标签:
编写一个程序,定义一个抽象类“Shape”,包含两个方法,计算周长和计算面积。然后定义两个子类,矩形(Rect)和圆形(Circle)。矩形有长和宽属性,圆形有半径属性,但两个类都要实现抽象类中的周长和计算面积方法。
编写测试类测试上述类。
1.定义一个抽象类“Shape”,包含两个方法,计算周长和计算面积。
packagecom.shen.shape; //定义一个抽象类“Shape”,包含两个方法,计算周长和计算面积。 publicabstractclass Shape { publicabstractdoublegetCircumference(); //计算周长 publicabstractdoublegetArea(); //计算面积 }
2.定义子类矩形(Rect)继承自抽象类“Shape”
packagecom.shen.shape; //定义子类矩形(Rect)继承自抽象类“Shape” publicclassRectextends Shape{ privatedoublewidth; //矩形的长 privatedoubleheight; //矩形的宽 //构造函数 publicRect(double width, double height) { super(); this.width = width; this.height = height; } //求矩形的周长 @Override publicdoublegetCircumference() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return (width+height)/2.0; } //求矩形的面积 @Override publicdoublegetArea() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub returnwidth*height; } }
3.定义子类圆形(Circle)继承自抽象类“Shape”
packagecom.shen.shape; //定义子类圆形(Circle)继承自抽象类“Shape” publicclass Circle extends Shape{ privatedoubler; //圆的半径 //构造函数 public Circle(double r) { super(); this.r = r; } //求圆的周长 @Override publicdoublegetCircumference() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 2*Math.PI*r; } //求圆的面积 @Override publicdoublegetArea() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub returnMath.PI*r*r; } }
4.定义一个测试类Main测试上述类。
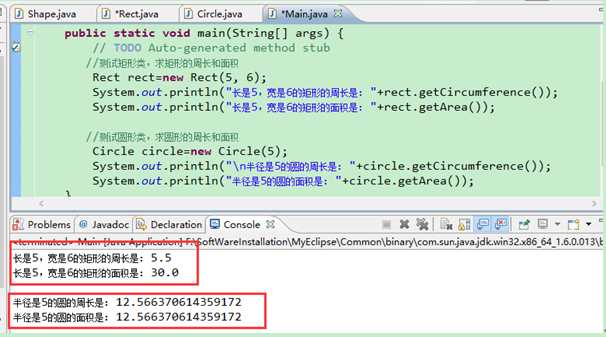
packagecom.shen.shape; //这是一个测试类Main publicclass Main { /** * @paramargs */ publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //测试矩形类,求矩形的周长和面积 Rectrect=newRect(5, 6); System.out.println("长是5,宽是6的矩形的周长是: "+rect.getCircumference()); System.out.println("长是5,宽是6的矩形的面积是: "+rect.getArea()); //测试圆形类,求圆形的周长和面积 Circle circle=new Circle(5); System.out.println("\n半径是5的圆的周长是: "+circle.getCircumference()); System.out.println("半径是5的圆的面积是: "+circle.getArea()); } }
5.结果截图如下所示:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shenxiaolin/p/5723845.html