使用的。它的优点是:把验证逻辑和你代码的业务逻辑分别开了。这就是AOP的思想。就是横切关注点。你只需要关注某一个模块。这样就保证了代码的纯洁度。
Fluent Validation开源地址:https://github.com/JeremySkinner/fluentvalidation
例句:
Aspect-oriented program is a new software development paradigm that enables modular implementation of cross-cutting concerns,and poses difficulties for slicing of aspect-oriented programs.
面向方面程序设计作为一种新的软件开发范型,能够实现横切关注点的模块化,其特有的语言元素和功能为切片增加了难度。
好了,废话太多,直接进入正题,
首先我们新建一个空白的MVC项目:在Model文件夹下新建一个类Customer:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
namespace Server_Side_Validation_IN_MVC.Models
{
public class Customer
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
}
}
然后新建一个文件夹Validator,在里面添加一个类CustomerValidator
既然是要使用Fluent Validation,那么就是要引用它的类库了。
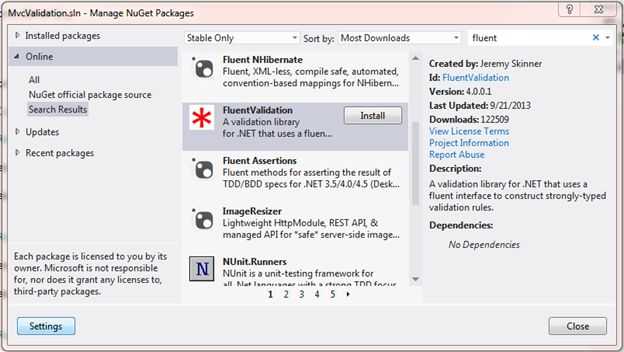
CustomerValidator类中,继承AbstractValidator抽象类,(PS:这里和EF中的Fluent API类似,EF中是继承EntityTypeConfiguration类)
using FluentValidation;
using Server_Side_Validation_IN_MVC.Models;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
namespace Server_Side_Validation_IN_MVC.Validator
{
public class CustomerValidator:AbstractValidator<Customer>
{
public CustomerValidator()
{
RuleFor(s => s.Name).NotEmpty().WithMessage("名字不能为空");
RuleFor(s => s.Email).NotEmpty().WithMessage("电子邮件不能为空");
RuleFor(s => s.Email).EmailAddress().WithMessage("电子邮件格式不合法");
}
}
}
控制器中的代码:
using FluentValidation.Results;
using Server_Side_Validation_IN_MVC.Models;
using Server_Side_Validation_IN_MVC.Validator;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace Server_Side_Validation_IN_MVC.Controllers
{
public class CustomerController : Controller
{
// GET: Customer
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Index(Customer model)
{
CustomerValidator validator = new CustomerValidator();
ValidationResult result = validator.Validate(model);
if (result.IsValid)
{
ViewBag.Name = model.Name;
ViewBag.Email = model.Email;
}
else
{
foreach (var item in result.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(item.PropertyName, item.ErrorMessage);
}
}
return View(model);
}
}
}
修改一下,默认的路由:
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Customer", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
运行项目:
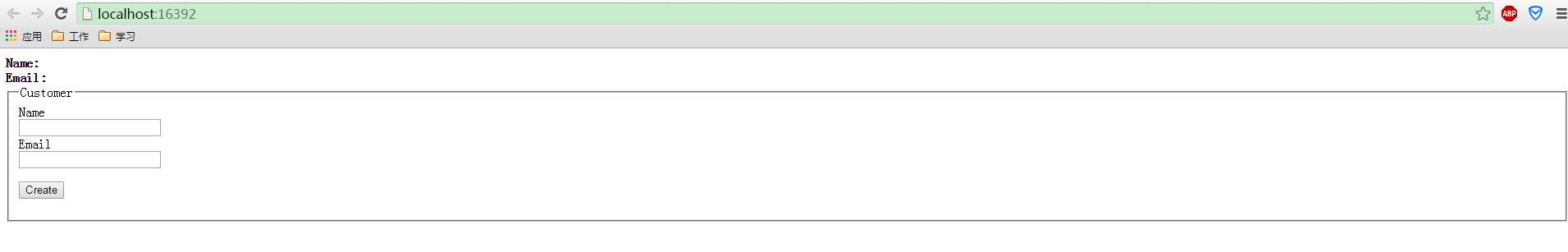
什么都不输入,直接点击Create:
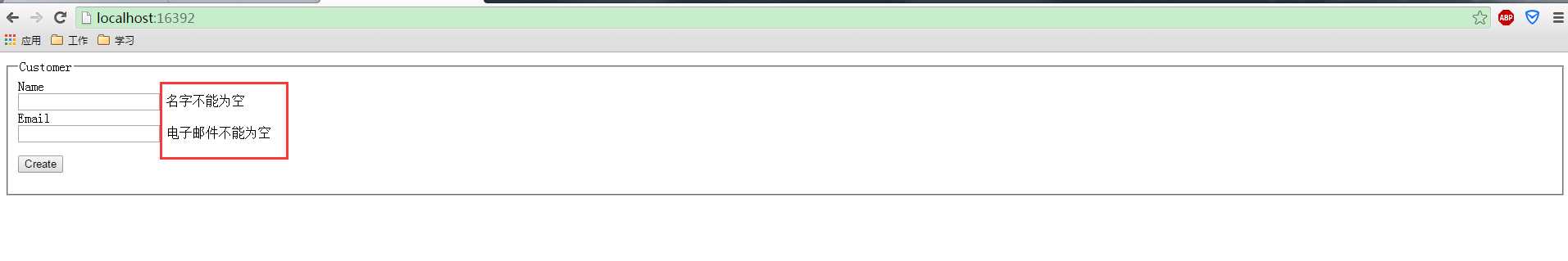
输入Name,不输入Email
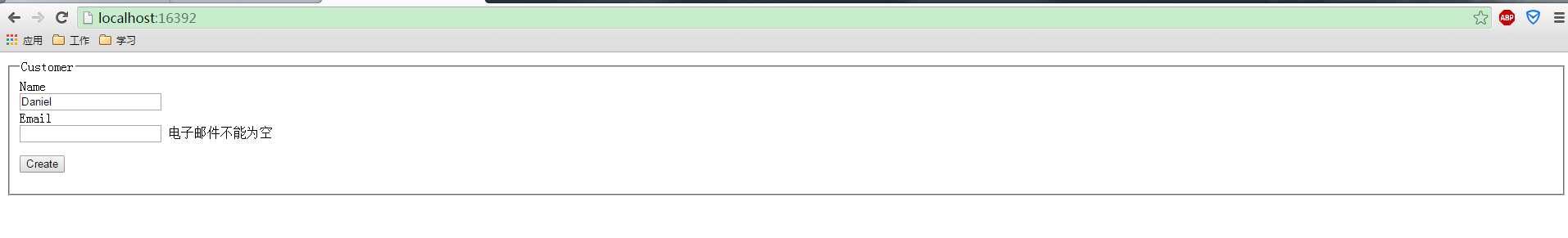
输入Name,Email输入非法的数据
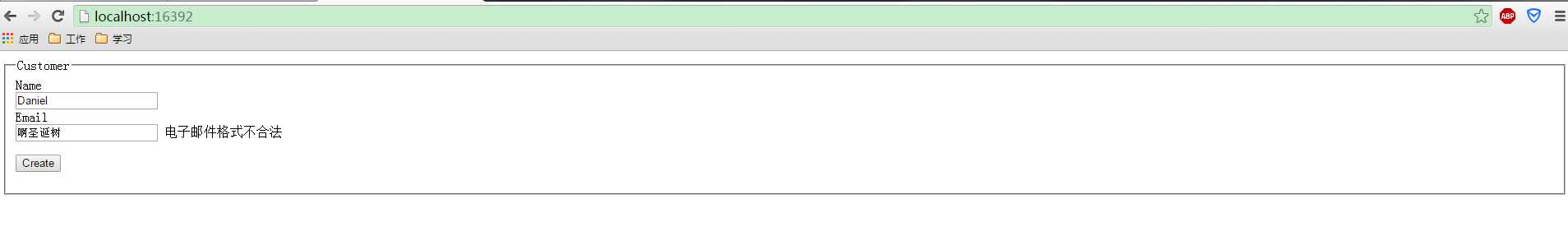
输入合法的数据:
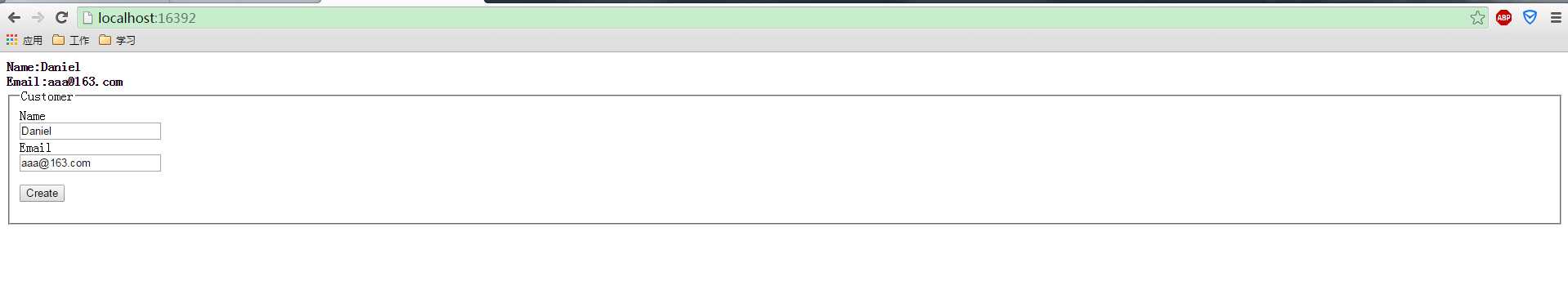
这里就完成了Fluent Validation验证。大家可以看到,这样的验证是不是干净简洁多了,配置信息都在一个类中,方便维护和扩展。不想数据注解那样,把验证信息和实体混合了。。
MVC学习系列12---验证系列之Fluent Validation
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/caofangsheng/p/5690543.html