标签:
先来看一下构造函数
1 public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, 2 int maximumPoolSize, 3 long keepAliveTime, 4 TimeUnit unit, 5 BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, 6 ThreadFactory threadFactory, 7 RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { 8 if (corePoolSize < 0 || 9 maximumPoolSize <= 0 || 10 maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || 11 keepAliveTime < 0) 12 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 13 if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) 14 throw new NullPointerException(); 15 this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; 16 this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; 17 this.workQueue = workQueue; 18 this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); 19 this.threadFactory = threadFactory; 20 this.handler = handler; 21 }
重点讲解:
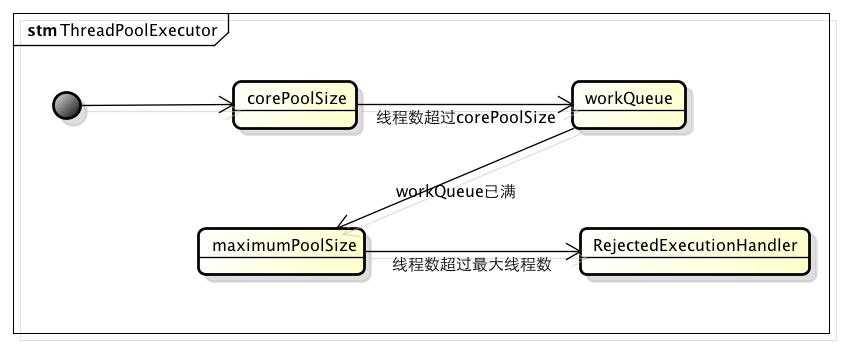
1、当线程池小于corePoolSize时,新提交任务将创建一个新线程执行任务,即使此时线程池中存在空闲线程。
2、当线程池达到corePoolSize时,新提交任务将被放入workQueue中,等待线程池中任务调度执行
3、当workQueue已满,且maximumPoolSize>corePoolSize时,新提交任务会创建新线程执行任务
4、当提交任务数超过maximumPoolSize时,新提交任务由RejectedExecutionHandler处理
5、当线程池中超过corePoolSize线程,空闲时间达到keepAliveTime时,关闭空闲线程
6、当设置allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true)时,线程池中corePoolSize线程空闲时间达到keepAliveTime也将关闭
配置方案:
1、构造一个固定线程数目的线程池,配置的corePoolSize与maximumPoolSize大小相同,同时使用了一个无界LinkedBlockingQueue存放阻塞任务,因此多余的任务将存在再阻塞队列,不会由RejectedExecutionHandler处理
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }
2、构造一个缓冲功能的线程池,配置corePoolSize=0,maximumPoolSize=Integer.MAX_VALUE,keepAliveTime=60s,以及一个无容量的阻塞队列 SynchronousQueue,因此任务提交之后,将会创建新的线程执行;线程空闲超过60s将会销毁
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }
3、构造一个只支持一个线程的线程池,配置corePoolSize=maximumPoolSize=1,无界阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue;保证任务由一个线程串行执行
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }
4、构造有定时功能的线程池,配置corePoolSize,无界延迟阻塞队列DelayedWorkQueue;有意思的是:maximumPoolSize=Integer.MAX_VALUE,由于DelayedWorkQueue是无界队列,所以这个值是没有意义的
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); } public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool( int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory); } public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) { super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS, new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory); }
总结:
1、用ThreadPoolExecutor自定义线程池,看线程是的用途,如果任务量不大,可以用无界队列,如果任务量非常大,要用有界队列,防止OOM
2、如果任务量很大,还要求每个任务都处理成功,要对提交的任务进行阻塞提交,重写拒绝机制,改为阻塞提交。保证不抛弃一个任务
3、最大线程数一般设为2N+1最好,N是CPU核数
4、核心线程数,看应用,如果是任务,一天跑一次,设置为0,合适,因为跑完就停掉了,如果是常用线程池,看任务量,是保留一个核心还是几个核心线程数
5、如果要获取任务执行结果,用CompletionService,但是注意,获取任务的结果的要重新开一个线程获取,如果在主线程获取,就要等任务都提交后才获取,就会阻塞大量任务结果,队列过大OOM,所以最好异步开个线程获取结果
java基础回顾(六)——ThreadPoolExecutor
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lyysz/p/5912046.html