标签:
---恢复内容开始---
在移动端,越来越倾向于页面内跳转,而页面内跳转就需要用到history的管理,html5的history是一种解决方案。
在没有history ap之前,我们经常使用散列值来改变页面内容,特别是那些对页面特别重要的内容。因为没有刷新,所以对于单页面应用,改变其URL是不可能的。此外,当你改变URL的散列值,它对浏览器的历史记录没有任何影响。通过增加location.hash,并用onhashchange来达到目的。
现在对于HTML 5的History API来说,这些都是可以轻易实现的,但是由于单页面应用没必要使用散列值,它可能需要额外的开发脚本。它也允许我们用一种对SEO友好的方式建立新应用。
HTML 5提供了两个新方法:pushstate跟replaceState,两个方法参数一样
params {
state:存储JSON字符串,可以用在popstate事件中,可以通过locaton.state获取。
title:现在大多数浏览器不支持或者忽略这个参数,最好用null代替
url:任意有效的URL,用于更新浏览器的地址栏,并不在乎URL是否已经存在地址列表中。更重要的是,它不会重新加载页面。
}
两个方法的主要区别就是:pushState()是在history栈中添加一个新的条目,replaceState()是替换当前的记录值。用pushState的时候会产生一条新的history,replaceState则不会产生。
当我们使用pushState()和replaceState()进行处理时或者点击浏览器的前进后退的时候,popstate事件会被触发,通过监听popstate事件可以达到一系列功能。
history在某些浏览器上支持还不是特别好,可以引用这个实现兼容的js
https://github.com/browserstate/history.js
通过点击页面的导航,实现页面内跳转,根据popstate监听URL的改变显示不同的页面.
这种路由方式还需要服务器端的支持,不然刷新页面会出现404
如果入口是index,apache可以在根目录下建个.htaccess文件,配置如下,
RewriteEngine On RewriteBase / RewriteRule ^index\.html$ - [L] RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d RewriteRule . /index.html [L]
如果你用的ngnix,配置如下
server {
...
location / {
try_files $uri /index.html;
}
}
index.html
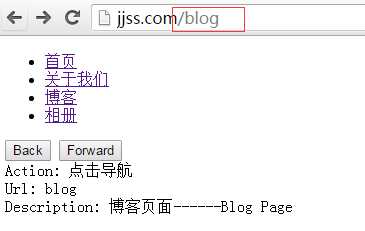
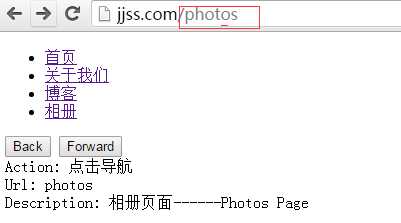
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>History API</title> <meta charset="utf-8" /> </head> <body> <ul id="menu"> <li><a href="/home">首页</a></li> <li><a href="/about">关于我们</a></li> <li><a href="/blog">博客</a></li> <li><a href="/photos">相册</a></li> </ul> <button id="back">Back</button> <button id="forward">Forward</button> <div> Action: <span id="action"></span><br/> Url: <span id="url"></span><br/> Description: <span id="description"></span> </div> </body> </html>
js代码
document.addEventListener(‘DOMContentLoaded‘, function(){ var act, historyState; var menu = document.querySelectorAll(‘li a‘); historyState = { home : { description : "我是首页------Index Page" }, about : { description : "关于我们------About Page" }, blog : { description : "博客页面------Blog Page" }, photos : { description : "相册页面------Photos Page" } }; for( let i =0; i < menu.length; i++ ) { menu[i].addEventListener(‘click‘, function(e){ e.preventDefault(); var hash = menu[i].getAttribute(‘href‘); var key = hash.replace(‘/‘,‘‘); act = "点击导航"; historyState[key].url = key; //history.pushState(historyState[key], null, hash); history.replaceState(historyState[key], null, hash); setStateInfo( historyState[key] ); },false); } window.addEventListener(‘popstate‘, function(event){ var state = history.state || event.state || window.event.state; if( state) setStateInfo(state); },false); document.querySelector("#back").addEventListener(‘click‘, function(){ act = "点击后退按钮"; history.back(); }, false); document.querySelector("#forward").addEventListener(‘click‘, function(){ act = "点击前进按钮"; history.go(1); }); function setStateInfo( state ){ //ajax处理不同的数据 document.querySelector(‘#action‘).innerHTML = act; document.querySelector("#url").innerHTML = state.url; document.querySelector(‘#description‘).innerHTML = state.description; } //第一次加载进来的时候 var path = location.pathname; var arr = path.split(‘/‘); var index = arr[arr.length - 1] || ‘home‘ act = "刷新页面"; historyState[index].url = index; setStateInfo(historyState[index]); //history.pushState(historyState[index], null, ‘/home‘) history.replaceState(historyState[index], null, hash); },false);
通过切换就可以达到页面跳转和ajax刷新的效果,而不再出现hash散列值
---恢复内容结束---
HTML5 history pushState/replaceState实例
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/micotan/p/5887460.html