标签:
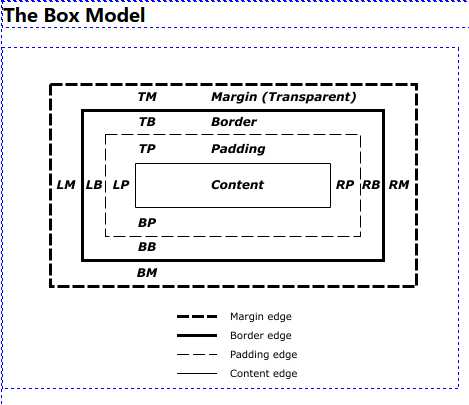
The margin is the space around the element. The larger the margin, the more space between our element and the elements around it. We can adjust the margin to move our HTML elements closer to or farther from each other.
margin: auto; put equal left and right margins on our element, centering it on the page
margin-top: /*some value*/
margin-right: /*some value*/
margin-bottom: /*some value*/
margin-left: /*some-value*/
one time to set: margin: 1px 2px 3px 4px;
The border is the edge of the element. It‘s what we‘ve been making visible every time we set the border property.
The padding is the spacing between the content and the border. We can adjust this value with CSS to move the border closer to or farther from the content.
The content is the actual "stuff" in the box. If we‘re talking about a <p> element, the "stuff" is the text of the paragraph.
float: right
clear: right or left or both;
position: absolute
When an element is set to position: absolute, it‘s then positioned in relation to the first parent element it has that doesn‘t have position: static, If there‘s no such element, the element with position: absolute gets positioned relative to <html>.
Relative positioning is more straightforward: it tells the element to move relative to where it would have landed if it just had the default static positioning.
fixed position anchors an element to browser window, If you scroll up and down, the fixed element stays put even as other elements scroll past.
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/elewei/p/5732475.html