标签:
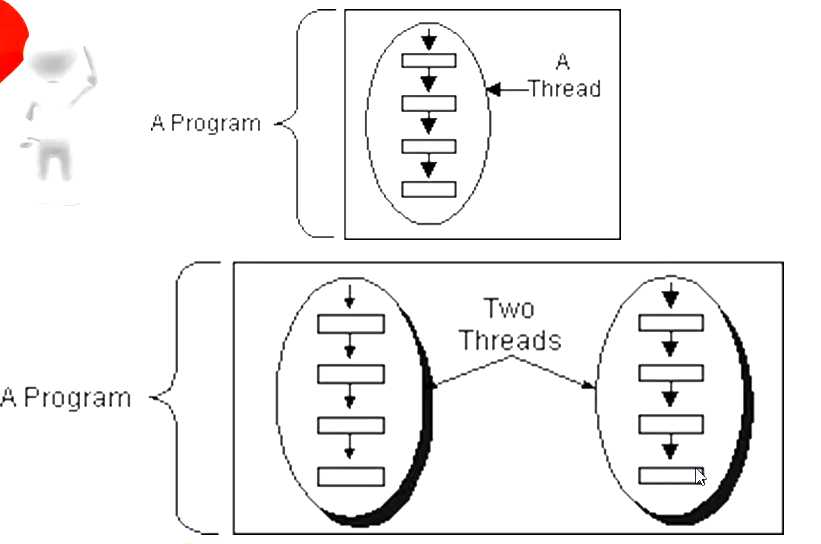
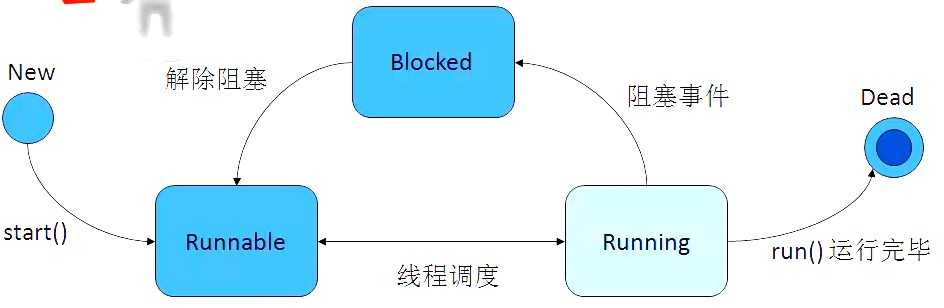
classFirstThread extends Thread{publicvoid run(){for(int i =0; i <10; i++){System.out.println("FirstThread-->"+ i);}}}classTest{publicstaticvoid main(String arg []){//生成线程的对象FirstThread ft =newFirstThread();//启动线程//ft.run(); 千万不能这样写,这样就是单线程,会先执行run()中的方法 ft.start();//线程交替运行,并且没有规律for(int i =0; i <10; i++){System.out.println("main-->"+ i);}}}classMyThread implements Runnable{int i =10;publicvoid run(){while(true){/* synchronized称为同步代码块; this代表调用run()方法的对象,称为同步锁; 功能:获得同步锁才有资格运行代码; **/ synchronized(this){/* currentThread()是Thread的静态方法,获取当前代码在哪个线程中运行; Thread.currentThread().getName()可以获得线程的名字; **/System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ i); i--;Thread.yield();if(i <0){break;}}}}}classTest{publicstaticvoid main(String arg []){MyThread myThread =newMyThread();//生成两个Thread对象,但是这两个Thread对象共用一个线程体Thread t1 =newThread(myThread);Thread t2 =newThread(myThread);/*每一个线程都有名字,可以通过Thread对象的setName()方法设置 也可以使用getName方法来获取线程的名字;**/ t1.setName("线程a"); t2.setName("线程b");//分别启动两个线程 t1.start(); t2.start();}}标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/arroneve/p/5815464.html