标签:linux
sed 是一种在线编辑器,它一次处理一行内容。处理时,把当前处理的行存储在临时缓冲
区中,称为 “模式空间” (pattern space),接着用 sed命令处理缓冲区中的内容,处理完成后,
把缓冲区的内容送往屏幕。接着处理下一行,这样不断重复,直到文件末尾。文件内容并
没有 改变,除非你使用重定向存储输出。 Sed主要用来自动编辑一个或多个文件;简化对文
件的反复操作;
基本使用:
1. /pattern/p :打印匹配pattern的行
使用 p命令需要注意 ,sed 是把待处理文件的内容连同处理结果一起输出到标准输出的 ,因此
p命令 表示除了把文件内容打印出来之外还额外打印一遍匹配 pattern的行。比如一个文
件log的内 容是
要想只输出处理结果 ,应加上 -n选项 ,这种用法相当于 grep命令
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/ /p‘ file 11111111111111111111 2222222222222222222 3333333333333333333 44444444444444444 5555555555555555555 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/*/p‘ file 11111111111111111111 2222222222222222222 3333333333333333333 44444444444444444 5555555555555555555 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/1/p‘ file 11111111111111111111 11111111111111111111 2222222222222222222 3333333333333333333 44444444444444444 5555555555555555555 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/.*/p‘ file 11111111111111111111 11111111111111111111 2222222222222222222 2222222222222222222 3333333333333333333 3333333333333333333 44444444444444444 44444444444444444 5555555555555555555 5555555555555555555 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/.*/p‘ file 11111111111111111111 2222222222222222222 3333333333333333333 44444444444444444 5555555555555555555
2. /pattern/d :删除匹配pattern的行
注意,sed命令不会修改原文件,删除命令只表示某些行不打印输出 ,而不是从原文件中删去。
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/11*/d‘ file 2222222222222222222 3333333333333333333 44444444444444444 5555555555555555555
3. /pattern/s/pattern1/pattern2/ :查找符合pattern的行 ,将该行第一个匹配
pattern1的字符串替换为pattern2
4. /pattern/s/pattern1/pattern2/g :查找符合pattern的行 ,将该行所有匹配
pattern1的字符串替换为pattern2
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat file aabbccdd aabbaabb aabbaabb [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/aa*/s/aa/ff/‘ file ffbbccdd ffbbaabb ffbbaabb [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/aa*/s/aa/ff/g‘ file ffbbccdd ffbbffbb ffbbffbb [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/a/s/a/-f-/g‘ file -f--f-bbccdd -f--f-bb-f--f-bb -f--f-bb-f--f-bb [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/^[a-z]\+/s/\([a-c]\+\)/\1--/‘ file aabbcc--dd aabbaabb-- aabbaabb--
pattern2中的& 表示原文件的当前行中与pattern1相匹配的字符串
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘/^[a-z]\+/s/\([a-c]\+\)/\-&-/‘ file -aabbcc-dd -aabbaabb- -aabbaabb-
pattern2中的\1 表示与pattern1的第一个 ()括号相匹配的内容 ,\2表示与 pattern1的
第二个()括号 相匹配的内容。
sed默认使用Basic正则表达式规范,如果指定了-r选项则使用Extended规范 ,那 么 ()括号就不必转义了
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f1 <html><head><title>Hello World</title> <body>Welcome to the world of regexp!</body></html>
sed/grep 匹配 是贪心的 总是匹配最长的 所以下面方法是错误的
下面才是去除<。。。>的正确方法 用[]做限定 防止<>中间再有< 或> 把整句都匹配了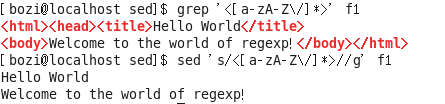
5. sed -i : 做的操作会修改原文件
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f2 11111111111 22222222222 33333333333 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘$d‘ f2 11111111111 22222222222 [bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f2 11111111111 22222222222 33333333333 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -i ‘$d‘ f2 [bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f2 11111111111 22222222222
6. 定址
定址用于决定对哪些行进行编辑。地址的形式可以是数字、正则表达式、或二者的结合。
如果没有指定地址, sed将处理输入文件的所有行。
sed -n ‘3p’ file #打印第三行
sed -n ‘100,300p’ file # 打印100~ 300行的信息(包括 100和 300)
地址是逗号分隔的,那么需要处理的地址是这两行之间的范围(包括这两行在内)。范
围可以用数字、正则表达式、或二者的组合表示。
sed ‘2,5d’ file #删除第二行到第五行
sed ‘/start/ ,/end/d’ file # 删除包含’start’行和 ’end’行之间的行
sed ‘/start/, 10d’ file # 删除包含’start’ 的行到第十行的内容
等等,例子如下:
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f2 11111111111 start 22222222222 33333333333 44444444444444 555555555 end 66666666 7777777 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/start/,8p‘ f2 start 22222222222 33333333333 44444444444444 555555555 end 66666666 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/start/,/end/p‘ f2 start 22222222222 33333333333 44444444444444 555555555 end [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘4p‘ f2 33333333333 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘2,4p‘ f2 start 22222222222 33333333333 [bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 6 | sed -n ‘2,4p‘ 2 3 4
’0~3p‘表示 从0开始 每次行号加3的行 ~表示每次行号加几
[bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 6 | sed -n ‘0~3p‘ 3 6 [bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 6 | sed -n ‘0~2p‘ 2 4 6 [bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 6 | sed -n ‘0~1p‘ 1 2 3 4 5 6
7. 命令和选项
sed命令告诉sed 如何处理由地址指定的各输入行,如果没有指定地址则处理所有的输入
行。
命令
a\ :在当前行后添加一行或多行。多行时除最后一行外,每行末尾需用 “\”续行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘2a nihao \hello‘ f3 11111111111 22222222222 nihao hello 33333333333 44444444444
c\ :用此符号后的新文本替换当前行中的文本。多行时除最后一行外,每行末尾需用 ”\"
续行
i\ :在当前行之前插入文本。多行时除最后一行外,每行末尾需用 ”\"续行 d删除行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘2i nihao \hello‘ f3 11111111111 nihao hello 22222222222 33333333333 44444444444
h : 把模式空间里的内容复制到暂存缓冲区
H :把模式空间里的内容追加到暂存缓冲区
g :把暂存缓冲区里的内容复制到模式空间,覆盖原有的内容
G:把暂存缓冲区的内容追加到模式空间里,追加在原有内容的后面
l :列出非打印字符
p :打印行
n :读入下一输入行,并从下一条命令而不是第一条命令开始对其的处理
q :结束或退出sed
r :从文件中读取输入行
! : 对所选行以外的所有行应用命令
s :用一个字符串替换另一个
g :在行内进行全局替换
w :将所选的行写入文件
x :交换暂存缓冲区与模式空间的内容
y :将字符替换为另一字符(不能对正则表达式使用 y命令)
选项
-e :进行多项编辑,即对输入行应用多条 sed命令时使用
[bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 6 | sed -e ‘1d‘ -e ‘5d‘ 2 3 4 6
-n :取消默认的输出
-f :指定sed 脚本的文件名
8. 退出状态
sed不向grep 一样,不管是否找到指定的模式,它的退出状态都是 0。只有当命令存在语法
错误时, sed的退出状态才不是 0。
正则表达式 练习
sed使用的正则表达式是括在斜杠线 "/"之间的模式。如果要把正则表达式分隔符 "/"改为另一个字符,比如 o,只要在这个字符前加一个反斜线,
在字符后跟上正则表达式,再跟上这个字符即可。例如: sed -n ‘\o^Myop‘ datafile
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘\u^myup‘ log my1111111
^:行首定位符:/^my/ 匹配所有以 my开头的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat log 111111111 my1111111 11my 111111111my 3333333333 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/^my/p‘ log my1111111
$:行尾定位符:/my$/ 匹配所有以 my结尾的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/my$/p‘ log 11my 111111111my
.:匹配除换行符以外的单个字符: /m..y/ 匹配包含字母 m,后跟两个任意字符,再跟字母y的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/1..y/p‘ log 11my 111111111my
*:匹配零个或多个前导字符: /test*/ 匹配包含 string tes,后跟零个或多个 t字母的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/test*/p‘ f4 test testy tesa tests testttt [bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4 test testy tesa tests testttt tea tebs
[]:匹配指定字符组内的任一字符 : /t[eE]st/ 匹配包含 test或 tEst的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4 test tebs tEsta tEstsad tast tfst [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/t[eE]st/p‘ f4 test tEsta tEstsad
[^]:匹配不在指定字符组内的任一字符: /t[^eE]st/ 匹配 string 以 t开头,但 st之前的
那个字符不是 e或 E的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4 test tebs tEsta tEstsad tast tfst [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/t[^eE]st/p‘ f4 tast tfst
\(..\):保存已匹配的字符: 标记元字符之间的模式,并将其保存为标签 1,之后可以使用
\1来引用它。最多可以定义 9个标签,从左边开始编号,最左边的是第一个。此例中,对第
1到第3 行进行处理, tes被保存为标签 1,如果发现 tes或tEs,则替换为 tes-或tEs。
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4 test tebs tEsta tEstsad tast tfst [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘1,3s/\(t[Ee]s\)/\1-/g‘ f4 tes-t tebs tEs-ta tEstsad tast tfst
&:保存查找串以便在替换串中引用: s/test/*&*/g 符号& 代表查找串。test将被替换为
*test*
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4 test tebs tEsta tEstsad tast tfst [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘s/t[eE]st/*&*/g‘ f4 *test* tebs *tEst*a *tEst*sad tast tfst
\<:词首定位符:/\<my/ 匹配包含以 my开头的单词的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4 test tebs tEsta tEstsad tast tfst [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/\<te/p‘ f4 test tebs
\>:词尾定位符:/my\>/ 匹配包含以 my结尾的单词的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4 test tebs tEsta tEstsad tast tfst [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/st\>/p‘ f4 test tast tfst
x\{m\}:连续m 个x :/m\{5\}/ 匹配包含连续5个 m的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4
test
tebs
tEsta
tEstsad
tast
tfst
OOOOmmmmmmmmmUUUU
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/\m\{5\}/p‘ f4
OOOOmmmmmmmmmUUUUx\{m,\}:至少m 个x :/m\{5,\}/ 匹配包含至少连续 5个 m的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4
test
tebs
tEsta
tEstsad
tast
mmmmm
mmmmmm
OOOOmmmmmmmmmUUUU
mmmm
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/m\{5,\}/p‘ f4
mmmmm
mmmmmm
OOOOmmmmmmmmmUUUUx\{m,n\}:至少m 个,但不超过n个 x: /m\{5,7\}/ 匹配包含连续 5到 7个 m的行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f4
test
tebs
tEsta
tEstsad
tast
mmmmm
mmmmmm
OOOOmmmmmmmmmUUUU
mmmm
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘/m\{5,7\}/p‘ f4
mmmmm
mmmmmm
OOOOmmmmmmmmmUUUU 【注意 这个还是会匹配到的】模式空间保持空间(高级用法,难度较高)
sed在正常情况下,将处理的行读入模式空间( pattern space),脚本中的“sedcommand (sed命令)” 就一条接着一条进行处理,直到脚本执行完毕。然后该行呗输出,模式( pattern space)被清空;接着,在重复执行刚才的动作,文件中的
新的一行被读入,直到文件处理完毕。
一般情况下,数据的处理只使用模式空间( pattern space),按照如上的逻辑即可
完成主要任务。但是某些时候,使用通过使用保持空间( hold space),还可以带
来意想不到的效果。
模式空间:可以想成工程里面的流水线,数据之间在它上面进行处理。
保持空间:可以想象成仓库,我们在进行数据处理的时候,作为数据的暂存区域。
正常情况下,如果不显示使用某些高级命令,保持空间不会使用到!
小写命令 表示 清除
大写的命令 表示 追加
+ g :[address[,address]]g 将hold space 中的内容拷贝到 pattern space中,
原来pattern space里的内容清除
+ G :[address[,address]]G 将hold space 中的内容append到 pattern
space\n后
+ h :[address[,address]]h 将pattern space 中的内容拷贝到 hold space中,
原来的hold space里的内容被清除
+ H :[address[,address]]H 将pattern space 中的内容append到 hold
space\n后
+ d :[address[,address]]d 删除pattern中的所有行,并读入下一新行到
pattern中
+ D: [address[,address]]D 删除multiline pattern 中的第一行,不读入下一行
+ x:交换保持空间和模式空间的内容
例子:
1. 给每行结尾添加一行空行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f5 0 hello 1 hello 2 hello 3 hello 4 hello 5 hello 6 hello 7 hello [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘G‘ f5 【模式空间 为空 按行处理 追加到模式空间 就相当于追加空行 】 0 hello 1 hello 2 hello 3 hello 4 hello 5 hello 6 hello 7 hello [bozi@localhost sed]$
2. 用sed 模拟出tac的功能(倒序输出)
[bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 10 > f6 [bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
先理解这个
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘G;h;‘ f6 【先将保持空间的 追加到模式空间 (第一次是空 所以1后面是空 ) 然后是将模式空间的(1 空 )拷贝到保持空间 输出 下一次从保持空间 到 模式空间追加的就是 (1 空 ) 所以第二次为 2 1 空 以此类推】
1 2 1 3 2 1 4 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 6 5 4 3 2 1 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
再理解这个
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘G;h;2,3!d‘ f6 【2,3!d】表示按行删除时第二次和第三次处理时候 不删除模式空间的所有行 2 1 3 2 1
最后理解这个
1!G第1 行不执行“G”命令,从第 2行开始执行。 $!d,最后一行不删除(保留最后 1行)
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed ‘1!G;h;$!d‘ f6 【1!G】表示再追加的时候 第一次按行处理是不追加保持空间的空行到模式空间 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
3. 追加匹配行到文件结尾
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f5 0 hello 1 hello 2 hello 3 hello 4 hello 5 hello 6 hello 7 hello [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -e ‘/[234].*/H‘ -e ‘$G‘ f5 0 hello 1 hello 2 hello 3 hello 4 hello 5 hello 6 hello 7 hello 2 hello 3 hello 4 hello
4. 行列转化
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘H;${x;s/\n/-/g;p}‘ f6
-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10 【说明 每行显示 是最前面有一个\n被替换】
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘H;${x;s/\n//g;p}‘ f6
12345678910
[bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘H;${x;s/\n/ /g;p}‘ f6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10H表示把pattern space 的内容追加到hold space中去, H可以带一个地址,这里
用的是$,表示到文件的末尾,然后用 x将之取到 pattern space中,把 \n替换成空格再打印即可。
5.同上,求1 100的求和
[bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 100 | sed -n ‘H;${x;s/\n/+/g;s/^+//;p}‘
1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10+11+12+13+14+15+16+17+18+19+20+21+22+23+24+25+26+27+28+29+30+31+32+33+34+35+36+37+38+39+40+41+42+43+44+45+46+47+48+49+50+51+52+53+54+55+56+57+58+59+60+61+62+63+64+65+66+67+68+69+70+71+72+73+74+75+76+77+78+79+80+81+82+83+84+85+86+87+88+89+90+91+92+93+94+95+96+97+98+99+100
[bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 100 | sed -n ‘H;${x;s/\n/+/g;s/^+//;p}‘|bc
50506. 打印奇偶数行
[bozi@localhost sed]$ cat f6 1 2 3 4 5 6 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘n;p‘ f6 【‘n;p‘ n是清除当前行 读取下一行】 2 4 6 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘p;n‘ f6 1 3 5 [bozi@localhost sed]$ sed -n ‘n;n;p‘ f6 3 6
7.再求1 ~100求和
先看这个
[bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 10 | sed ‘:a;N;s/\n/+/;‘ 【N 表示多读取一行】 1+2 3+4 5+6 7+8 9+10
再看这个
[bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 10 | sed ‘:a;N;s/\n/+/;ba‘ 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10 [bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 10 | sed ‘:c;N;s/\n/+/;bc‘ 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10 [bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 100 | sed ‘:c;N;s/\n/+/;bc‘|bc 5050 [bozi@localhost sed]$ seq 100 | sed ‘:f;N;s/\n/+/;bf‘|bc 5050
:a表示标签a ,ba 表示跳转到a标签, $表示最后一行,!表示不做后续操作,所
以,$!ba表示最后一行不用跳转到 a标签,结束此次操作。
相关博客:
讨论:互换模式空间和保持空间的内容
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-10540984-id-316081.html
http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com/2561410/767862/
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-9950859-id-98222.html
http://czmmiao.iteye.com/blog/1899880
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_46ecf5890100jtip.html (vi和 sed结合)
本文出自 “城市猎人” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://alick.blog.51cto.com/10786574/1841255
标签:linux
原文地址:http://alick.blog.51cto.com/10786574/1841255