标签:style blog http color 使用 os io strong
一、流的概念
为什么要使用缓冲区而不直接从文件中读取数据到内存或者直接有内存写入文件呢?我们的文件通常都存在磁盘中,程序从磁盘读取一个字符需要大量的硬件活动,速度非常慢。缓冲方法则从磁盘上读取大量信息,将这些信息存储在缓冲区,然后每次从缓冲区里读取一个字节,因为从内存中读取单个字节的速度比从硬盘上读取快很多,所以这种方法更快,也更方便。说了这么多,只需知道缓冲方法更高效就可以了。
二、流库(stream library)介绍
使用继承的方法建立的输入输出类库,包含两个平行的基本类:streambuf和ios类,所有流类均以两者之一作为基类。
本文主要介绍ios,因为ios是编程中几乎必用的类,而streambuf类很少直接使用。下面图片来自网络:
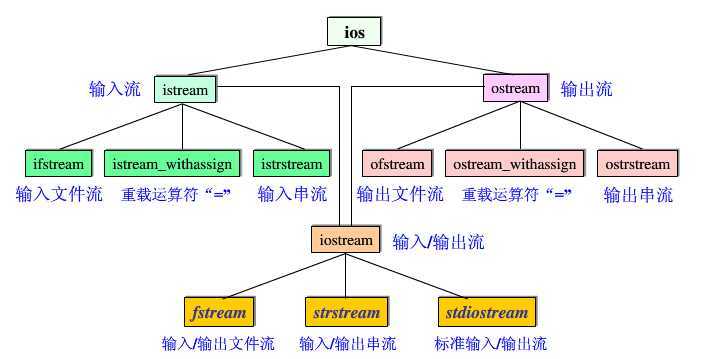
三、文件打开与关闭
文件打开用成员函数open();
| 标志 | 含义 |
| ios::ate | 打开文件并移动到文件尾 |
| ios::app | 追加到文件尾 |
| ios:in | 作为输入文件(ifstream默认) |
| ios::out | 作为输出文件(ofstream默认) |
| ios::trunc | 若文件存在,清除文件内容(默认) |
| ios::nocreate | 若文件不存在,返回错误 |
| ios::noreplace | 若文件存在,返回错误 |
| ios::binary | 以二进制方式打开 |
文件打开的方法:
1 ifstream f1; //定义文件输入流对象f1
2 f1.open( “d:\\vcprg\\7-3.cpp”); //打开D盘vcprg文件夹(目录)下的7-3.cpp文件,可进行文件读操作
ifstream f1( “d:\\vcprg\\7-3.cpp”)
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include <fstream>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 void main(void)
7 {
8 ifstream f1; //定义文件输入流对象
9 f1.open("d:\\vcprg\\7-3.cpp"); //打开文件
10 char c;
11 while(!f1.eof()) //判断文件未结束则循环,eof()在文件结束时返回true
12 {
13 f1.get(c);
14 cout << c;
15 }
16 cout << endl;
17 f1.close(); //关闭文件
18 }
文件访问方式:
1 fstream f;
2 f.open(“file.cpp”,ios_base::in|ios_base::out)
例:将D盘vcprg文件夹(目录)下的7-3.cpp文件,复制为text.txt文件。
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <fstream>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 void main(void)
7 {
8 ifstream f1; //定义文件输入流对象
9 ofstream f2;
10 f1.open("d:\\vcprg\\7-3.cpp"); //以读方式打开文件
11 f2.open("d:\\vcprg\\text.txt"); //以写方式打开文件
12 char c;
13 while(!f1.eof()) //判断文件未结束则循环,eof()会在文件结束时返回true
14 {
15 f1.get(c);
16 f2<<c;
17 }
18 cout << "文件复制成功" << endl;
19 f1.close(); //关闭文件
20 f2.close();
21 }
文件异常处理:
(1) 用条件语句判断文件流标志位failbit是否为true。
if(!文件流对象){<异常处理程序>}
if(文件流对象){<正常处理程序>}(上面一段示例的13行就是用这种方式)
(2)用成员fail()函数
if(文件流对象.fail()){<异常处理程序>}
if(!文件流对象.fail()){<正常处理程序>}
(3)用成员函数good()
if(!文件流对象.good()){<异常处理程序>}
if(文件流对象.good()){<正常处理程序>}
(4)较新的C++实现提供了一种更好的方式is_open()方法,推荐用此方法,但是老式C++没有实现这种方法,用上面三种均可
文件的关闭:
格式:文件流对象.close();
例如:
1 ofstream ofile ; // 创建输出文件流
2
3 ofile . open ( "myfile1" ) ; // ofile流与文件“myfile1”相关联
4
5 …… // 访问文件“myfile1”
6
7 ofile . close ( ) ; // 关闭文件“myfile1”
8
9 ofile . open ( "myfile2" ) ; // 重用ofile流
四、文件读写
文本文件的读写:
方法get(char&)和get()提供不跳过空白的单字符输入功能;
方法put(char&)和put()提供不跳过空白的单字符输出功能;
函数get(char*,int,char)和getline(char*,int,char)在默认情况下读取整行;
二进制文件的读写:
1 #include <fstream>
2 #include <iomanip>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6
7 int main ()
8 {
9 ofstream ost ;
10 ost.open ( "d:\\my2.dat" ) ;
11 ost << "1234567890" << endl ;
12 int a = 123 ;
13 ost << a << endl ;
14 ost << setw ( 10 ) << a << endl ;
15 ost << resetiosflags ( ios :: right ) << setiosflags ( ios :: left )
16 << setfill ( ‘#‘ ) << setw ( 10 ) << a << endl ;
17 ost << resetiosflags ( ios :: left ) << setiosflags ( ios :: right )
18 << setprecision ( 5 ) << setw ( 10 ) << 12.34567890 << endl ;
19 ost . close ( ) ;
20 return 0;
21 }
建立一个包含学生学号、姓名、成绩的文本文件:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <fstream>
3 #include <cstdlib>
4
5 using namespace std;
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 char fileName[30] , name[30] ;
10 int number , score ;
11
12 ofstream outstuf; //建立输出流对象
13
14 cout << "Please input the name of students file :\n" ;
15 cin >> fileName ; //输入文件名
16
17 outstuf.open(fileName, ios::out) ; //以输出方式打开文件
18
19 if ( !outstuf )
20 {
21 cerr << "File could not be open." << endl ;
22 exit(1);
23 }
24 outstuf << "学生成绩文件\n" ;
25 cout << "Input the number, name, and score : (Enter Ctrl-Z to end input)\n? " ;//windows中Ctrl-Z 结束输入和输出
26
27 while( cin >> number >> name >> score )
28 {
29 outstuf << number << ‘ ‘ << name << ‘ ‘ << score << ‘\n‘ ;
30 cout << "? " ;
31 }
32 outstuf.close() ;
33 return 0;
34 }
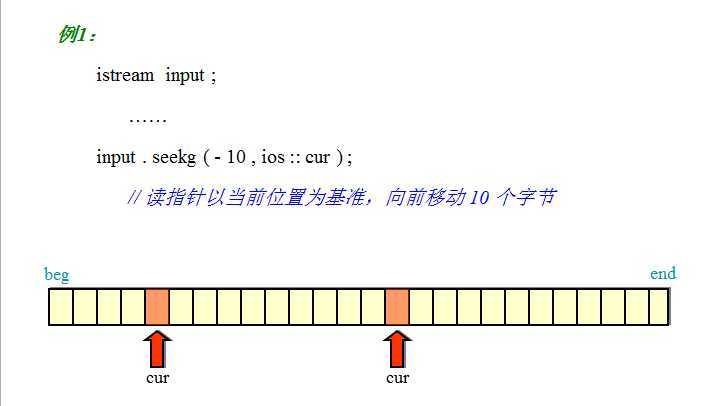
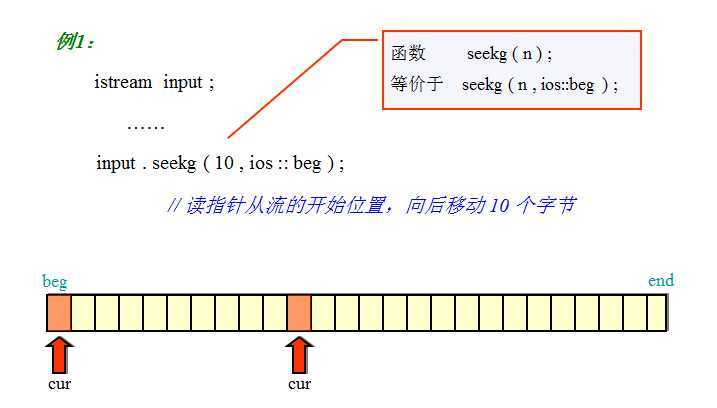
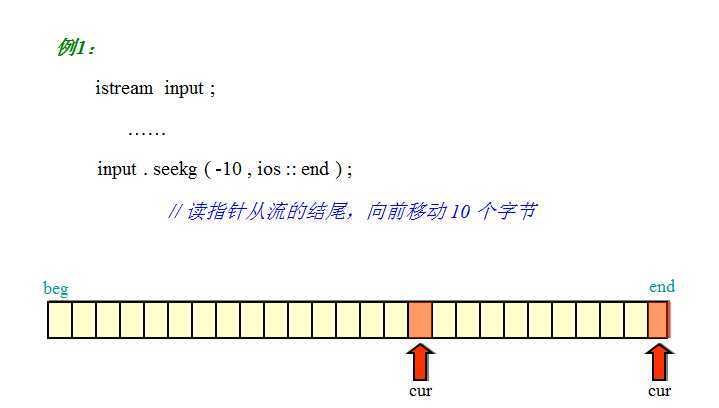
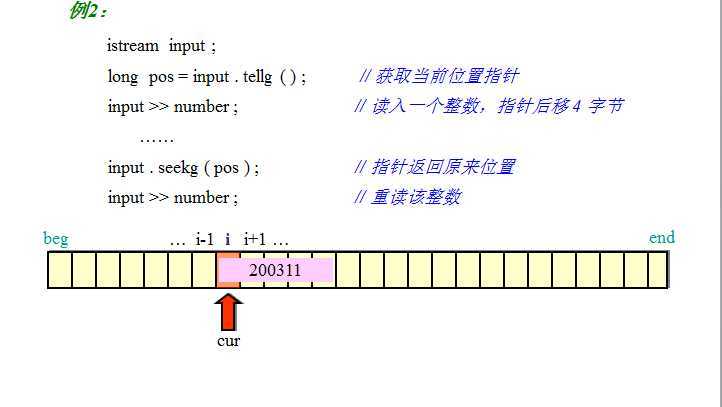
二进制文件,从一个学校教程里搜罗的图,讲的很清晰:



五、总结
C++学习笔记之输入、输出和文件,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style blog http color 使用 os io strong
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/90zeng/p/Cpp_in_out_file.html