标签:
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();//先获取map集合的所有键的Set集合entrySet()方式:
Iterator<String> it = keySet.iterator();//有了Set集合,就可以获取其迭代器
while (it.hasNext()) {
String key = it.next();
String value = map.get(key);//有了键可以通过map集合的get方法获取其对应的值。
}
//通过entrySet()方法将map集合中的映射关系取出(这个关系就是Map.Entry类型)
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
//将关系集合entrySet进行迭代,存放到迭代器中
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it2 = entrySet.iterator();
while (it2.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> me = it2.next();//获取Map.Entry关系对象me
String key2 = me.getKey();//通过关系对象获取key
String value2 = me.getValue();//通过关系对象获取value
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> keySetMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
HashMap<String, String> entrySetMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
keySetMap.put("" + i, "keySet");
entrySetMap.put("" + i, "entrySet");
}
long startTimeOne = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<String> keySetIterator = keySetMap.keySet().iterator();
while (keySetIterator.hasNext()) {
String key = keySetIterator.next();
String value = keySetMap.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "," + value);
}
System.out.println("keyset spent times:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimeOne));
long startTimeTwo = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> entryKeyIterator = entrySetMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (entryKeyIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> e = entryKeyIterator.next();
System.out.println(e.getKey() + "," + e.getValue());
}
System.out.println("entrySet spent times:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimeTwo));
}
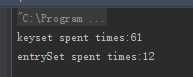
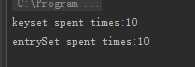
Java之Map遍历方式性能分析:ketSet与entrySet
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/linux007/p/5777975.html