标签:
一. SET集合
set是一个无序且不重复的元素集

class set(object): """ set() -> new empty set object set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements. """ def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 添加 """ """ Add an element to a set. This has no effect if the element is already present. """ pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements from this set. """ pass def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a shallow copy of a set. """ pass def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.) """ pass def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 删除当前set中的所有包含在 new set 里的元素 """ """ Remove all elements of another set from this set. """ pass def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 移除元素 """ """ Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing. """ pass def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 取交集,新创建一个set """ """ Return the intersection of two or more sets as a new set. (i.e. elements that are common to all of the sets.) """ pass def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 取交集,修改原来set """ """ Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. """ pass def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 如果没有交集,返回true """ """ Return True if two sets have a null intersection. """ pass def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 是否是子集 """ """ Report whether another set contains this set. """ pass def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 是否是父集 """ """ Report whether this set contains another set. """ pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 移除 """ """ Remove and return an arbitrary set element. Raises KeyError if the set is empty. """ pass def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 移除 """ """ Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. """ pass def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 差集,创建新对象""" """ Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.) """ pass def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 差集,改变原来 """ """ Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. """ pass def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 并集 """ """ Return the union of sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in either set.) """ pass def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 更新 """ """ Update a set with the union of itself and others. """ pass def __and__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ pass def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ pass def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x. """ pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__(‘name‘) <==> x.name """ pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __iand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iand__(y) <==> x&=y """ pass def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of set.__init__ """ set() -> new empty set object set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements. # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __ior__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ior__(y) <==> x|=y """ pass def __isub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__isub__(y) <==> x-=y """ pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ pass def __ixor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ixor__(y) <==> x^=y """ pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __or__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """ pass def __rand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """ pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return state information for pickling. """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __ror__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """ pass def __rsub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ pass def __rxor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """ pass def __sub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ pass def __xor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """ pass __hash__ = None set Set
练习:寻找差异,打印出需要更新的、新增的、删除的
# 数据库中原有old_dict = { "#1":{ ‘hostname‘:c1, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 }, "#2":{ ‘hostname‘:c1, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 } "#3":{ ‘hostname‘:c1, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 }}# cmdb 新汇报的数据new_dict = { "#1":{ ‘hostname‘:c1, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 800 }, "#3":{ ‘hostname‘:c1, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 } "#4":{ ‘hostname‘:c2, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 }}
1 # 数据库中原有 2 old_dict = { 3 "#1":{ ‘hostname‘:‘1.1.1.1‘, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 }, 4 "#2":{ ‘hostname‘:‘1.1.1.1‘, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 }, 5 "#3":{ ‘hostname‘:‘1.1.1.1‘, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 } 6 } 7 8 # cmdb 新汇报的数据 9 new_dict = { 10 "#1":{ ‘hostname‘:‘1.1.1.1‘, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 800 }, 11 "#3":{ ‘hostname‘:‘1.1.1.1‘, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 }, 12 "#4":{ ‘hostname‘:‘2.2.2.2‘, ‘cpu_count‘: 2, ‘mem_capicity‘: 80 } 13 } 14 15 old_set = set(old_dict.keys()) 16 update_list = list(old_set.intersection(new_dict.keys())) 17 18 new_list = [] 19 del_list = [] 20 21 for i in new_dict.keys(): 22 if i not in update_list: 23 new_list.append(i) 24 25 for i in old_dict.keys(): 26 if i not in update_list: 27 del_list.append(i) 28 29 print(update_list,new_list,del_list) 30 31 demo
二、深浅拷贝
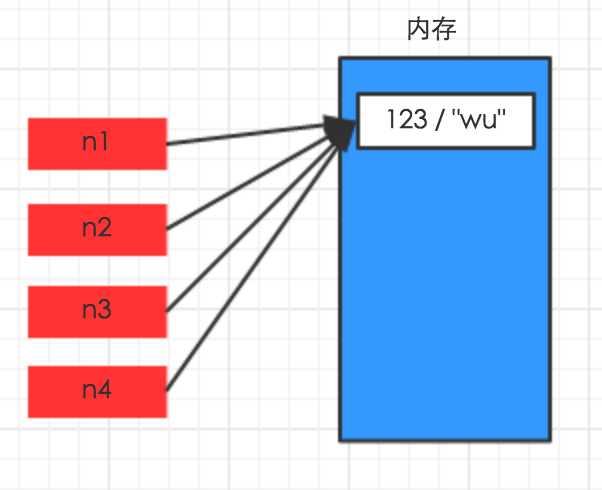
对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import copy# ######### 数字、字符串 #########n1 = 123# n1 = "i am alex age 10"print(id(n1))# ## 赋值 ##n2 = n1print(id(n2))# ## 浅拷贝 ##n2 = copy.copy(n1)print(id(n2))# ## 深拷贝 ##n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1)print(id(n3)) |
对于字典、元祖、列表 而言,进行赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝时,其内存地址的变化是不同的。
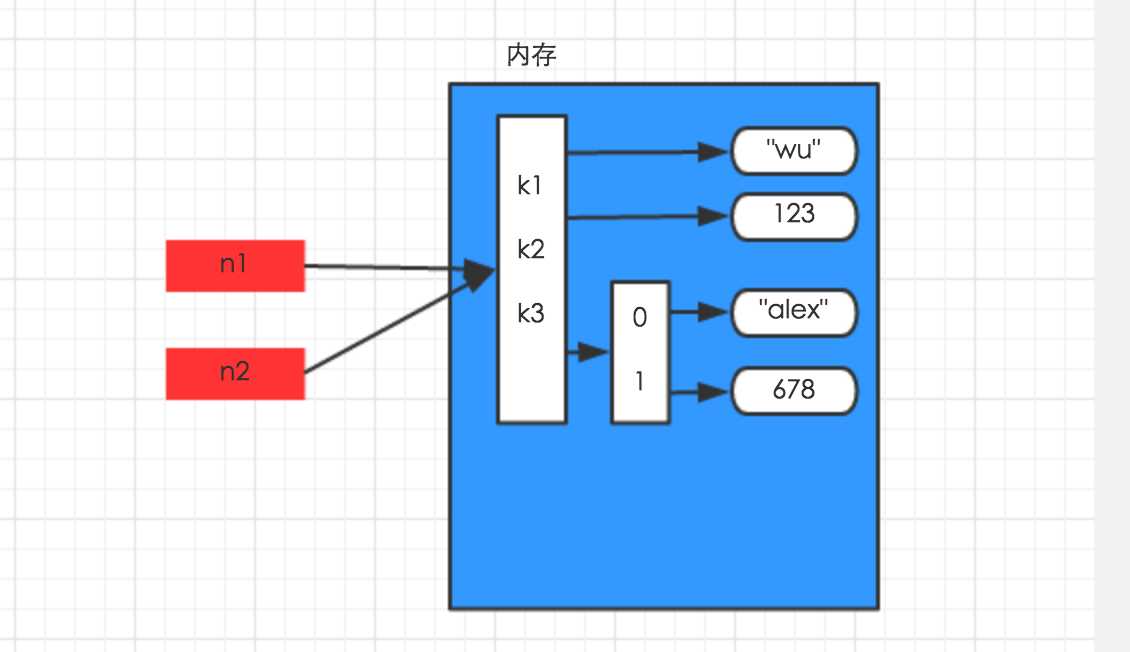
赋值,只是创建一个变量,该变量指向原来内存地址,如:
|
1
2
3
|
n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}n2 = n1 |
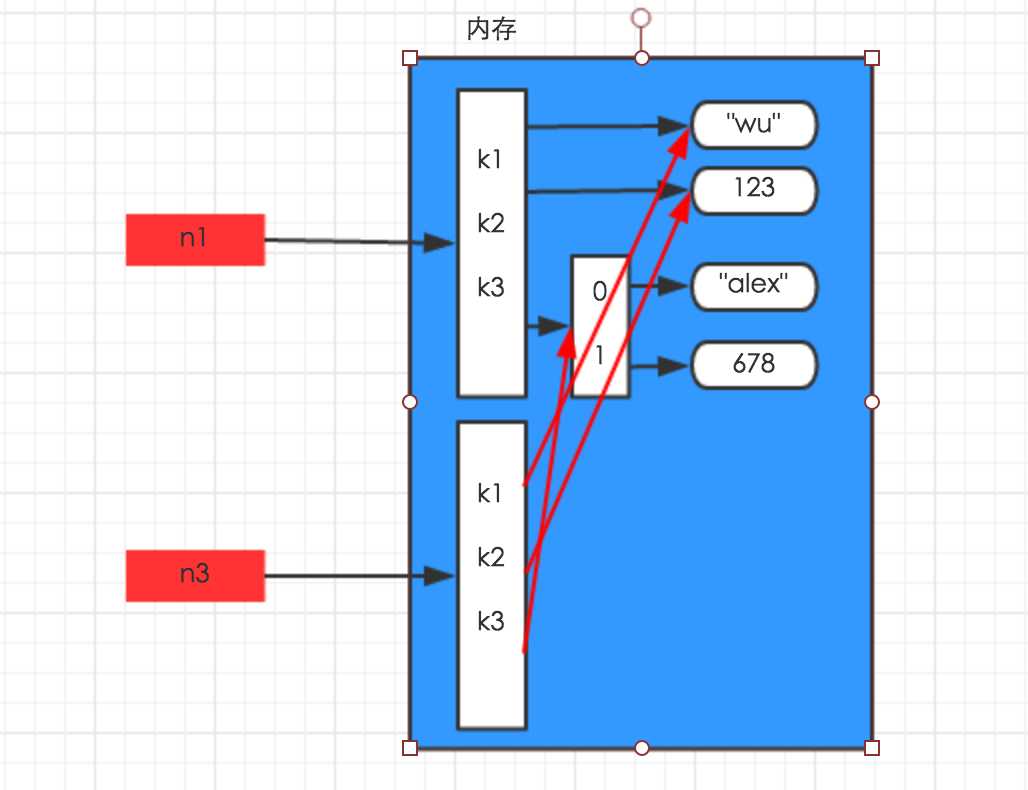
浅拷贝,在内存中只额外创建第一层数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
import copyn1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}n3 = copy.copy(n1) |
三、函数
在学习函数之前,一直遵循:面向过程编程,即:根据业务逻辑从上到下实现功能,其往往用一长段代码来实现指定功能,开发过程中最常见的操作就是粘贴复制,也就是将之前实现的代码块复制到现需功能处,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
while True: if cpu利用率 > 90%: #发送邮件提醒 连接邮箱服务器 发送邮件 关闭连接 if 硬盘使用空间 > 90%: #发送邮件提醒 连接邮箱服务器 发送邮件 关闭连接 if 内存占用 > 80%: #发送邮件提醒 连接邮箱服务器 发送邮件 关闭连接 |
腚眼一看上述代码,if条件语句下的内容可以被提取出来公用,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
def 发送邮件(内容) #发送邮件提醒 连接邮箱服务器 发送邮件 关闭连接 while True: if cpu利用率 > 90%: 发送邮件(‘CPU报警‘) if 硬盘使用空间 > 90%: 发送邮件(‘硬盘报警‘) if 内存占用 > 80%: |
函数的定义主要有如下要点:
以上要点中,比较重要有参数和返回值:
1、返回值
函数是一个功能块,该功能到底执行成功与否,需要通过返回值来告知调用者。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
def 发送短信(): 发送短信的代码... if 发送成功: return True else: return False while True: # 每次执行发送短信函数,都会将返回值自动赋值给result # 之后,可以根据result来写日志,或重发等操作 result = 发送短信() if result == False: 记录日志,短信发送失败... |
四、open函数
该函数用于文件处理,操作文件时,一般需要经历如下步骤:
1、打开文件
|
1
|
文件句柄 = open(‘文件路径‘, ‘模式‘) |
打开文件时,需要指定文件路径和以何等方式打开文件,打开后,即可获取该文件句柄,日后通过此文件句柄对该文件操作。
打开文件的模式有:
"+" 表示可以同时读写某个文件
"U"表示在读取时,可以将 \r \n \r\n自动转换成 \n (与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
"b"表示处理二进制文件(如:FTP发送上传ISO镜像文件,linux可忽略,windows处理二进制文件时需标注)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Sit-on-the-fence/p/5760919.html