标签:
虽然骚尼手机卖的不怎么样,但是有些东西还是做的挺好的,工业设计就不用说了,索尼的相册的双指任意缩放功能也是尤其炫酷。其桌面小部件滚动相册我觉得也挺好的,比谷歌原生的相册墙功能好多了,网上搜了一下也没发现有人写这个,于是,下面就介绍下我的高A货。
首先是效果图:
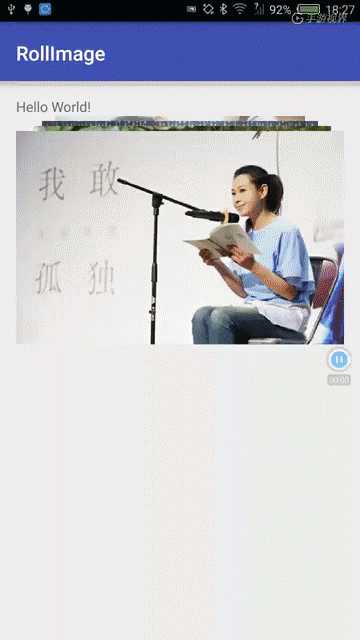
主要手势操作有:
该小部件的主要优点:在屏幕内的小范围内提供一个很好的图片选择/浏览部件,尤其是切换图片时有很强的靠近/远离动画感,增加好感。
代码分析
刚开始想这个小部件的时候以为是利用多个ImageView叠加实现的效果,例如谷歌原生的该部件就是利用多个ImageView叠加形成的,但是效果远比不上这个。但觉得通过多个ImageView叠加可能会没这么流畅,性能上也不好。该效果本身也比较规律,应该可以通过一个View来实现,达到更好的性能。于是通过View Hierarchy分析,sony这个果然是通过一个View实现的,于是通过如下方式这个小部件。
代码主要由三个部分组成:

/** * get all rects for drawing image * @return */ public Cell[] getCells(); /** * * @param distance the motion distance during the period from ACTION_DOWN to this moment * @return 0 means no roll, positive number means roll forward and negative means roll backward */ public int setStatus(float distance); /** * set the dimen of view * @param widht * @param height */ public void setDimen(int widht, int height); /** * set to the status for static */ public void setStatic();

/** * the images shown roll forward */ public void rollForward(); /** * the images shown roll backward */ public void rollBackward(); /** * get bitmaps * @return */ public Bitmap[] getBitmap(); /** * use invalidate to invalidate the view * @param invalidate */ public void setInvalidate(RollImageView.InvalidateView invalidate); /** * set the dimen of view * @param width * @param height */ public void setDimen(int width, int height); /** * the image path to be show * @param paths */ public void setImagePaths(List<String> paths); /** * get large bitmap while static */ public void loadCurrentLargeBitmap();
下面分析每个部分的核心代码。
RollImageView
View的主要职责是draw各个bitmap以及响应用户的手势操作,相对比较简单。
绘制部分就是把从ImageLoader获得的的各个Bitmap按照从CellCalculater中获得的绘制区域以及透明度绘制到屏幕上,目前本代码实现的比较简单,没有考虑不同尺寸的图片需要进行一些更加协调的显示方式,比如像ImageView.ScaleType中定义的一些显示方式。
@Override public void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); Bitmap[] bitmaps = mImageLoader.getBitmap(); Cell[] cells = mCellCalculator.getCells(); //得到每张Image的显示区域与透明度 canvas.translate(getWidth() / 2, 0); for (int i = SHOW_CNT - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //从最底层的Image开始绘制 Bitmap bitmap = bitmaps[i]; Cell cell = cells[i]; if (bitmap != null && !bitmap.isRecycled()) { mPaint.setAlpha(cell.getAlpha()); LOG("ondraw " + i + bitmap.getWidth() + " " + cell.getRectF() + " alpha " + cell.getAlpha()); canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, null, cell.getRectF(), mPaint); } } }
手势部分采用了GestureListener,主要代码如下:

@Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { if (event.getPointerCount() > 1) { return false; } mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(event); switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: //这里主要用于处理没有触发Fling事件时,使界面保持没有移动的状态 if(!mIsFling){ if(mRollResult == CellCalculator.ROLL_FORWARD){ mImageLoader.rollForward(); } else if (mRollResult == CellCalculator.ROLL_BACKWARD && !mScrollRollBack){ mImageLoader.rollBackward(); } LOG("OnGestureListener ACTION_UP setstatic " ); mCellCalculator.setStatic(); mImageLoader.loadCurrentLargeBitmap(); } break; default: break; } return true; } //缓慢拖动 @Override public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY) { mScrollDistance += distanceY; if(mScrollDistance > 0 && !mScrollRollBack){ mImageLoader.rollBackward(); mScrollRollBack = true; } else if(mScrollDistance < 0 && mScrollRollBack){ mImageLoader.rollForward(); mScrollRollBack = false; } LOG("OnGestureListener onScroll " + distanceY + " all" + mScrollDistance); mRollResult = mCellCalculator.setStatus(-mScrollDistance); invalidate(); return true; } //快速拖动 @Override public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY) { if (Math.abs(velocityY) > MIN_FLING) { LOG("OnGestureListener onFling " + velocityY); if (mExecutorService == null) { mExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); } mIsFling = true; mExecutorService.submit(new FlingTask(velocityY)); } return true; } //利用一个异步任务来处理滚动多张Images private class FlingTask implements Runnable { float mVelocity; float mViewHeight; int mSleepTime; boolean mRollBackward; FlingTask(float velocity) { mRollBackward = velocity < 0 ? true : false; mVelocity = Math.abs(velocity / 4); mViewHeight = RollImageView.this.getHeight() / 2; mSleepTime = (int)(4000 / Math.abs(velocity) * 100); //the slower velocity of fling, the longer interval for roll } @Override public void run() { int i = 0; try{ while (mVelocity > mViewHeight) { mCellCalculator.setStatus(mRollBackward ? -mViewHeight : mViewHeight); mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_INVALATE); //determines the count of roll. The using of mViewHeight has no strictly logical mVelocity -= mViewHeight; if (((i++) & 1) == 0) { //roll forward once for every two setStatus if(mRollBackward){ mImageLoader.rollBackward(); }else { mImageLoader.rollForward(); } } Thread.sleep(mSleepTime); } mCellCalculator.setStatic(); mImageLoader.loadCurrentLargeBitmap(); mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_INVALATE); } catch(Exception e){ } finally{ } } }
CellCalculater分析
首先阐明下向前移动/向后移动的概念。需要显示的图片路径存储为一个List,假设显示在最前的图片的索引为index,则当前显示的图片为[index,index+3],向前则表示index加1,向后则表示index减1.
CellCalculater的计算情形主要在于用户通过手势操作,表达了需要向前或者向后移动一张图片的意图。在View中能够获取到的只是手势移动的距离,所以在CellCalculater中需要对传进来的移动距离进行处理,输出移动结果。在我的实现中,当移动距离超过图片高度一半的时候,就表示显示的图片需要移动一位,否则当手势操作结束的时候就设置为static状态。主要代码如下:

public DefaultCellCalculator(int showCnt){ mCnt = showCnt; mCells = new Cell[mCnt]; mAlphas = new float[mCnt]; STATIC_ALPHA = new int[mCnt]; STATIC_ALPHA[mCnt - 1] = 0; //最后一张图的透明度为0 int alphaUnit = (255 - FIRST_ALPHA) / (mCnt - 2); for(int i = mCnt - 2; i >= 0; i--){ //定义静态时每张图的透明度 STATIC_ALPHA[i] = FIRST_ALPHA + (mCnt - 2 - i) * alphaUnit; } } @Override public Cell[] getCells() { return mCells; } //用户手势移动,distance表示移动距离,正负值分别意味着需要向前/向后移动 @Override public int setStatus(float distance) { if(distance > 0){ return calculateForward(distance); } else if(distance < 0){ return calculateBackward(distance); } else{ initCells(); } return 0; } //设置RollImageView的尺寸,从而计算合适的显示区域 @Override public void setDimen(int widht, int height) { mViewWidth = widht; mViewHeight = height; mWidhtIndent = (int)(WIDHT_INDENT * mViewWidth); mWidths = new int[mCnt]; for(int i = 0; i < mCnt; i++){ mWidths[i] = mViewWidth - i * mWidhtIndent; } //每张图片的高度。 //假如显示四张图,那么在上面会有三个高度落差,然后最底部保留一个高度落差,所以是mcnt-1 mImageHeight = mViewHeight - (mCnt - 1) * HEIGHT_INDENT; LOG("mImageHeight " + mImageHeight); initCells(); } //静态时,即用户手势操作结束时 @Override public void setStatic() { initCells(); } //用户有需要向前移动一位的趋势 private int calculateForward(float status){ float scale = status / mImageHeight; LOG("scale " + scale + " mImageHeight " + mImageHeight + " status " + status); for(int i = 1; i < mCnt; i++){ mCells[i].setWidth(interpolate(scale * 3, mWidths[i], mWidths[i - 1])); // *3 使得后面的宽度快速增大,经验值 mCells[i].moveVertical(interpolate(scale * 10, 0, HEIGHT_INDENT)); //*10使得后面的图片迅速向前,向前的动画感更强 mCells[i].setAlpha((int)interpolate(scale, STATIC_ALPHA[i], STATIC_ALPHA[i - 1])); } mCells[0].moveVertical(status); mCells[0].setAlpha((int)interpolate(scale, 255, 0)); if(status >= mImageHeight / 3){ return ROLL_FORWARD; } else { return 0; } } //用户有需要向后移动一位的趋势 private int calculateBackward(float status){ float scale = Math.abs(status / mImageHeight); for(int i = 1; i < mCnt; i++){ mCells[i].setWidth(interpolate(scale, mWidths[i - 1], mWidths[i])); mCells[i].moveVertical(-scale * HEIGHT_INDENT); mCells[i].setAlpha((int)interpolate(scale, STATIC_ALPHA[i - 1], STATIC_ALPHA[i])); } mCells[0].resetRect(); mCells[0].setWidth(mWidths[0]); mCells[0].setHeight(mImageHeight); mCells[0].moveVertical(mImageHeight + status); mCells[0].setAlpha((int)interpolate(scale, 0, 255)); if(-status >= mImageHeight / 3){ return ROLL_BACKWARD; } else { return 0; } } /** * status without move */ private void initCells(){ int top = -HEIGHT_INDENT; for(int i = 0; i < mCnt; i++){ RectF rectF = new RectF(0,0,0,0); rectF.top = top + (mCnt - 1 - i) * HEIGHT_INDENT; rectF.bottom = rectF.top + mImageHeight; mCells[i] = new Cell(rectF, STATIC_ALPHA[i]); mCells[i].setWidth(mWidths[i]); } } //计算差值 private float interpolate(float scale, float start, float end){ if(scale > 1){ scale = 1; } return start + scale * (end - start); }
ImageLoader分析
ImageLoader其实比较简单,主要有如下两点:

//加载当前index以及向前向后三张大图 @Override public void loadCurrentLargeBitmap() { for(int i = mCurrentIndex - 1; i < mCurrentIndex + 2; i++){ if(i >= 0 && i < mImagesCnt - 1){ mBitmapCache.getLargeBitmap(mAllImagePaths[i]); } } } //index向前移动一位 @Override public void rollForward() { LOG("rollForward"); mCurrentIndex++; if(mCurrentIndex > mImagesCnt - 1){ mCurrentIndex = mImagesCnt - 1; } setCurrentPaths(); } //index向后移动一位 @Override public void rollBackward() { LOG("rollBackward"); mCurrentIndex--; if(mCurrentIndex < 0){ mCurrentIndex = 0; } setCurrentPaths(); } @Override public Bitmap[] getBitmap() { if(mCurrentPaths != null){ LOG("getBitmap paths nut null"); for(int i = mCurrentIndex, j = 0; j < mShowCnt; j++, i++){ if(i >= 0 && i < mImagesCnt){ mCurrentBitmaps[j] = mBitmapCache.getBimap(mAllImagePaths[i]); } else{ mCurrentBitmaps[j] = mBitmapCache.getBimap(NO_PATH); } } } return mCurrentBitmaps; }
最后,所有源代码:https://github.com/willhua/RollImage
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/willhua/p/5862386.html