标签:
摘要
从这一节起,介绍NHibernate Mapping的内容。前面文章都是使用的NHibernate XML Mapping。NHibernate XML Mapping是NHibernate最早最成熟的Mapping方法。其他的Mapping方法都是基于XML Mapping的思想进行的“变种”,要么暂时不能完全像XML Mapping那样功能丰富。其他的Mapping方法目前包括:Fluent Mapping、Attribute Mapping和Mapping by Conventions。他们各自都有优缺点。使用者应该根据实际情况选择适合自己项目的Mapping方式。
这篇文章介绍Fluent Mapping。本篇文章的代码可以到Fluent NHibernate下载。
1、Fluent Mapping的优点
2、Fluent Mapping的缺点
3、程序演示
继续使用以之前文章使用过的NHibernateDemoDB数据库。
1)新建工程Demo.Fluent。
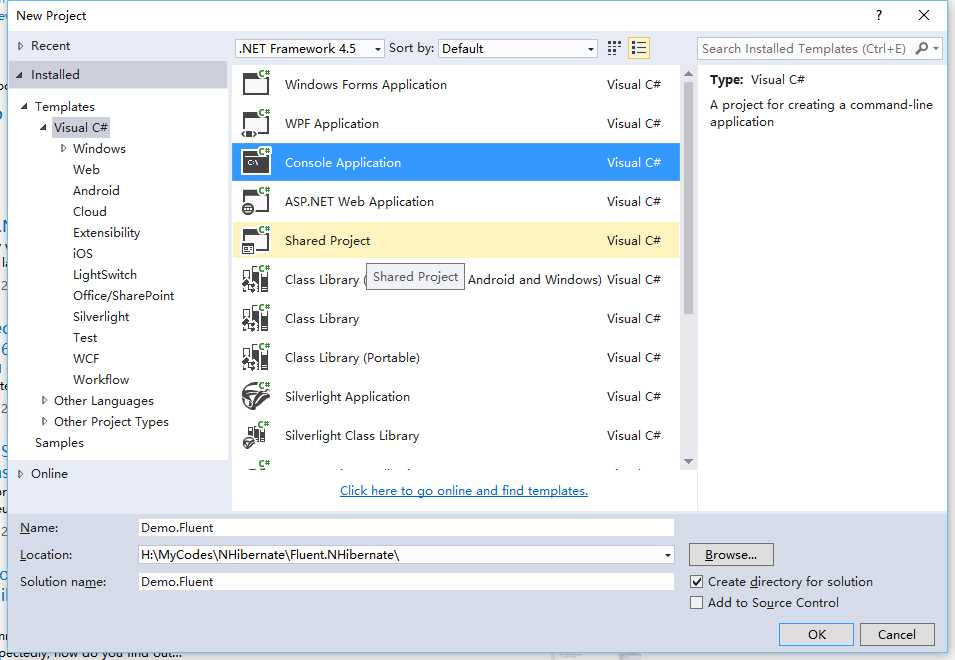
2)新建Class Library,名称为Demo.Fluent.Entities。移除Class1.cs文件。
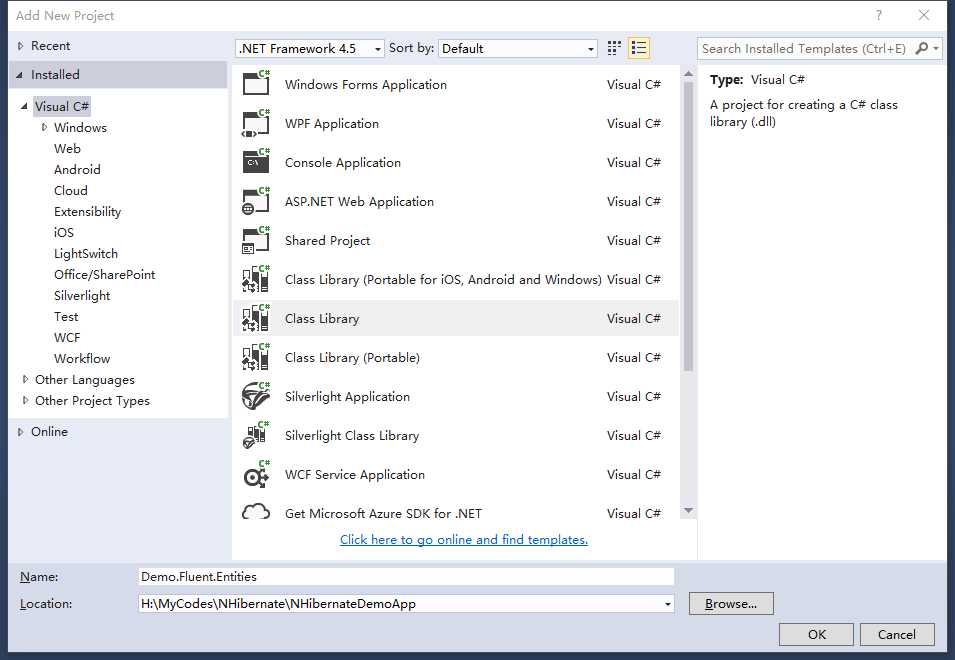
3)在新建的工程中,使用NuGet安装FluentNHibernate。
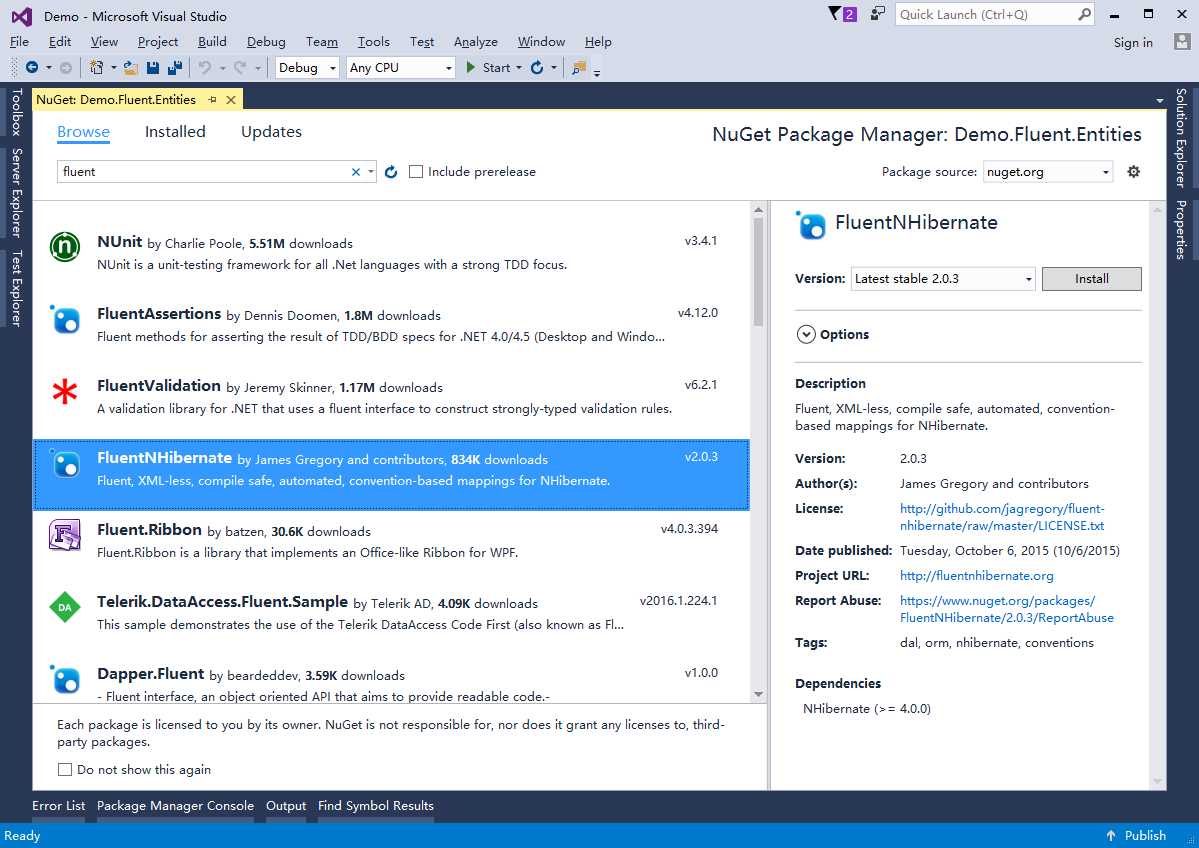
单击“Install”按钮,会出现Priview对话框,列出将要添加的引用。安装FluentNHibernate将会安装他所依赖的NHibernate和Isesi.Collections。
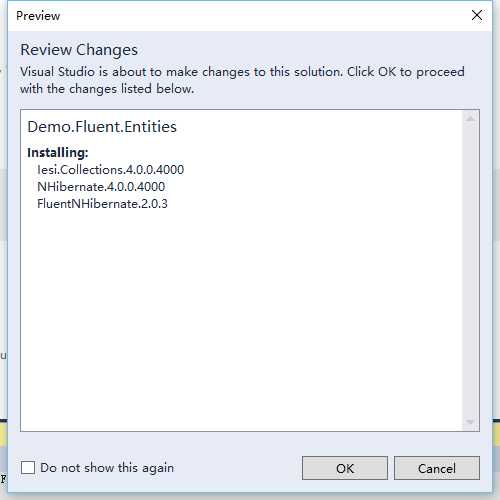
点击“OK”按钮。等上几分钟时间去喝口茶, 安装完成之后Output将显示Finished。
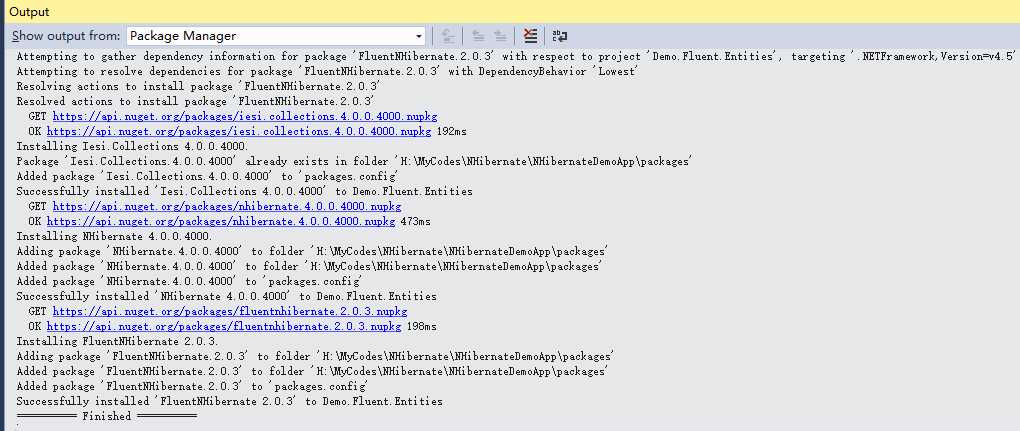
展开工程的Reference,看到已经将FluentNHibernate添加进来了。
4)添加Domain文件夹和Mapping文件夹。
5)在Domain文件夹内,添加实体类的抽象泛型基类Entity。
1 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain 2 { 3 public abstract class Entity<T> where T : Entity<T> 4 { 5 public virtual int Id { get; private set; } 6 7 public override bool Equals(object obj) 8 { 9 var other = obj as T; 10 if (other == null) return false; 11 var thisIsNew = Equals(Id, 0); 12 var otherIsNew = Equals(other.Id, 0); 13 if (thisIsNew && otherIsNew) 14 { 15 return ReferenceEquals(this, other); 16 } 17 return Id.Equals(other.Id); 18 } 19 20 private int? oldHashCode; 21 public override int GetHashCode() 22 { 23 // once we have a hashcode we‘ll never change it 24 if (oldHashCode.HasValue) 25 { 26 return oldHashCode.Value; 27 } 28 // when this instance is new we use the base hash code 29 // and remember it, so an instance can NEVER change its 30 // hash code. 31 var thisIsNew = Equals(Id, 0); 32 if (thisIsNew) 33 { 34 oldHashCode = base.GetHashCode(); 35 return oldHashCode.Value; 36 } 37 return Id.GetHashCode(); 38 } 39 40 public static bool operator ==(Entity<T> lhs, Entity<T> rhs) 41 { 42 return Equals(lhs, rhs); 43 } 44 public static bool operator !=(Entity<T> lhs, Entity<T> rhs) 45 { 46 return !Equals(lhs, rhs); 47 } 48 } 49 }
6)在Domain文件夹下,添加值对象类Address类、Name类,实体类:Customer类、Product类和Order类。
Address类
1 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain 2 { 3 public class Address 4 { 5 public virtual string Street { get; set; } 6 public virtual string City { get; set; } 7 public virtual string Province { get; set; } 8 public virtual string Country { get; set; } 9 10 public bool Equals(Address other) 11 { 12 if (other == null) return false; 13 if (ReferenceEquals(this, other)) return true; 14 return Equals(other.Street, Street) && 15 Equals(other.City, City) && 16 Equals(other.Province, Province) && 17 Equals(other.Country, Country); 18 } 19 20 public override bool Equals(object obj) 21 { 22 return Equals(obj as Address); 23 } 24 25 public override int GetHashCode() 26 { 27 unchecked 28 { 29 var result = Street.GetHashCode(); 30 result = (result * 397) ^ (City != null ? City.GetHashCode() : 0); 31 result = (result * 397) ^ Province.GetHashCode(); 32 result = (result * 397) ^ Country.GetHashCode(); 33 return result; 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 }
Name类
1 using System; 2 3 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain 4 { 5 public class Name 6 { 7 public string LastName { get; private set; } 8 public string FirstName { get; private set; } 9 10 public Name() { } 11 12 public Name(string firstName, string lastName) 13 { 14 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(firstName)) 15 { 16 throw new ArgumentException("First name must be defined."); 17 } 18 if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(lastName)) 19 { 20 throw new ArgumentException("Last name must be defined."); 21 } 22 FirstName = firstName; 23 LastName = lastName; 24 } 25 26 public override int GetHashCode() 27 { 28 unchecked 29 { 30 var result = FirstName.GetHashCode(); 31 result = (result * 397) ^ LastName.GetHashCode(); 32 return result; 33 } 34 } 35 36 public bool Equals(Name other) 37 { 38 if (other == null) return false; 39 if (ReferenceEquals(this, other)) return true; 40 return Equals(other.FirstName, FirstName) && 41 Equals(other.LastName, LastName); 42 } 43 44 public override bool Equals(object other) 45 { 46 return Equals(other as Name); 47 } 48 } 49 }
Address和Name两个类注意两点:
Customer类
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 4 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain 5 { 6 public class Customer : Entity<Customer> 7 { 8 public Customer() 9 { 10 MemberSince = DateTime.UtcNow; 11 } 12 13 public virtual Name Name { get; set; } 14 public virtual double AverageRating { get; set; } 15 public virtual int Points { get; set; } 16 public virtual bool HasGoldStatus { get; set; } 17 public virtual DateTime MemberSince { get; set; } 18 public virtual CustomerCreditRating CreditRating { get; set; } 19 public virtual Address Address { get; set; } 20 21 private readonly IList<Order> orders; 22 23 public virtual IList<Order> Orders 24 { 25 get 26 { 27 return orders; 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 32 public enum CustomerCreditRating 33 { 34 Excellent, VeryVeryGood, VeryGood, Good, Neutral, Poor, Terrible 35 } 36 }
这里有六个需要注意的地方:
Product类
1 using System.Collections.Generic; 2 3 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain 4 { 5 public class Product : Entity<Product> 6 { 7 public virtual string ProductCode { get; set; } 8 9 public virtual string ProductName { get; set; } 10 11 public virtual string Description { get; set; } 12 13 private readonly IList<Order> orders; 14 15 public virtual IList<Order> Orders 16 { 17 get 18 { 19 return orders; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }
Order类
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 4 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain 5 { 6 public class Order : Entity<Order> 7 { 8 public virtual DateTime Ordered { get; set; } 9 public virtual DateTime? Shipped { get; set; } 10 public virtual Address ShipTo { get; set; } 11 public virtual Customer Customer { get; set; } 12 13 private readonly IList<Product> products; 14 15 public virtual IList<Product> Products 16 { 17 get 18 { 19 return products; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }
7)在Mapping文件夹下,定义映射类AddressMap、NameMap、CustomerMap、ProductMap和OrderMap。
类名称必须是值对象类型名称或实体类名称后面跟Map。
在映射类的无参构造函数内,调用Fluent NHibernate的API函数,定义映射。
AddressMap类
1 using Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain; 2 using FluentNHibernate.Mapping; 3 4 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Mapping 5 { 6 public class AddressMap : ComponentMap<Address> 7 { 8 public AddressMap() 9 { 10 Map(x => x.Street).Length(100); 11 Map(x => x.City).Length(100); 12 Map(x => x.Province).Length(100); 13 Map(x => x.Country).Length(100); 14 } 15 } 16 }
NameMap类
1 using Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain; 2 using FluentNHibernate.Mapping; 3 4 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Mapping 5 { 6 public class NameMap : ComponentMap<Name> 7 { 8 public NameMap() 9 { 10 Map(x => x.LastName).Not.Nullable().Length(10); 11 Map(x => x.FirstName).Not.Nullable().Length(10); 12 } 13 } 14 }
CustomerMap类
1 using Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain; 2 using FluentNHibernate.Mapping; 3 4 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Mapping 5 { 6 public class CustomerMap : ClassMap<Customer> 7 { 8 public CustomerMap() 9 { 10 Id(x => x.ID).GeneratedBy.Native(); 11 Component(x => x.Address); 12 Component(x => x.Name); 13 Map(x => x.Points); 14 Map(x => x.HasGoldStatus); 15 Map(x => x.MemberSince); 16 Map(x => x.CreditRating).CustomType<int>(); 17 HasMany(x => x.Orders).Inverse().Cascade.AllDeleteOrphan().Fetch.Join(); 18 } 19 } 20 }
关系映射的API方法:
一对一:HasOne
一对多:HasMany
多对对:HasManyToMany
ProductMap类
using Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain; using FluentNHibernate.Mapping; namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Mapping { public class ProductMap : ClassMap<Product> { public ProductMap() { Id(x => x.ID).GeneratedBy.Native(); Map(x => x.ProductCode).Not.Nullable().Length(10); Map(x => x.ProductName).Not.Nullable().Length(50); Map(x => x.Description).Length(100); HasManyToMany(x => x.Orders).Table("ProductOrder").ParentKeyColumn("ProductId").ChildKeyColumn("OrderId").Cascade.AllDeleteOrphan(); } } }
OrderMap类
1 using FluentNHibernate.Mapping; 2 3 namespace Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain 4 { 5 public class OrderMap : ClassMap<Order> 6 { 7 public OrderMap() 8 { 9 Table("`Order`"); 10 Id(x => x.ID).GeneratedBy.Native(); 11 Map(x => x.Ordered); 12 Map(x => x.Shipped); 13 Component(x => x.ShipTo); 14 References(x => x.Customer).Column("CustomerId").Cascade.SaveUpdate(); 15 HasManyToMany(x => x.Products).Table("ProductOrder").ParentKeyColumn("OrderId").ChildKeyColumn("ProductId").Cascade.All(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
Table方法定义映射的表名称,因为Order是SQL Server关键字,因此调用此方法,传入字符串"`Order`"作为表名称。生成的SQL语句的表名称字符串是"[Order]"。
Many-to-One关系,实体类属性用Reference方法定义,指定外键列名称。
8)添加用于测试的控制台应用程序Demo.Fluent.Console工程。
9)添加用于NHibernate设置的FluentConfig类。
1 using Demo.Fluent.Entities.Mapping; 2 using FluentNHibernate.Cfg; 3 using FluentNHibernate.Cfg.Db; 4 using NHibernate; 5 6 namespace Demo.Fluent.Console 7 { 8 class FluentConfig 9 { 10 const string connString = "server=localhost;" + "database=NHibernateDemoDB;" + "integrated security=SSPI;"; 11 12 public static ISessionFactory CreateSessionFactory() 13 { 14 return Fluently.Configure() 15 .Database(MsSqlConfiguration.MsSql2008.ConnectionString(connString)) 16 .Mappings(m => m.FluentMappings.AddFromAssemblyOf<CustomerMap>()) 17 .BuildSessionFactory(); 18 } 19 } 20 }
9)修改Program类。
1 using Demo.Fluent.Entities.Domain; 2 using NHibernate.Linq; 3 using System.Linq; 4 5 namespace Demo.Fluent.Console 6 { 7 class Program 8 { 9 static void Main(string[] args) 10 { 11 var factory = FluentConfig.CreateSessionFactory(); 12 using (var session = factory.OpenSession()) 13 { 14 var customer = session.Get<Customer>(2); 15 System.Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", customer.Name.LastName, customer.Name.FirstName); 16 17 System.Console.WriteLine("order count: {0}",customer.Orders.Count()); 18 19 System.Console.WriteLine(); 20 System.Console.WriteLine("customers and their order count:"); 21 var queryCount = session.Query<Customer>().Select(c => new 22 { 23 CustomerId = c.Id, 24 CustomerName = c.Name.FirstName + " " + c.Name.LastName, 25 Count = c.Orders.Count() 26 }); 27 var listCount = queryCount.ToList(); 28 if (listCount.Count > 0) 29 { 30 listCount.ForEach(o => 31 { 32 System.Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1}: {2}", o.CustomerId, o.CustomerName, o.Count); 33 }); 34 } 35 36 System.Console.WriteLine(); 37 38 System.Console.WriteLine("customers whose oders count greater than 2:"); 39 var queryCountGreater = session.Query<Customer>().Where(c => c.Orders.Count > 2); 40 var listCountGreater = queryCountGreater.ToList(); 41 if (listCountGreater.Count > 0) 42 { 43 listCountGreater.ForEach(o => 44 { 45 System.Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1} {2}", o.Id, o.Name.FirstName, o.Name.LastName); 46 }); 47 } 48 } 49 System.Console.WriteLine(); 50 System.Console.WriteLine("Finished"); 51 System.Console.ReadLine(); 52 } 53 } 54 }
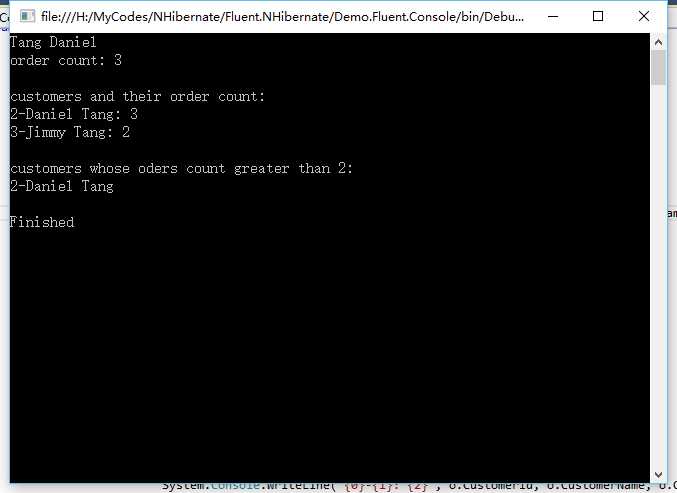
这里写了三个查询用来测试。第一个查询是通过Id查找Customer对象。第二个查询使用Linq to NHibernate对Customer和订单数量分组查询。第三个查询查找订单数大于2的Customer信息。
执行程序,得到结果(与数据库记录有关)。
结语
虽然Fluent NHibernate目前还不是很成熟,比如不支持枚举映射,但是绝大部分Mapping功能都已经可以能满足了。前面提过了他的优缺点,有兴趣的可以到Fluent NHibernate官网上去查看更详细的内容。
NHibernate系列文章二十七:NHibernate Mapping之Fluent Mapping(附程序下载)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/uncle_danny/p/5700765.html