标签:
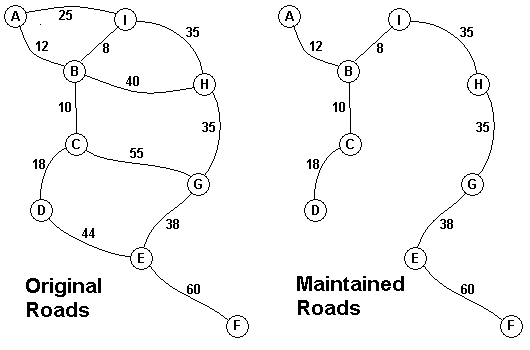
9 A 2 B 12 I 25 B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8 C 2 D 18 G 55 D 1 E 44 E 2 F 60 G 38 F 0 G 1 H 35 H 1 I 35 3 A 2 B 10 C 40 B 1 C 20 0
216 30
原题链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1301
http://poj.org/problem?id=1251
题意:输入n,代表景点数,接下来n-1行,每一行第一的字母代表景点,后面的数字代表与它相连的景点数,后面有n对字母与数字,代表与该景点相连的景点及距离。
#include <cstdio>//prime
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int dis[30];
int a[30][30];
bool vis[30];
int n,m;
int Prime()
{
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
dis[i]=a[0][i];
vis[i]=false;
}
dis[0]=0;
vis[0]=true;
int ans=0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
int p=-1;
int minn=INF;
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
if(!vis[j]&&dis[j]<minn)
minn=dis[p=j];
}
ans+=minn;
vis[p]=true;
for(int j=1; j<n; j++)
{
if(!vis[j]&&dis[j]>a[p][j])
dis[j]=a[p][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>n,n)
{
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
if(i==j) a[i][j]=0;
else a[i][j]=INF;
}
char ch1,ch2;
int x,y;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>ch1>>x;
while(x--)
{
cin>>ch2>>y;
if(a[ch1-'A'][ch2-'A']>y)
a[ch1-'A'][ch2-'A']=a[ch2-'A'][ch1-'A']=y;
}
}
printf("%d\n",Prime());
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
struct node
{
int s,e,w;
}a[500];
int fa[30];
int n,m;
int Find(int x)
{
if(x==fa[x])
return x;
return fa[x]=Find(fa[x]);
}
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{
return a.w<b.w;
}
int Kruskal()
{
sort(a,a+m,cmp);
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int fx=Find(a[i].s);
int fy=Find(a[i].e);
if(fx!=fy)
{
ans+=a[i].w;
fa[fx]=fy;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>n,n)
{
int x,y;
char ch1,ch2;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
fa[i]=i;
m=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>ch1>>x;
while(x--)
{
cin>>ch2>>y;
a[m].s=ch1-'A';
a[m].e=ch2-'A';
a[m++].w=y;
}
}
cout<<Kruskal()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
HDU 1301 &POJ 1215 Jungle Roads【最小生成树,Prime算法+Kruskal算法】
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/hurmishine/article/details/52123185