标签:
Tornado 是 FriendFeed 使用的可扩展的非阻塞式 web 服务器及其相关工具的开源版本。这个 Web 框架看起来有些像web.py 或者 Google 的 webapp,不过为了能有效利用非阻塞式服务器环境,这个 Web 框架还包含了一些相关的有用工具 和优化。
Tornado 和现在的主流 Web 服务器框架(包括大多数 Python 的框架)有着明显的区别:它是非阻塞式服务器,而且速度相当快。得利于其 非阻塞的方式和对 epoll 的运用,Tornado 每秒可以处理数以千计的连接,这意味着对于实时 Web 服务来说,Tornado 是一个理想的 Web 框架。我们开发这个 Web 服务器的主要目的就是为了处理 FriendFeed 的实时功能 ——在 FriendFeed 的应用里每一个活动用户都会保持着一个服务器连接。(关于如何扩容 服务器,以处理数以千计的客户端的连接的问题,请参阅 C10K problem。)
下载安装:
pip3 install tornado 源码安装 https://pypi.python.org/packages/source/t/tornado/tornado-4.3.tar.gz mac: brew install tornado
一、快速上手
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("Hello, world")
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
执行过程:
异步非阻塞示例:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
from tornado import httpclient
from tornado.web import asynchronous
from tornado import gen
import uimodules as md
import uimethods as mt
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
@asynchronous
@gen.coroutine
def get(self):
print ‘start get ‘
http = httpclient.AsyncHTTPClient()
http.fetch("http://127.0.0.1:8008/post/", self.callback)
self.write(‘end‘)
def callback(self, response):
print response.body
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘ui_methods‘: mt,
‘ui_modules‘: md,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8009)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
二、路由系统
路由系统其实就是 url 和 类 的对应关系,这里不同于其他框架,其他很多框架均是 url 对应 函数,Tornado中每个url对应的是一个类。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("Hello, world")
class StoryHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self, story_id):
self.write("You requested the story " + story_id)
class BuyHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("buy.wupeiqi.com/index")
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/story/([0-9]+)", StoryHandler),
])
application.add_handlers(‘buy.wupeiqi.com$‘, [
(r‘/index‘,BuyHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(80)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
Tornado中原生支持二级域名的路由,如:
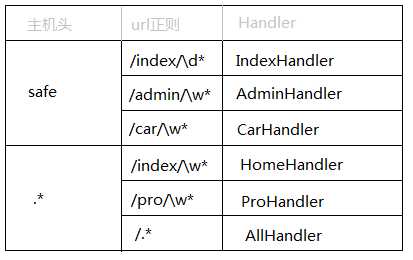
三、模板引擎
Tornao中的模板语言和django中类似,模板引擎将模板文件载入内存,然后将数据嵌入其中,最终获取到一个完整的字符串,再将字符串返回给请求者。
Tornado 的模板支持“控制语句”和“表达语句”,控制语句是使用 {% 和 %} 包起来的 例如 {% if len(items) > 2 %}。表达语句是使用 {{ 和 }} 包起来的,例如 {{ items[0] }}。
控制语句和对应的 Python 语句的格式基本完全相同。我们支持 if、for、while 和 try,这些语句逻辑结束的位置需要用 {% end %} 做标记。还通过 extends 和 block 语句实现了模板继承。这些在 template 模块 的代码文档中有着详细的描述。
注:在使用模板前需要在setting中设置模板路径:"template_path" : "tpl"
1、基本使用
app.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# app.py
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render("index.html", list_info = [11,22,33])
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>老男孩</title>
<link href="{{static_url("css/common.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
{% for item in list_info %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
</ul>
</div>
<script src="{{static_url("js/jquery-1.8.2.min.js")}}"></script>
</body>
</html>
其他方法:
在模板中默认提供了一些函数、字段、类以供模板使用: escape: tornado.escape.xhtml_escape 的別名 xhtml_escape: tornado.escape.xhtml_escape 的別名 url_escape: tornado.escape.url_escape 的別名 json_encode: tornado.escape.json_encode 的別名 squeeze: tornado.escape.squeeze 的別名 linkify: tornado.escape.linkify 的別名 datetime: Python 的 datetime 模组 handler: 当前的 RequestHandler 对象 request: handler.request 的別名 current_user: handler.current_user 的別名 locale: handler.locale 的別名 _: handler.locale.translate 的別名 static_url: for handler.static_url 的別名 xsrf_form_html: handler.xsrf_form_html 的別名 其他方法
2、母版

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/> 5 <title>老男孩</title> 6 <link href="{{static_url("css/common.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" /> 7 {% block CSS %}{% end %} 8 </head> 9 <body> 10 11 <div class="pg-header"> 12 13 </div> 14 15 {% block RenderBody %}{% end %} 16 17 <script src="{{static_url("js/jquery-1.8.2.min.js")}}"></script> 18 19 {% block JavaScript %}{% end %} 20 </body> 21 </html> 22 23 layout.html

1 {% extends ‘layout.html‘%} 2 {% block CSS %} 3 <link href="{{static_url("css/index.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" /> 4 {% end %} 5 6 {% block RenderBody %} 7 <h1>Index</h1> 8 9 <ul> 10 {% for item in li %} 11 <li>{{item}}</li> 12 {% end %} 13 </ul> 14 15 {% end %} 16 17 {% block JavaScript %} 18 19 {% end %} 20 21 index.html
3、导入

1 <div> 2 <ul> 3 <li>1024</li> 4 <li>42区</li> 5 </ul> 6 </div> 7 8 header.html

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/> 5 <title>老男孩</title> 6 <link href="{{static_url("css/common.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" /> 7 </head> 8 <body> 9 10 <div class="pg-header"> 11 {% include ‘header.html‘ %} 12 </div> 13 14 <script src="{{static_url("js/jquery-1.8.2.min.js")}}"></script> 15 16 </body> 17 </html>
4、自定义UIMethod以UIModule
a. 定义
# uimethods.py
def tab(self):
return ‘UIMethod‘
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# uimodules.py
from tornado.web import UIModule
from tornado import escape
class custom(UIModule):
def render(self, *args, **kwargs):
return escape.xhtml_escape(‘<h1>wupeiqi</h1>‘)
#return escape.xhtml_escape(‘<h1>wupeiqi</h1>‘)
b. 注册
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
from tornado.escape import linkify
import uimodules as md
import uimethods as mt
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘index.html‘)
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘ui_methods‘: mt,
‘ui_modules‘: md,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8009)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
c. 使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<link href="{{static_url("commons.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello</h1>
{% module custom(123) %}
{{ tab() }}
</body>
四、静态文件
对于静态文件,可以配置静态文件的目录和前段使用时的前缀,并且Tornaodo还支持静态文件缓存。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# app.py
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘home/index.html‘)
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(80)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
<!--index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<link href="{{static_url("commons.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello</h1>
</body>
</html>
静态文件缓存的实现
def get_content_version(cls, abspath):
"""Returns a version string for the resource at the given path.
This class method may be overridden by subclasses. The
default implementation is a hash of the file‘s contents.
.. versionadded:: 3.1
"""
data = cls.get_content(abspath)
hasher = hashlib.md5()
if isinstance(data, bytes):
hasher.update(data)
else:
for chunk in data:
hasher.update(chunk)
return hasher.hexdigest()
五、cookie
Tornado中可以对cookie进行操作,并且还可以对cookie进行签名以放置伪造。
1、基本操作
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
if not self.get_cookie("mycookie"):
self.set_cookie("mycookie", "myvalue")
self.write("Your cookie was not set yet!")
else:
self.write("Your cookie was set!")
2、加密cookie(签名)
Cookie 很容易被恶意的客户端伪造。加入你想在 cookie 中保存当前登陆用户的 id 之类的信息,你需要对 cookie 作签名以防止伪造。Tornado 通过 set_secure_cookie 和 get_secure_cookie 方法直接支持了这种功能。 要使用这些方法,你需要在创建应用时提供一个密钥,名字为 cookie_secret。 你可以把它作为一个关键词参数传入应用的设置中:
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
if not self.get_secure_cookie("mycookie"):
self.set_secure_cookie("mycookie", "myvalue")
self.write("Your cookie was not set yet!")
else:
self.write("Your cookie was set!")
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/", MainHandler),
], cookie_secret="61oETzKXQAGaYdkL5gEmGeJJFuYh7EQnp2XdTP1o/Vo=")
内部算法:

1 def _create_signature_v1(secret, *parts): 2 hash = hmac.new(utf8(secret), digestmod=hashlib.sha1) 3 for part in parts: 4 hash.update(utf8(part)) 5 return utf8(hash.hexdigest()) 6 7 # 加密 8 def _create_signature_v2(secret, s): 9 hash = hmac.new(utf8(secret), digestmod=hashlib.sha256) 10 hash.update(utf8(s)) 11 return utf8(hash.hexdigest()) 12 13 def create_signed_value(secret, name, value, version=None, clock=None, 14 key_version=None): 15 if version is None: 16 version = DEFAULT_SIGNED_VALUE_VERSION 17 if clock is None: 18 clock = time.time 19 20 timestamp = utf8(str(int(clock()))) 21 value = base64.b64encode(utf8(value)) 22 if version == 1: 23 signature = _create_signature_v1(secret, name, value, timestamp) 24 value = b"|".join([value, timestamp, signature]) 25 return value 26 elif version == 2: 27 # The v2 format consists of a version number and a series of 28 # length-prefixed fields "%d:%s", the last of which is a 29 # signature, all separated by pipes. All numbers are in 30 # decimal format with no leading zeros. The signature is an 31 # HMAC-SHA256 of the whole string up to that point, including 32 # the final pipe. 33 # 34 # The fields are: 35 # - format version (i.e. 2; no length prefix) 36 # - key version (integer, default is 0) 37 # - timestamp (integer seconds since epoch) 38 # - name (not encoded; assumed to be ~alphanumeric) 39 # - value (base64-encoded) 40 # - signature (hex-encoded; no length prefix) 41 def format_field(s): 42 return utf8("%d:" % len(s)) + utf8(s) 43 to_sign = b"|".join([ 44 b"2", 45 format_field(str(key_version or 0)), 46 format_field(timestamp), 47 format_field(name), 48 format_field(value), 49 b‘‘]) 50 51 if isinstance(secret, dict): 52 assert key_version is not None, ‘Key version must be set when sign key dict is used‘ 53 assert version >= 2, ‘Version must be at least 2 for key version support‘ 54 secret = secret[key_version] 55 56 signature = _create_signature_v2(secret, to_sign) 57 return to_sign + signature 58 else: 59 raise ValueError("Unsupported version %d" % version) 60 61 # 解密 62 def _decode_signed_value_v1(secret, name, value, max_age_days, clock): 63 parts = utf8(value).split(b"|") 64 if len(parts) != 3: 65 return None 66 signature = _create_signature_v1(secret, name, parts[0], parts[1]) 67 if not _time_independent_equals(parts[2], signature): 68 gen_log.warning("Invalid cookie signature %r", value) 69 return None 70 timestamp = int(parts[1]) 71 if timestamp < clock() - max_age_days * 86400: 72 gen_log.warning("Expired cookie %r", value) 73 return None 74 if timestamp > clock() + 31 * 86400: 75 # _cookie_signature does not hash a delimiter between the 76 # parts of the cookie, so an attacker could transfer trailing 77 # digits from the payload to the timestamp without altering the 78 # signature. For backwards compatibility, sanity-check timestamp 79 # here instead of modifying _cookie_signature. 80 gen_log.warning("Cookie timestamp in future; possible tampering %r", 81 value) 82 return None 83 if parts[1].startswith(b"0"): 84 gen_log.warning("Tampered cookie %r", value) 85 return None 86 try: 87 return base64.b64decode(parts[0]) 88 except Exception: 89 return None 90 91 92 def _decode_fields_v2(value): 93 def _consume_field(s): 94 length, _, rest = s.partition(b‘:‘) 95 n = int(length) 96 field_value = rest[:n] 97 # In python 3, indexing bytes returns small integers; we must 98 # use a slice to get a byte string as in python 2. 99 if rest[n:n + 1] != b‘|‘: 100 raise ValueError("malformed v2 signed value field") 101 rest = rest[n + 1:] 102 return field_value, rest 103 104 rest = value[2:] # remove version number 105 key_version, rest = _consume_field(rest) 106 timestamp, rest = _consume_field(rest) 107 name_field, rest = _consume_field(rest) 108 value_field, passed_sig = _consume_field(rest) 109 return int(key_version), timestamp, name_field, value_field, passed_sig 110 111 112 def _decode_signed_value_v2(secret, name, value, max_age_days, clock): 113 try: 114 key_version, timestamp, name_field, value_field, passed_sig = _decode_fields_v2(value) 115 except ValueError: 116 return None 117 signed_string = value[:-len(passed_sig)] 118 119 if isinstance(secret, dict): 120 try: 121 secret = secret[key_version] 122 except KeyError: 123 return None 124 125 expected_sig = _create_signature_v2(secret, signed_string) 126 if not _time_independent_equals(passed_sig, expected_sig): 127 return None 128 if name_field != utf8(name): 129 return None 130 timestamp = int(timestamp) 131 if timestamp < clock() - max_age_days * 86400: 132 # The signature has expired. 133 return None 134 try: 135 return base64.b64decode(value_field) 136 except Exception: 137 return None 138 139 140 def get_signature_key_version(value): 141 value = utf8(value) 142 version = _get_version(value) 143 if version < 2: 144 return None 145 try: 146 key_version, _, _, _, _ = _decode_fields_v2(value) 147 except ValueError: 148 return None 149 150 return key_version
签名Cookie的本质是:
写cookie过程:
- 将值进行base64加密
- 对除值以外的内容进行签名,哈希算法(无法逆向解析)
- 拼接 签名 + 加密值
读cookie过程:
- 读取 签名 + 加密值
- 对签名进行验证
- base64解密,获取值内容
注:许多API验证机制和安全cookie的实现机制相同。
基于Cookie实现用户验证-Demo:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
login_user = self.get_secure_cookie("login_user", None)
if login_user:
self.write(login_user)
else:
self.redirect(‘/login‘)
class LoginHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.current_user()
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘‘})
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
username = self.get_argument(‘name‘)
password = self.get_argument(‘pwd‘)
if username == ‘wupeiqi‘ and password == ‘123‘:
self.set_secure_cookie(‘login_user‘, ‘武沛齐‘)
self.redirect(‘/‘)
else:
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘用户名或密码错误‘})
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘cookie_secret‘: ‘aiuasdhflashjdfoiuashdfiuh‘
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/login", LoginHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
基于签名Cookie实现用户验证-Demo:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class BaseHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get_current_user(self):
return self.get_secure_cookie("login_user")
class MainHandler(BaseHandler):
@tornado.web.authenticated
def get(self):
login_user = self.current_user
self.write(login_user)
class LoginHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.current_user()
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘‘})
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
username = self.get_argument(‘name‘)
password = self.get_argument(‘pwd‘)
if username == ‘wupeiqi‘ and password == ‘123‘:
self.set_secure_cookie(‘login_user‘, ‘武沛齐‘)
self.redirect(‘/‘)
else:
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘用户名或密码错误‘})
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘cookie_secret‘: ‘aiuasdhflashjdfoiuashdfiuh‘,
‘login_url‘: ‘/login‘
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/login", LoginHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
3、JavaScript操作Cookie
由于Cookie保存在浏览器端,所以在浏览器端也可以使用JavaScript来操作Cookie。
/*
设置cookie,指定秒数过期
*/
function setCookie(name,value,expires){
var temp = [];
var current_date = new Date();
current_date.setSeconds(current_date.getSeconds() + 5);
document.cookie = name + "= "+ value +";expires=" + current_date.toUTCString();
}
对于参数:
注:jQuery中也有指定的插件 jQuery Cookie 专门用于操作cookie,猛击这里
六、CSRF
Tornado中的夸张请求伪造和Django中的相似,跨站伪造请求(Cross-site request forgery)
配置:
settings = {
"xsrf_cookies": True,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/", MainHandler),
(r"/login", LoginHandler),
], **settings)
使用 - 普通表单:
<form action="/new_message" method="post">
{{ xsrf_form_html() }}
<input type="text" name="message"/>
<input type="submit" value="Post"/>
</form>
使用 - AJAX:
function getCookie(name) {
var r = document.cookie.match("\\b" + name + "=([^;]*)\\b");
return r ? r[1] : undefined;
}
jQuery.postJSON = function(url, args, callback) {
args._xsrf = getCookie("_xsrf");
$.ajax({url: url, data: $.param(args), dataType: "text", type: "POST",
success: function(response) {
callback(eval("(" + response + ")"));
}});
};
Ajax使用时,本质上就是去获取本地的cookie,携带cookie再来发送请求
七、上传文件
1、Form表单上传
html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>上传文件</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="my_form" name="form" action="/index" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" >
<input name="fff" id="my_file" type="file" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
python:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘index.html‘)
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
file_metas = self.request.files["fff"]
# print(file_metas)
for meta in file_metas:
file_name = meta[‘filename‘]
with open(file_name,‘wb‘) as up:
up.write(meta[‘body‘])
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8000)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
2、AJAX上传

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <input type="file" id="img" /> 9 <input type="button" onclick="UploadFile();" /> 10 <script> 11 function UploadFile(){ 12 var fileObj = document.getElementById("img").files[0]; 13 14 var form = new FormData(); 15 form.append("k1", "v1"); 16 form.append("fff", fileObj); 17 18 var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); 19 xhr.open("post", ‘/index‘, true); 20 xhr.send(form); 21 } 22 </script> 23 </body> 24 </html> 25 26 HTML - XMLHttpRequest

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <input type="file" id="img" /> 9 <input type="button" onclick="UploadFile();" /> 10 <script> 11 function UploadFile(){ 12 var fileObj = $("#img")[0].files[0]; 13 var form = new FormData(); 14 form.append("k1", "v1"); 15 form.append("fff", fileObj); 16 17 $.ajax({ 18 type:‘POST‘, 19 url: ‘/index‘, 20 data: form, 21 processData: false, // tell jQuery not to process the data 22 contentType: false, // tell jQuery not to set contentType 23 success: function(arg){ 24 console.log(arg); 25 } 26 }) 27 } 28 </script> 29 </body> 30 </html> 31 32 HTML - jQuery

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form id="my_form" name="form" action="/index" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" > 9 <div id="main"> 10 <input name="fff" id="my_file" type="file" /> 11 <input type="button" name="action" value="Upload" onclick="redirect()"/> 12 <iframe id=‘my_iframe‘ name=‘my_iframe‘ src="" class="hide"></iframe> 13 </div> 14 </form> 15 16 <script> 17 function redirect(){ 18 document.getElementById(‘my_iframe‘).onload = Testt; 19 document.getElementById(‘my_form‘).target = ‘my_iframe‘; 20 document.getElementById(‘my_form‘).submit(); 21 22 } 23 24 function Testt(ths){ 25 var t = $("#my_iframe").contents().find("body").text(); 26 console.log(t); 27 } 28 </script> 29 </body> 30 </html> 31 32 HTML - iframe

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 4 import tornado.ioloop 5 import tornado.web 6 7 8 class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): 9 def get(self): 10 11 self.render(‘index.html‘) 12 13 def post(self, *args, **kwargs): 14 file_metas = self.request.files["fff"] 15 # print(file_metas) 16 for meta in file_metas: 17 file_name = meta[‘filename‘] 18 with open(file_name,‘wb‘) as up: 19 up.write(meta[‘body‘]) 20 21 settings = { 22 ‘template_path‘: ‘template‘, 23 } 24 25 application = tornado.web.Application([ 26 (r"/index", MainHandler), 27 ], **settings) 28 29 30 if __name__ == "__main__": 31 application.listen(8000) 32 tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start() 33 34 Python

1 <script type="text/javascript"> 2 3 $(document).ready(function () { 4 5 $("#formsubmit").click(function () { 6 7 var iframe = $(‘<iframe name="postiframe" id="postiframe" style="display: none"></iframe>‘); 8 9 $("body").append(iframe); 10 11 var form = $(‘#theuploadform‘); 12 form.attr("action", "/upload.aspx"); 13 form.attr("method", "post"); 14 15 form.attr("encoding", "multipart/form-data"); 16 form.attr("enctype", "multipart/form-data"); 17 18 form.attr("target", "postiframe"); 19 form.attr("file", $(‘#userfile‘).val()); 20 form.submit(); 21 22 $("#postiframe").load(function () { 23 iframeContents = this.contentWindow.document.body.innerHTML; 24 $("#textarea").html(iframeContents); 25 }); 26 27 return false; 28 29 }); 30 31 }); 32 33 </script> 34 35 36 <form id="theuploadform"> 37 <input id="userfile" name="userfile" size="50" type="file" /> 38 <input id="formsubmit" type="submit" value="Send File" /> 39 </form> 40 41 <div id="textarea"> 42 </div> 43 44 扩展:基于iframe实现Ajax上传示例
八、验证码
验证码原理在于后台自动创建一张带有随机内容的图片,然后将内容通过img标签输出到页面。
安装图像处理模块:
pip3 install pillow
示例截图:
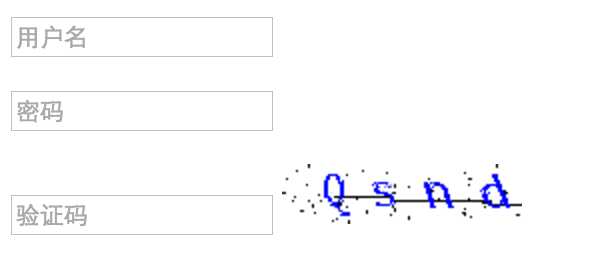
验证码Demo源码下载:猛击这里
一、Session
1、面向对象基础
面向对象中通过索引的方式访问对象,需要内部实现 __getitem__ 、__delitem__、__setitem__方法
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Foo(object):
def __getitem__(self, key):
print ‘__getitem__‘,key
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
print ‘__setitem__‘,key,value
def __delitem__(self, key):
print ‘__delitem__‘,key
obj = Foo()
result = obj[‘k1‘]
#obj[‘k2‘] = ‘zhangsan‘
#del obj[‘k1‘]
2、Tornado扩展
Tornado框架中,默认执行Handler的get/post等方法之前默认会执行 initialize方法,所以可以通过自定义的方式使得所有请求在处理前执行操作...
class BaseHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def initialize(self):
self.xxoo = "wupeiqi"
class MainHandler(BaseHandler):
def get(self):
print(self.xxoo)
self.write(‘index‘)
class IndexHandler(BaseHandler):
def get(self):
print(self.xxoo)
self.write(‘index‘)
3、session
session其实就是定义在服务器端用于保存用户回话的容器,其必须依赖cookie才能实现。

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 4 import tornado.ioloop 5 import tornado.web 6 from hashlib import sha1 7 import os, time 8 9 session_container = {} 10 11 create_session_id = lambda: sha1(‘%s%s‘ % (os.urandom(16), time.time())).hexdigest() 12 13 14 class Session(object): 15 16 session_id = "__sessionId__" 17 18 def __init__(self, request): 19 session_value = request.get_cookie(Session.session_id) 20 if not session_value: 21 self._id = create_session_id() 22 else: 23 self._id = session_value 24 request.set_cookie(Session.session_id, self._id) 25 26 def __getitem__(self, key): 27 return session_container[self._id][key] 28 29 def __setitem__(self, key, value): 30 if session_container.has_key(self._id): 31 session_container[self._id][key] = value 32 else: 33 session_container[self._id] = {key: value} 34 35 def __delitem__(self, key): 36 del session_container[self._id][key] 37 38 39 class BaseHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): 40 41 def initialize(self): 42 # my_session[‘k1‘]访问 __getitem__ 方法 43 self.my_session = Session(self) 44 45 46 class MainHandler(BaseHandler): 47 48 def get(self): 49 print self.my_session[‘c_user‘] 50 print self.my_session[‘c_card‘] 51 self.write(‘index‘) 52 53 class LoginHandler(BaseHandler): 54 55 def get(self): 56 self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘‘}) 57 58 def post(self, *args, **kwargs): 59 60 username = self.get_argument(‘name‘) 61 password = self.get_argument(‘pwd‘) 62 if username == ‘wupeiqi‘ and password == ‘123‘: 63 64 self.my_session[‘c_user‘] = ‘wupeiqi‘ 65 self.my_session[‘c_card‘] = ‘12312312309823012‘ 66 67 self.redirect(‘/index‘) 68 else: 69 self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘用户名或密码错误‘}) 70 71 settings = { 72 ‘template_path‘: ‘template‘, 73 ‘static_path‘: ‘static‘, 74 ‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘, 75 ‘cookie_secret‘: ‘aiuasdhflashjdfoiuashdfiuh‘, 76 ‘login_url‘: ‘/login‘ 77 } 78 79 application = tornado.web.Application([ 80 (r"/index", MainHandler), 81 (r"/login", LoginHandler), 82 ], **settings) 83 84 85 if __name__ == "__main__": 86 application.listen(8888) 87 tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start() 88 89 自定义Session
4、分布式Session

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding:utf-8 3 4 import sys 5 import math 6 from bisect import bisect 7 8 9 if sys.version_info >= (2, 5): 10 import hashlib 11 md5_constructor = hashlib.md5 12 else: 13 import md5 14 md5_constructor = md5.new 15 16 17 class HashRing(object): 18 """一致性哈希""" 19 20 def __init__(self,nodes): 21 ‘‘‘初始化 22 nodes : 初始化的节点,其中包含节点已经节点对应的权重 23 默认每一个节点有32个虚拟节点 24 对于权重,通过多创建虚拟节点来实现 25 如:nodes = [ 26 {‘host‘:‘127.0.0.1:8000‘,‘weight‘:1}, 27 {‘host‘:‘127.0.0.1:8001‘,‘weight‘:2}, 28 {‘host‘:‘127.0.0.1:8002‘,‘weight‘:1}, 29 ] 30 ‘‘‘ 31 32 self.ring = dict() 33 self._sorted_keys = [] 34 35 self.total_weight = 0 36 37 self.__generate_circle(nodes) 38 39 40 41 def __generate_circle(self,nodes): 42 for node_info in nodes: 43 self.total_weight += node_info.get(‘weight‘,1) 44 45 for node_info in nodes: 46 weight = node_info.get(‘weight‘,1) 47 node = node_info.get(‘host‘,None) 48 49 virtual_node_count = math.floor((32*len(nodes)*weight) / self.total_weight) 50 for i in xrange(0,int(virtual_node_count)): 51 key = self.gen_key_thirty_two( ‘%s-%s‘ % (node, i) ) 52 if self._sorted_keys.__contains__(key): 53 raise Exception(‘该节点已经存在.‘) 54 self.ring[key] = node 55 self._sorted_keys.append(key) 56 57 def add_node(self,node): 58 ‘‘‘ 新建节点 59 node : 要添加的节点,格式为:{‘host‘:‘127.0.0.1:8002‘,‘weight‘:1},其中第一个元素表示节点,第二个元素表示该节点的权重。 60 ‘‘‘ 61 node = node.get(‘host‘,None) 62 if not node: 63 raise Exception(‘节点的地址不能为空.‘) 64 65 weight = node.get(‘weight‘,1) 66 67 self.total_weight += weight 68 nodes_count = len(self._sorted_keys) + 1 69 70 virtual_node_count = math.floor((32 * nodes_count * weight) / self.total_weight) 71 for i in xrange(0,int(virtual_node_count)): 72 key = self.gen_key_thirty_two( ‘%s-%s‘ % (node, i) ) 73 if self._sorted_keys.__contains__(key): 74 raise Exception(‘该节点已经存在.‘) 75 self.ring[key] = node 76 self._sorted_keys.append(key) 77 78 def remove_node(self,node): 79 ‘‘‘ 移除节点 80 node : 要移除的节点 ‘127.0.0.1:8000‘ 81 ‘‘‘ 82 for key,value in self.ring.items(): 83 if value == node: 84 del self.ring[key] 85 self._sorted_keys.remove(key) 86 87 def get_node(self,string_key): 88 ‘‘‘获取 string_key 所在的节点‘‘‘ 89 pos = self.get_node_pos(string_key) 90 if pos is None: 91 return None 92 return self.ring[ self._sorted_keys[pos]].split(‘:‘) 93 94 def get_node_pos(self,string_key): 95 ‘‘‘获取 string_key 所在的节点的索引‘‘‘ 96 if not self.ring: 97 return None 98 99 key = self.gen_key_thirty_two(string_key) 100 nodes = self._sorted_keys 101 pos = bisect(nodes, key) 102 return pos 103 104 def gen_key_thirty_two(self, key): 105 106 m = md5_constructor() 107 m.update(key) 108 return long(m.hexdigest(), 16) 109 110 def gen_key_sixteen(self,key): 111 112 b_key = self.__hash_digest(key) 113 return self.__hash_val(b_key, lambda x: x) 114 115 def __hash_val(self, b_key, entry_fn): 116 return (( b_key[entry_fn(3)] << 24)|(b_key[entry_fn(2)] << 16)|(b_key[entry_fn(1)] << 8)| b_key[entry_fn(0)] ) 117 118 def __hash_digest(self, key): 119 m = md5_constructor() 120 m.update(key) 121 return map(ord, m.digest()) 122 123 124 """ 125 nodes = [ 126 {‘host‘:‘127.0.0.1:8000‘,‘weight‘:1}, 127 {‘host‘:‘127.0.0.1:8001‘,‘weight‘:2}, 128 {‘host‘:‘127.0.0.1:8002‘,‘weight‘:1}, 129 ] 130 131 ring = HashRing(nodes) 132 result = ring.get_node(‘98708798709870987098709879087‘) 133 print result 134 135 """ 136 137 一致性哈西

1 from hashlib import sha1 2 import os, time 3 4 5 create_session_id = lambda: sha1(‘%s%s‘ % (os.urandom(16), time.time())).hexdigest() 6 7 8 class Session(object): 9 10 session_id = "__sessionId__" 11 12 def __init__(self, request): 13 session_value = request.get_cookie(Session.session_id) 14 if not session_value: 15 self._id = create_session_id() 16 else: 17 self._id = session_value 18 request.set_cookie(Session.session_id, self._id) 19 20 def __getitem__(self, key): 21 # 根据 self._id ,在一致性哈西中找到其对应的服务器IP 22 # 找到相对应的redis服务器,如: r = redis.StrictRedis(host=‘localhost‘, port=6379, db=0) 23 # 使用python redis api 链接 24 # 获取数据,即: 25 # return self._redis.hget(self._id, name) 26 27 def __setitem__(self, key, value): 28 # 根据 self._id ,在一致性哈西中找到其对应的服务器IP 29 # 使用python redis api 链接 30 # 设置session 31 # self._redis.hset(self._id, name, value) 32 33 34 def __delitem__(self, key): 35 # 根据 self._id 找到相对应的redis服务器 36 # 使用python redis api 链接 37 # 删除,即: 38 return self._redis.hdel(self._id, name) 39 40 session
二、表单验证
在Web程序中往往包含大量的表单验证的工作,如:判断输入是否为空,是否符合规则。
html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<link href="{{static_url("commons.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello</h1>
<form action="/index" method="post">
<p>hostname: <input type="text" name="host" /> </p>
<p>ip: <input type="text" name="ip" /> </p>
<p>port: <input type="text" name="port" /> </p>
<p>phone: <input type="text" name="phone" /> </p>
<input type="submit" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
python:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
from hashlib import sha1
import os, time
import re
class MainForm(object):
def __init__(self):
self.host = "(.*)"
self.ip = "^(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)(\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)){3}$"
self.port = ‘(\d+)‘
self.phone = ‘^1[3|4|5|8][0-9]\d{8}$‘
def check_valid(self, request):
form_dict = self.__dict__
for key, regular in form_dict.items():
post_value = request.get_argument(key)
# 让提交的数据 和 定义的正则表达式进行匹配
ret = re.match(regular, post_value)
print key,ret,post_value
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘index.html‘)
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
obj = MainForm()
result = obj.check_valid(self)
self.write(‘ok‘)
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘cookie_secret‘: ‘aiuasdhflashjdfoiuashdfiuh‘,
‘login_url‘: ‘/login‘
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
由于验证规则可以代码重用,所以可以如此定义:

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 4 import tornado.ioloop 5 import tornado.web 6 import re 7 8 9 class Field(object): 10 11 def __init__(self, error_msg_dict, required): 12 self.id_valid = False 13 self.value = None 14 self.error = None 15 self.name = None 16 self.error_msg = error_msg_dict 17 self.required = required 18 19 def match(self, name, value): 20 self.name = name 21 22 if not self.required: 23 self.id_valid = True 24 self.value = value 25 else: 26 if not value: 27 if self.error_msg.get(‘required‘, None): 28 self.error = self.error_msg[‘required‘] 29 else: 30 self.error = "%s is required" % name 31 else: 32 ret = re.match(self.REGULAR, value) 33 if ret: 34 self.id_valid = True 35 self.value = ret.group() 36 else: 37 if self.error_msg.get(‘valid‘, None): 38 self.error = self.error_msg[‘valid‘] 39 else: 40 self.error = "%s is invalid" % name 41 42 43 class IPField(Field): 44 REGULAR = "^(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)(\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)){3}$" 45 46 def __init__(self, error_msg_dict=None, required=True): 47 48 error_msg = {} # {‘required‘: ‘IP不能为空‘, ‘valid‘: ‘IP格式错误‘} 49 if error_msg_dict: 50 error_msg.update(error_msg_dict) 51 52 super(IPField, self).__init__(error_msg_dict=error_msg, required=required) 53 54 55 class IntegerField(Field): 56 REGULAR = "^\d+$" 57 58 def __init__(self, error_msg_dict=None, required=True): 59 error_msg = {‘required‘: ‘数字不能为空‘, ‘valid‘: ‘数字格式错误‘} 60 if error_msg_dict: 61 error_msg.update(error_msg_dict) 62 63 super(IntegerField, self).__init__(error_msg_dict=error_msg, required=required) 64 65 66 class CheckBoxField(Field): 67 68 def __init__(self, error_msg_dict=None, required=True): 69 error_msg = {} # {‘required‘: ‘IP不能为空‘, ‘valid‘: ‘IP格式错误‘} 70 if error_msg_dict: 71 error_msg.update(error_msg_dict) 72 73 super(CheckBoxField, self).__init__(error_msg_dict=error_msg, required=required) 74 75 def match(self, name, value): 76 self.name = name 77 78 if not self.required: 79 self.id_valid = True 80 self.value = value 81 else: 82 if not value: 83 if self.error_msg.get(‘required‘, None): 84 self.error = self.error_msg[‘required‘] 85 else: 86 self.error = "%s is required" % name 87 else: 88 if isinstance(name, list): 89 self.id_valid = True 90 self.value = value 91 else: 92 if self.error_msg.get(‘valid‘, None): 93 self.error = self.error_msg[‘valid‘] 94 else: 95 self.error = "%s is invalid" % name 96 97 98 class FileField(Field): 99 REGULAR = "^(\w+\.pdf)|(\w+\.mp3)|(\w+\.py)$" 100 101 def __init__(self, error_msg_dict=None, required=True): 102 error_msg = {} # {‘required‘: ‘数字不能为空‘, ‘valid‘: ‘数字格式错误‘} 103 if error_msg_dict: 104 error_msg.update(error_msg_dict) 105 106 super(FileField, self).__init__(error_msg_dict=error_msg, required=required) 107 108 def match(self, name, value): 109 self.name = name 110 self.value = [] 111 if not self.required: 112 self.id_valid = True 113 self.value = value 114 else: 115 if not value: 116 if self.error_msg.get(‘required‘, None): 117 self.error = self.error_msg[‘required‘] 118 else: 119 self.error = "%s is required" % name 120 else: 121 m = re.compile(self.REGULAR) 122 if isinstance(value, list): 123 for file_name in value: 124 r = m.match(file_name) 125 if r: 126 self.value.append(r.group()) 127 self.id_valid = True 128 else: 129 self.id_valid = False 130 if self.error_msg.get(‘valid‘, None): 131 self.error = self.error_msg[‘valid‘] 132 else: 133 self.error = "%s is invalid" % name 134 break 135 else: 136 if self.error_msg.get(‘valid‘, None): 137 self.error = self.error_msg[‘valid‘] 138 else: 139 self.error = "%s is invalid" % name 140 141 def save(self, request, upload_path=""): 142 143 file_metas = request.files[self.name] 144 for meta in file_metas: 145 file_name = meta[‘filename‘] 146 with open(file_name,‘wb‘) as up: 147 up.write(meta[‘body‘]) 148 149 150 class Form(object): 151 152 def __init__(self): 153 self.value_dict = {} 154 self.error_dict = {} 155 self.valid_status = True 156 157 def validate(self, request, depth=10, pre_key=""): 158 159 self.initialize() 160 self.__valid(self, request, depth, pre_key) 161 162 def initialize(self): 163 pass 164 165 def __valid(self, form_obj, request, depth, pre_key): 166 """ 167 验证用户表单请求的数据 168 :param form_obj: Form对象(Form派生类的对象) 169 :param request: Http请求上下文(用于从请求中获取用户提交的值) 170 :param depth: 对Form内容的深度的支持 171 :param pre_key: Html中name属性值的前缀(多层Form时,内部递归时设置,无需理会) 172 :return: 是否验证通过,True:验证成功;False:验证失败 173 """ 174 175 depth -= 1 176 if depth < 0: 177 return None 178 form_field_dict = form_obj.__dict__ 179 for key, field_obj in form_field_dict.items(): 180 print key,field_obj 181 if isinstance(field_obj, Form) or isinstance(field_obj, Field): 182 if isinstance(field_obj, Form): 183 # 获取以key开头的所有的值,以参数的形式传至 184 self.__valid(field_obj, request, depth, key) 185 continue 186 if pre_key: 187 key = "%s.%s" % (pre_key, key) 188 189 if isinstance(field_obj, CheckBoxField): 190 post_value = request.get_arguments(key, None) 191 elif isinstance(field_obj, FileField): 192 post_value = [] 193 file_list = request.request.files.get(key, None) 194 for file_item in file_list: 195 post_value.append(file_item[‘filename‘]) 196 else: 197 post_value = request.get_argument(key, None) 198 199 print post_value 200 # 让提交的数据 和 定义的正则表达式进行匹配 201 field_obj.match(key, post_value) 202 if field_obj.id_valid: 203 self.value_dict[key] = field_obj.value 204 else: 205 self.error_dict[key] = field_obj.error 206 self.valid_status = False 207 208 209 class ListForm(object): 210 def __init__(self, form_type): 211 self.form_type = form_type 212 self.valid_status = True 213 self.value_dict = {} 214 self.error_dict = {} 215 216 def validate(self, request): 217 name_list = request.request.arguments.keys() + request.request.files.keys() 218 index = 0 219 flag = False 220 while True: 221 pre_key = "[%d]" % index 222 for name in name_list: 223 if name.startswith(pre_key): 224 flag = True 225 break 226 if flag: 227 form_obj = self.form_type() 228 form_obj.validate(request, depth=10, pre_key="[%d]" % index) 229 if form_obj.valid_status: 230 self.value_dict[index] = form_obj.value_dict 231 else: 232 self.error_dict[index] = form_obj.error_dict 233 self.valid_status = False 234 else: 235 break 236 237 index += 1 238 flag = False 239 240 241 class MainForm(Form): 242 243 def __init__(self): 244 # self.ip = IPField(required=True) 245 # self.port = IntegerField(required=True) 246 # self.new_ip = IPField(required=True) 247 # self.second = SecondForm() 248 self.fff = FileField(required=True) 249 super(MainForm, self).__init__() 250 251 # 252 # class SecondForm(Form): 253 # 254 # def __init__(self): 255 # self.ip = IPField(required=True) 256 # self.new_ip = IPField(required=True) 257 # 258 # super(SecondForm, self).__init__() 259 260 261 class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): 262 def get(self): 263 self.render(‘index.html‘) 264 def post(self, *args, **kwargs): 265 # for i in dir(self.request): 266 # print i 267 # print self.request.arguments 268 # print self.request.files 269 # print self.request.query 270 # name_list = self.request.arguments.keys() + self.request.files.keys() 271 # print name_list 272 273 # list_form = ListForm(MainForm) 274 # list_form.validate(self) 275 # 276 # print list_form.valid_status 277 # print list_form.value_dict 278 # print list_form.error_dict 279 280 # obj = MainForm() 281 # obj.validate(self) 282 # 283 # print "验证结果:", obj.valid_status 284 # print "符合验证结果:", obj.value_dict 285 # print "错误信息:" 286 # for key, item in obj.error_dict.items(): 287 # print key,item 288 # print self.get_arguments(‘favor‘),type(self.get_arguments(‘favor‘)) 289 # print self.get_argument(‘favor‘),type(self.get_argument(‘favor‘)) 290 # print type(self.get_argument(‘fff‘)),self.get_argument(‘fff‘) 291 # print self.request.files 292 # obj = MainForm() 293 # obj.validate(self) 294 # print obj.valid_status 295 # print obj.value_dict 296 # print obj.error_dict 297 # print self.request,type(self.request) 298 # obj.fff.save(self.request) 299 # from tornado.httputil import HTTPServerRequest 300 # name_list = self.request.arguments.keys() + self.request.files.keys() 301 # print name_list 302 # print self.request.files,type(self.request.files) 303 # print len(self.request.files.get(‘fff‘)) 304 305 # obj = MainForm() 306 # obj.validate(self) 307 # print obj.valid_status 308 # print obj.value_dict 309 # print obj.error_dict 310 # obj.fff.save(self.request) 311 self.write(‘ok‘) 312 313 314 315 settings = { 316 ‘template_path‘: ‘template‘, 317 ‘static_path‘: ‘static‘, 318 ‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘, 319 ‘cookie_secret‘: ‘aiuasdhflashjdfoiuashdfiuh‘, 320 ‘login_url‘: ‘/login‘ 321 } 322 323 application = tornado.web.Application([ 324 (r"/index", MainHandler), 325 ], **settings) 326 327 328 if __name__ == "__main__": 329 application.listen(8888) 330 tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/allan-king/p/5799695.html