标签:
SPFA算法
一.算法简介
SPFA(Shortest Path Faster Algorithm)算法是求单源最短路径的一种算法,它是Bellman-ford的队列优化,它是一种十分高效的最短路算法。
很多时候,给定的图存在负权边,这时类似Dijkstra等算法便没有了用武之地,而Bellman-Ford算法的复杂度又过高,SPFA算法便派上用场了。SPFA的复杂度大约是O(kE),k是每个点的平均进队次数(一般的,k是一个常数,在稀疏图中小于2)。
实现方法:建立一个队列,初始时队列里只有起始点,在建立一个表格记录起始点到所有点的最短路径(该表格的初始值要赋为极大值,该点到他本身的路径赋为0)。然后执行松弛操作,用队列里有的点去刷新起始点到所有点的最短路,如果刷新成功且被刷新点不在队列中则把该点加入到队列最后。重复执行直到队列为空。
此外,SPFA算法还可以判断图中是否有负权环,即一个点入队次数超过N。
二.算法图解
给定一个有向图,求A~E的最短路。
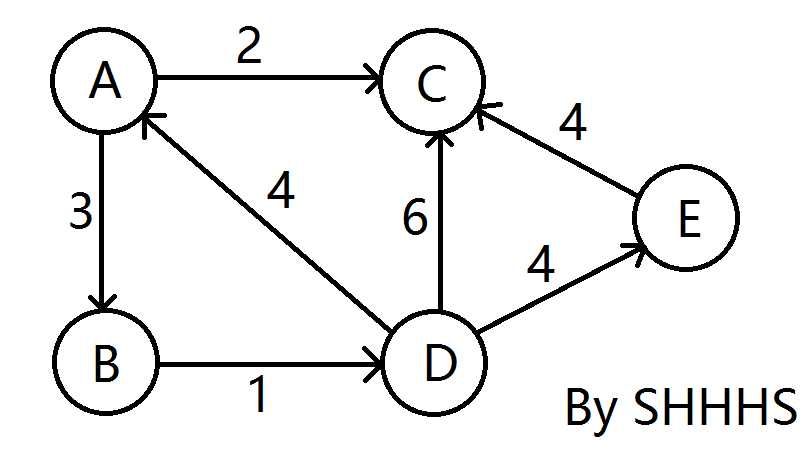
源点A首先入队,并且AB松弛
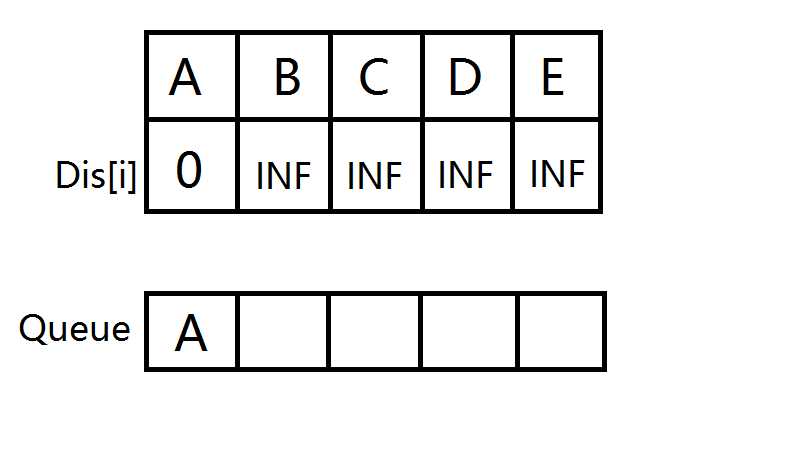
扩展与A相连的边,B,C 入队并松弛。
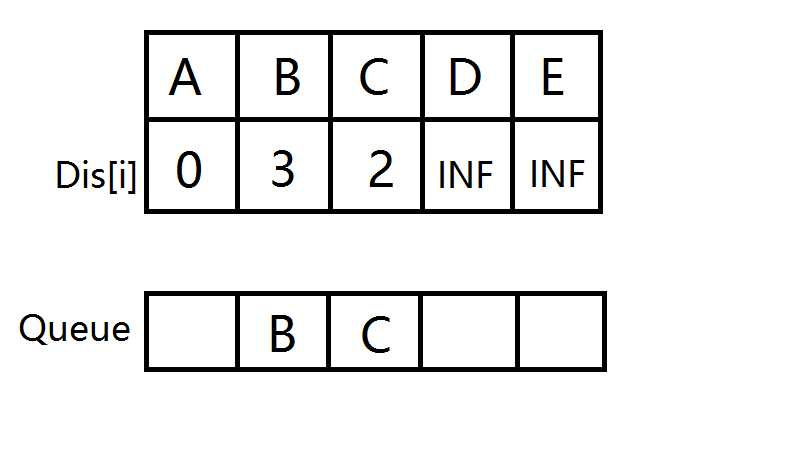
B,C分别开始扩展,D入队并松弛
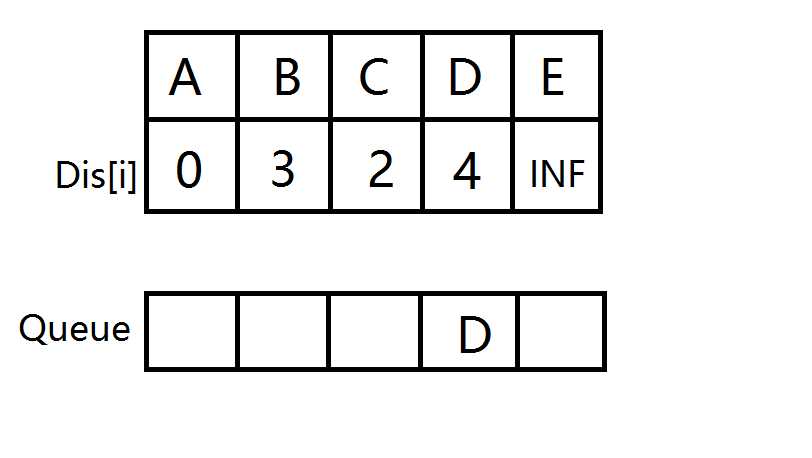
D出队,E入队并松弛。
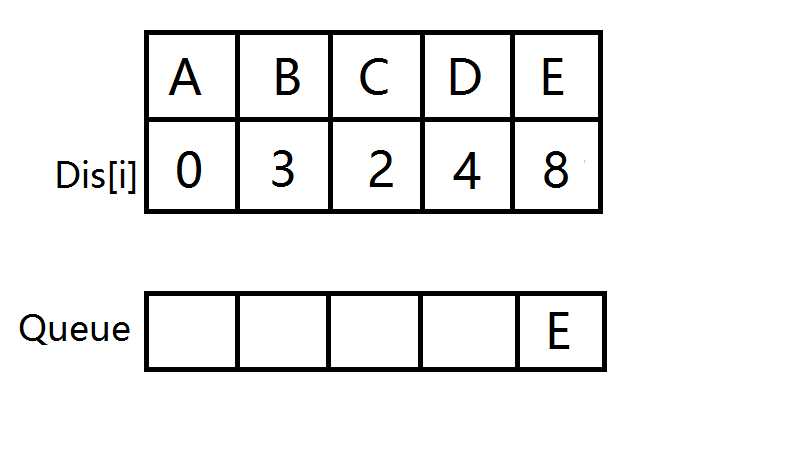
E出队,此时队列为空,源点到所有点的最短路已被找到,A->E的最短路即为8
以上就是SPFA算法的过程。
三.算法模板
1 #include "bits/stdc++.h" 2 3 using namespace std; 4 const int maxN = 200010 ; 5 struct Edge 6 { 7 int to , next , w ; 8 } e[ maxN ]; 9 10 int n,m,cnt,p[ maxN ],Dis[ maxN ]; 11 int In[maxN ]; 12 bool visited[ maxN ]; 13 14 void Add_Edge(const int x,const int y,const int z) 15 { 16 e[++cnt].to=y; 17 e[cnt].next=p[x]; 18 e[cnt].w=z; 19 p[x]=cnt; 20 return ; 21 } 22 23 bool Spfa(const int S) 24 { 25 int i,t,temp; 26 queue<int> Q; 27 memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited)); 28 memset(Dis,0x3f,sizeof(Dis)); 29 memset(In,0,sizeof(In)); 30 31 Q.push(S); 32 visited[S]=true; 33 Dis[S]=0; 34 35 while(!Q.empty()) 36 { 37 t=Q.front();Q.pop();visited[t]=false; 38 for(i=p[t];i;i=e[i].next) 39 { 40 temp=e[i].to; 41 if(Dis[temp]>Dis[t]+e[i].w) 42 { 43 Dis[temp]=Dis[t]+e[i].w; 44 if(!visited[temp]) 45 { 46 Q.push(temp); 47 visited[temp]=true; 48 if(++In[temp]>n)return false; 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 return true; 54 } 55 56 int main ( ) 57 { 58 int S , T ; 59 60 scanf ( "%d%d%d%d" , &n , &m , &S , &T ) ; 61 for(int i=1 ; i<=m ; ++i ) 62 { 63 int x , y , _ ; 64 scanf ( "%d%d%d" , &x , &y , &_ ) ; 65 Add_Edge ( x , y , _ ) ; 66 } 67 68 if ( !Spfa ( S ) ) printf ( "FAIL!\n" ) ; 69 else printf ( "%d\n" , Dis[ T ] ) ; 70 71 return 0; 72 }
(完)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shadowland/p/5870640.html