标签:
Exception

1.java 异常是java提供的用于处理程序中错误(指在程序运行的过程中发生的一些异常事件)的一种机制
2.java程序的执行过程中如果发生异常事件则自动生产一个异常类对象,该对象封装了异常事件的信息并被提交给java运行时系统,这过程称为throw异常;
当java运行时系统接收到异常对象时会寻找能处理这一异常的代码并交其处理,这过程称为catch异常
1 public class TestEx1 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 TestEx1 test = new TestEx1();
4
5 //捕获异常
6 try {
7 test.m(0);
8 System.out.println("a"); //不会被执行
9 } catch(ArithmeticException e) {
10 e.printStackTrace();
11 //System.out.println(e);
12 }
13
14 //try{}里面包含可能会出错的代码,如果里面出错了,他会交给catch{}处理,不影响你之后的代码运行
16 //但是如果你try{}里面有多行代码第一行,第二行,第三行,如果第二行出错了,第三行是不执行的
17 //如果有finally{},finally里面代码是处理后事的。比如说,你try里面有操作工作流的,那么如果出错了fianlly
18 //可以关闭工作流对象,避免浪费资源。finally{}是必须执行的,不管是出错了,还是不出错。
19 System.out.println("b"); //会被执行
20
21 }
22
23 //声明该方法可能抛出的异常
24 public void m(int j) throws ArithmeticException {
25 //手动往外抛异常
26 if(j == 0) {
27 throw new ArithmeticException("分母不能为0");
28 }
29 }
30 }
3.在一个try语句块中,父类异常的捕获语句不可以写在子类异常捕获语句的上面
4.重写方法需要抛出与原方法相同的异常或者不抛出
5.自定义异常:
-1 通过继承Exception类声明自己的异常类
-2 在方法的声明部分用throws语句声明该方法可能抛出的异常
-3 在方法适当的位置生成自定义异常的实例并用throw语句抛出
1 public class TestEx3 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 TestEx3 t = new TestEx3();
4 t.manager();
5 }
6
7 public void manager() {
8 try {
9 regist(-3);
10 } catch(MyException e) {
11 System.out.println("登记失败,出错类型码:" + e.getId());
12 e.printStackTrace();
13 }
14
15 System.out.println("操作结束");
16 }
17
18 //在方法的声明部分用throws语句声明该方法可能抛出的异常
19 public void regist(int num) throws MyException {
20 //在方法适当的位置生成自定义异常的实例并用throw语句抛出
21 if(num < 0) {
22 throw new MyException("人数为负值,不合理", 3);
23 }
24 System.out.println("登记人数:" + num);
25 }
26 }
27
28 //自定义异常,通过继承java.lang.Exception类声明自己的异常类
29 class MyException extends Exception {
30 private int id;
31
32 public MyException(String message, int id) {
33 super(message);
34 this.id = id;
35 }
36
37 public int getId() {
38 return id;
39 }
40 }
Array

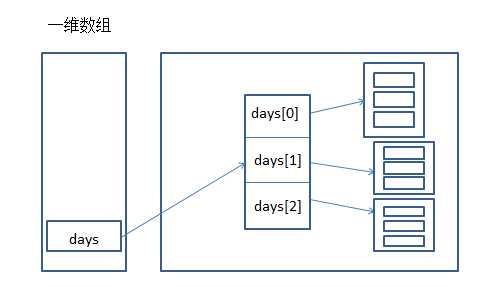
1 public class TestArr2 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Date[] days = new Date[3];
4
5 for(int i=0; i<days.length; i++) {
6 days[i] = new Date(2016, 7, i+1);
7 }
8
9 for(int i=0; i<days.length; i++) {
10 days[i].info();
11 }
12 }
13 }
14
15 class Date {
16 int day;
17 int month;
18 int year;
19
20 public Date(int year, int month, int day) {
21 this.year = year;
22 this.month = month;
23 this.day = day;
24 }
25
26 public void info() {
27 System.out.println("year:" + year + " month:" + month + " day:" + day);
28 }
29 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangdesheng1123/p/5763574.html