标签:
As we know,the Natural Constant,which usually called e,has two main ways of expressing:
1. \( \lim_{n \to \infty}\sum_{i=0}^{n}(\frac{1}{i!}) \)
2. \( \lim_{n \to \infty}(1+\frac{1}{n})^{n} \)
Let we have a try,the following two python(Version 3.4) program shows you the cruel fact.:(
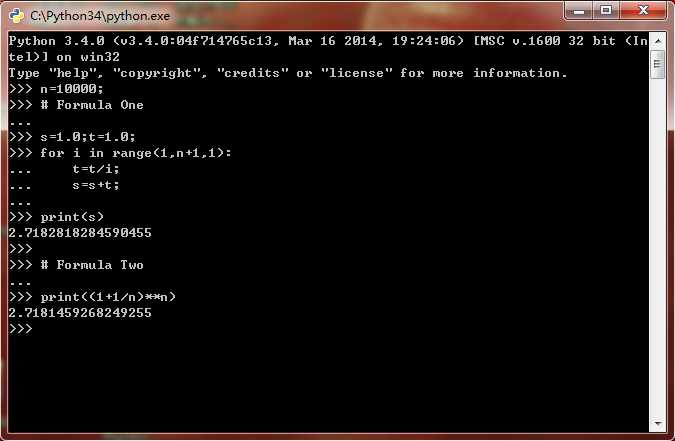
| Number | The level of deviation | |
| Number of Formula One | 2.7182818284590455 | \( {10}^{-16} \) |
| Number of Formula Two | 2.7181459268249255 | \( {10}^{-4} \) |
| The exact number of e | 2.7182818284590452 | ------ |
So obviously,the convergence rate of Formula One is much more fast-speed.Also the calculate time it costs is not far more than Formule One.
So take action.:)
Another fact is,what most of us care most is how many accurate digits we can reach,not how big or small the \( n \) is.
Though the high accuration calculation is required, the program still have two variables : \( s \) and \( t \) ,which is usually used to store the sum and the factorial.When the \( n \) is large enough, the very digit of s can be stable, which means the same digit of t is \( 0 \), to be safer ,we should put another sereval \( 0 \) behind it, which won‘t cost much more time.
The One billion(\( {10}^{9} \)) binary system should be used in order to minimize the time use.
So here is the program:
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string.h> #pragma warning(disable:4996) #define ll long long using namespace std; const int maxn=100010; ll *a,*b; int n,m,x; ll p; void div(int t){ //high-accuration division ll s=0; for (int i=x;i<=n;i++){ s=s*p+b[i]; b[i]=s/t; s%=t; } while (b[x]==0) x++; } string op(ll x,bool fx=false){ //Translate 10^9 number into string string s=""; for (int i=1;i<=m;i++){ string s1=""; s1=(char)(x%10+48); s1+=s;s=s1; x=x/10; } if (fx){ int i=0; while (s.at(i)==‘0‘) i++; s=s.substr(i); } return s; } int main(){ cin >> n;n++; m=9;int v=n;n=n/m+5; int nn=n;n=n+8; // some more space should be spared p=1;for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) p*=10; a=new ll[n+1];b=new ll[n+1]; for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) a[i]=0;a[1]=1;a[n+1]=1; for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) b[i]=0;b[1]=1;b[n+1]=1; // initialize a and b ,which means s and t. int t=1;x=1; while (x<=nn){ div(t++);ll k=0; for (int i=n;i>=1;i--){ a[i]+=b[i]+k; k=a[i]/p;a[i]%=p; } int i=x-1; while (k!=0){ a[i]+=k;k=a[i]/p; a[i]%=p;i--; //high-accuraton plus } } string s1=""; for (int i=1;i<=nn;i++) s1+= op(a[i],i==1); s1=s1.substr(0,v); string s2=s1.substr(0,1); s2+="."; s2+=s1.substr(1); printf("%s\n",s2.c_str()); return 0; } //This code can run properly on vs2012
| Number of digit required | Time use(ms) |
| 100 | 0 |
| 1000 | 31 |
| 5000 | 109 |
| 9500 | 265 |
| 10000 | 297 |
| 20000 | 873 |
| 50000 | 4446 |
| 100000 | 16365 |
| 1000000 | About 20min |
【C++】Calculate the exact number of e.
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Fefnir/p/5911409.html