标签:
排序,真的非常重要!
在其,没有罗列排序,不是说它不重要!
1、基础排序算法实战
2、二次排序算法实战
3、更高级别排序算法
4、更高级别排序算法
1、基础排序算法实战
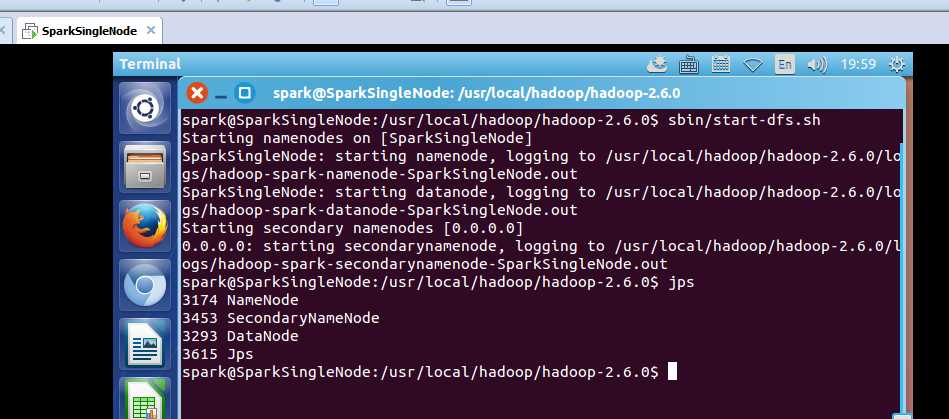
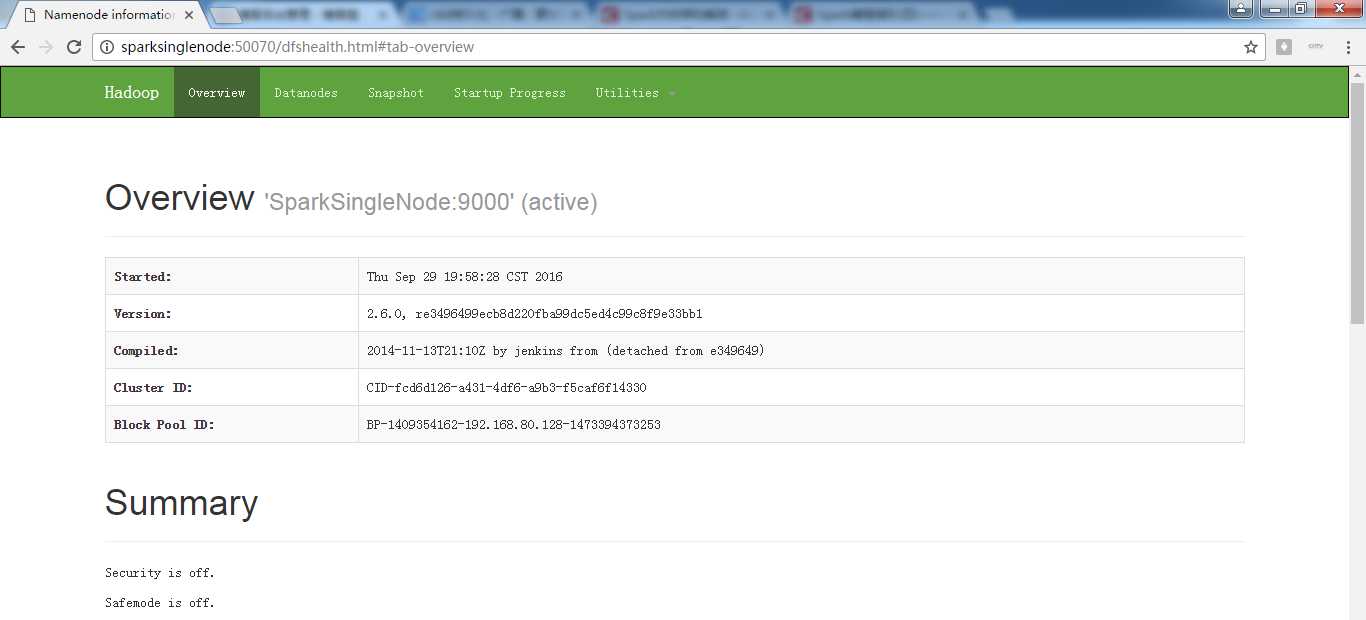
启动hdfs集群
spark@SparkSingleNode:/usr/local/hadoop/hadoop-2.6.0$ sbin/start-dfs.sh
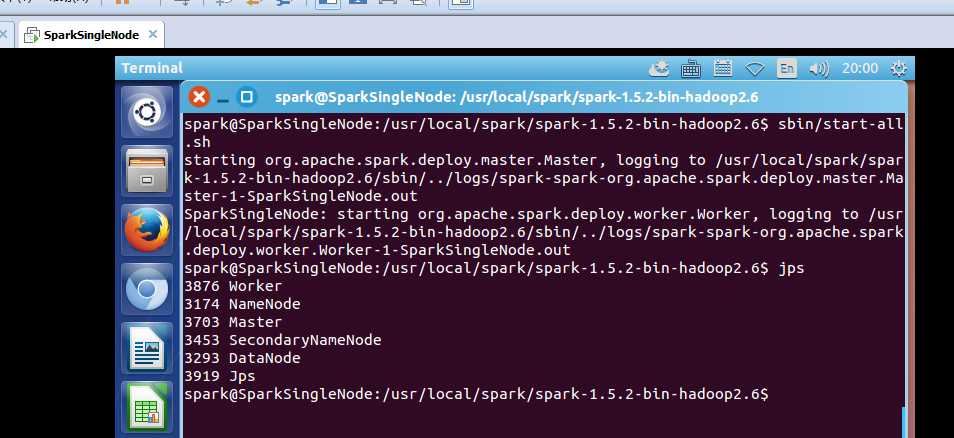
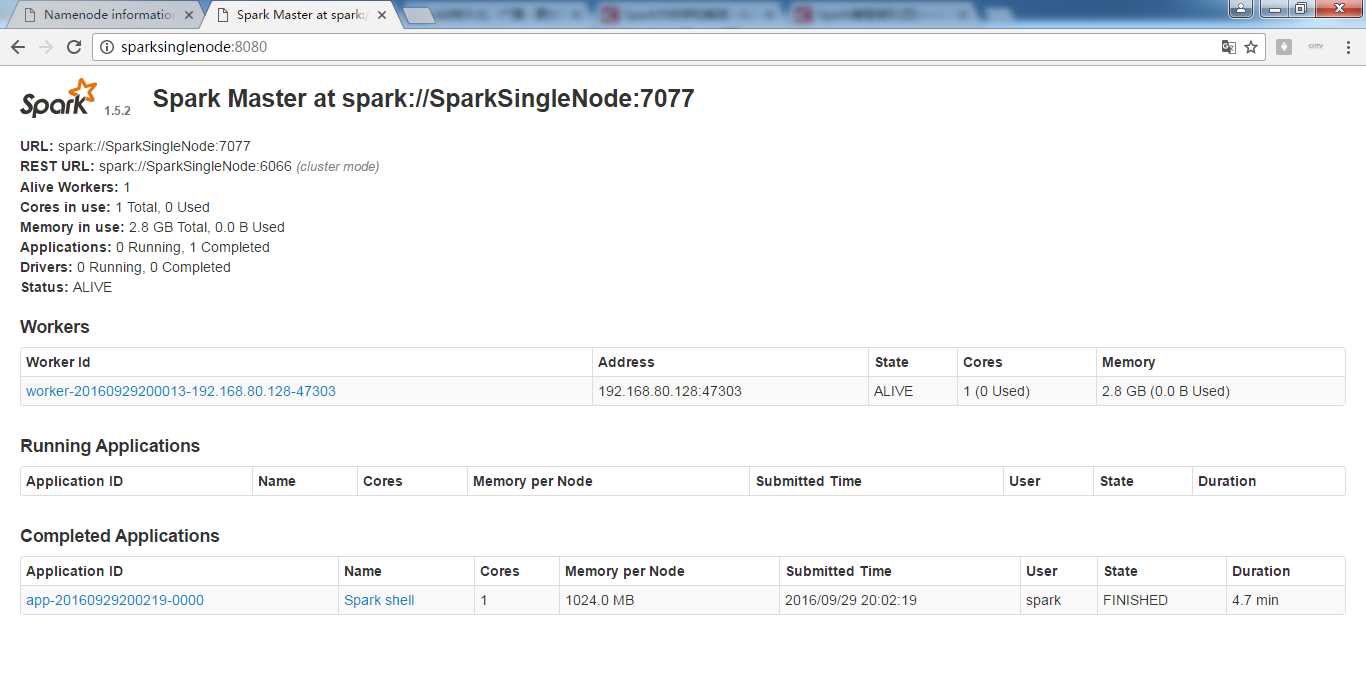
启动spark集群
spark@SparkSingleNode:/usr/local/spark/spark-1.5.2-bin-hadoop2.6$ sbin/start-all.sh
启动spark-shell
spark@SparkSingleNode:/usr/local/spark/spark-1.5.2-bin-hadoop2.6/bin$ ./spark-shell --master spark://SparkSingleNode:7077 --executor-memory 1g
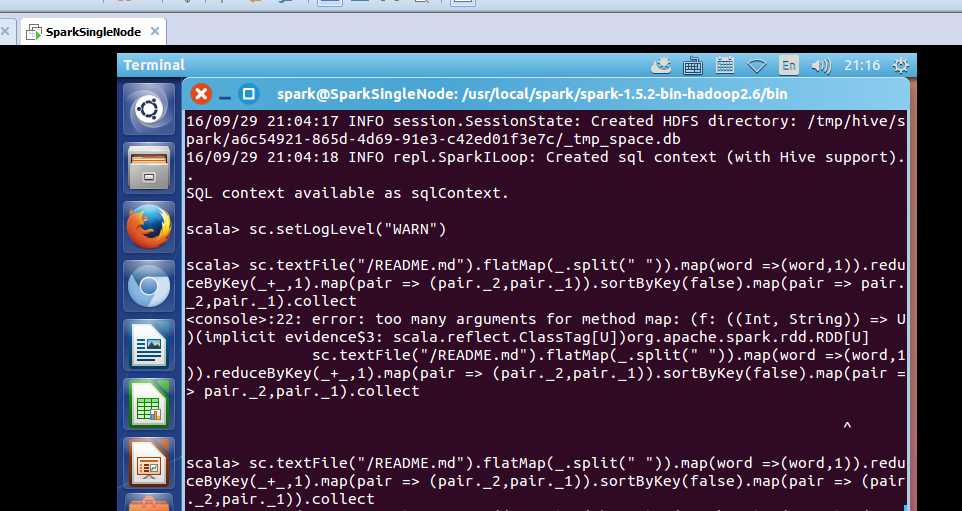
scala> sc.setLogLevel("WARN") //过滤日志提醒
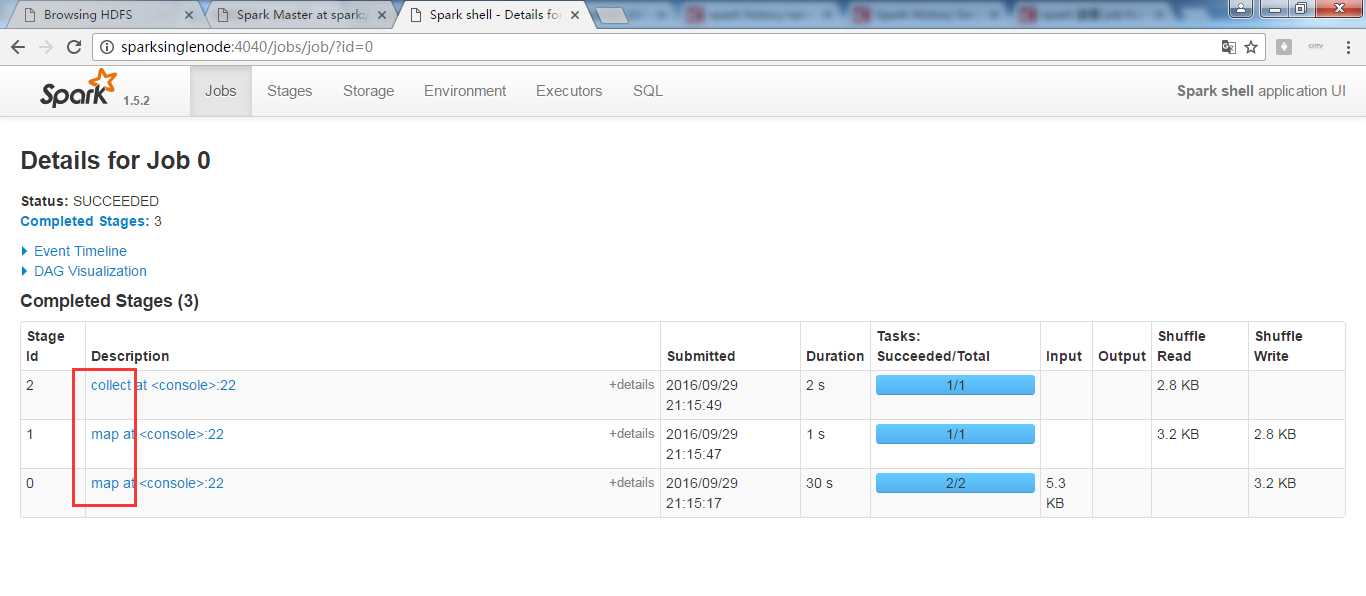
scala> sc.textFile("/README.md").flatMap(_.split(" ")).map(word =>(word,1)).reduceByKey(_+_,1).map(pair => (pair._2,pair._1)).sortByKey(false).map(pair => (pair._2,pair._1)).collect
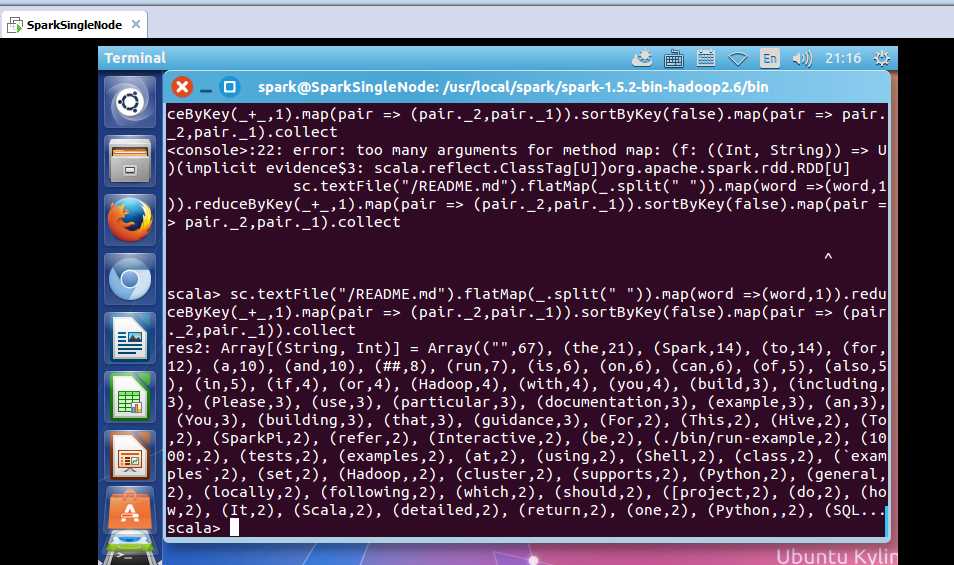
scala> sc.textFile("/README.md").flatMap(_.split(" ")).map(word =>(word,1)).reduceByKey(_+_,1).map(pair => (pair._2,pair._1)).sortByKey(false).map(pair => (pair._2,pair._1)).collect
res2: Array[(String, Int)] = Array(("",67), (the,21), (Spark,14), (to,14), (for,12), (a,10), (and,10), (##,8), (run,7), (is,6), (on,6), (can,6), (of,5), (also,5), (in,5), (if,4), (or,4), (Hadoop,4), (with,4), (you,4), (build,3), (including,3), (Please,3), (use,3), (particular,3), (documentation,3), (example,3), (an,3), (You,3), (building,3), (that,3), (guidance,3), (For,2), (This,2), (Hive,2), (To,2), (SparkPi,2), (refer,2), (Interactive,2), (be,2), (./bin/run-example,2), (1000:,2), (tests,2), (examples,2), (at,2), (using,2), (Shell,2), (class,2), (`examples`,2), (set,2), (Hadoop,,2), (cluster,2), (supports,2), (Python,2), (general,2), (locally,2), (following,2), (which,2), (should,2), ([project,2), (do,2), (how,2), (It,2), (Scala,2), (detailed,2), (return,2), (one,2), (Python,,2), (SQL...
scala>
则,可看出,是sortByKey(false)是按key排序且降序
sortByKey源码
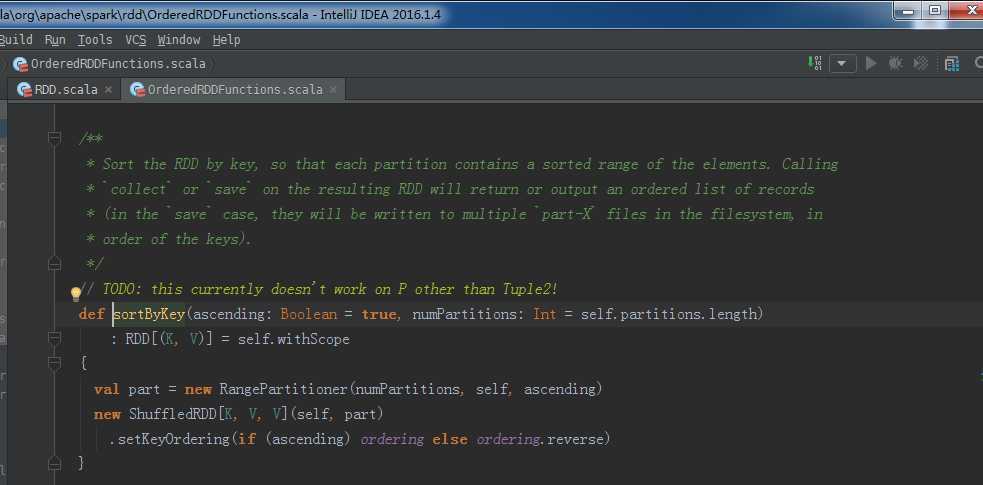
/**
* Sort the RDD by key, so that each partition contains a sorted range of the elements. Calling
* `collect` or `save` on the resulting RDD will return or output an ordered list of records
* (in the `save` case, they will be written to multiple `part-X` files in the filesystem, in
* order of the keys).
*/
// TODO: this currently doesn‘t work on P other than Tuple2!
def sortByKey(ascending: Boolean = true, numPartitions: Int = self.partitions.length)
: RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope
{
val part = new RangePartitioner(numPartitions, self, ascending)
new ShuffledRDD[K, V, V](self, part)
.setKeyOrdering(if (ascending) ordering else ordering.reverse)
}
由此,可看出,一旦排序,则产生ShuffledRDD。
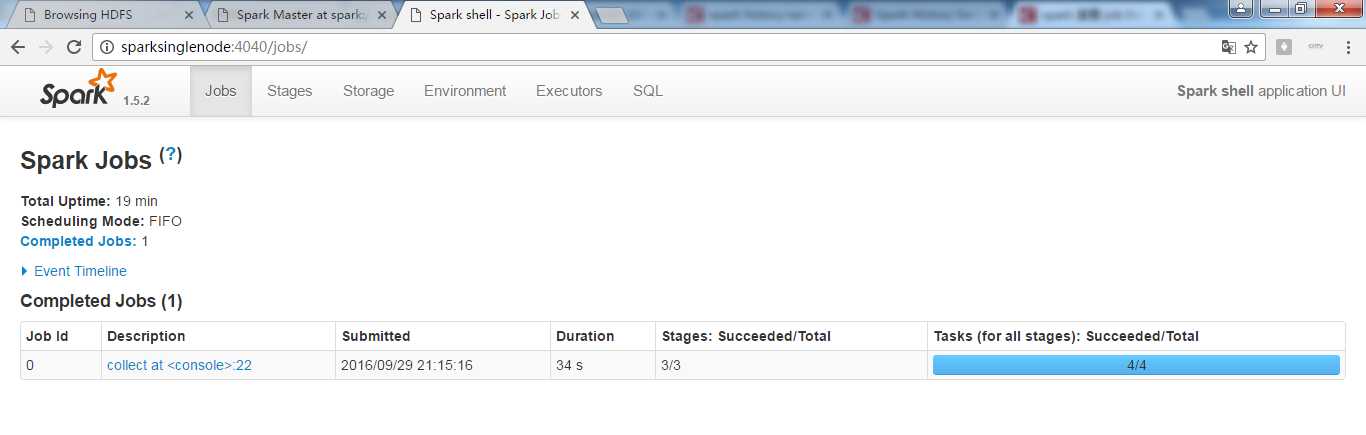
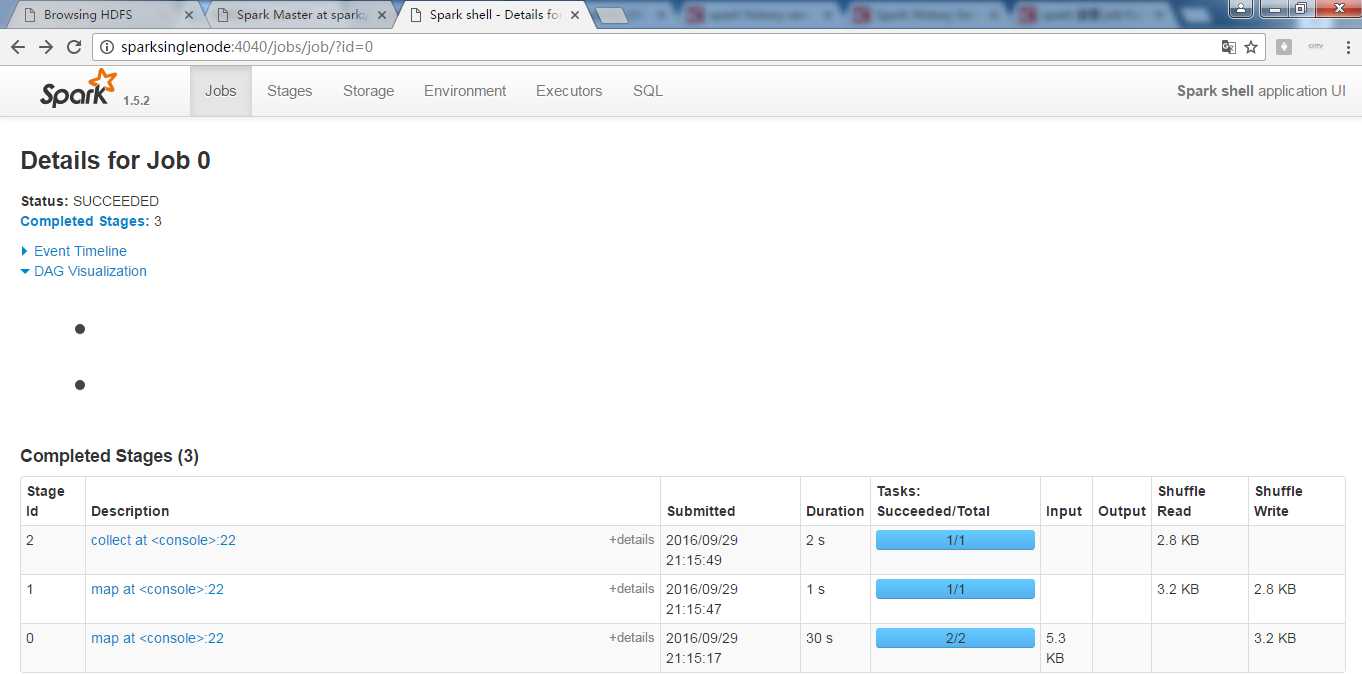
为什么我的是没显示出来?
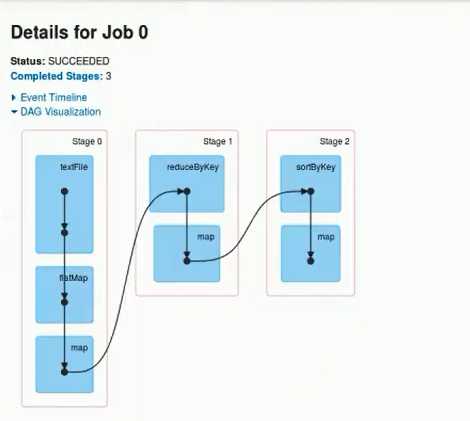
rangPartition是怎么排序的呢?
好的,基础排序算法实战至此。
2、二次排序算法实战
所谓,二次排序,就是指排序的时候考虑两个维度。
如,在第一列,按照降序排,第一列的key相同,那么,再怎么排呢?则,考虑第二列,按照降序排。即,用到了二次排序。
准备
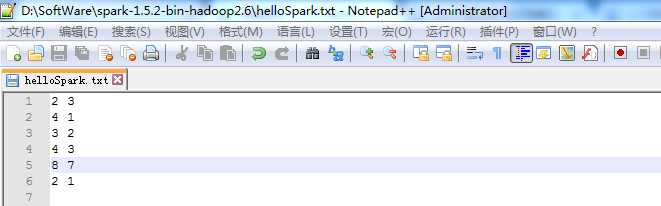
【数据文件Input】
2 3
4 1
3 2
4 3
8 7
2 1
【运行结果Output】
2 1
2 3
3 2
4 1
4 3
8 7
如果是去大公司的话,则要掌握,5个维度,甚至8个维度,而不是才2个维度而已。加油!zhouls。
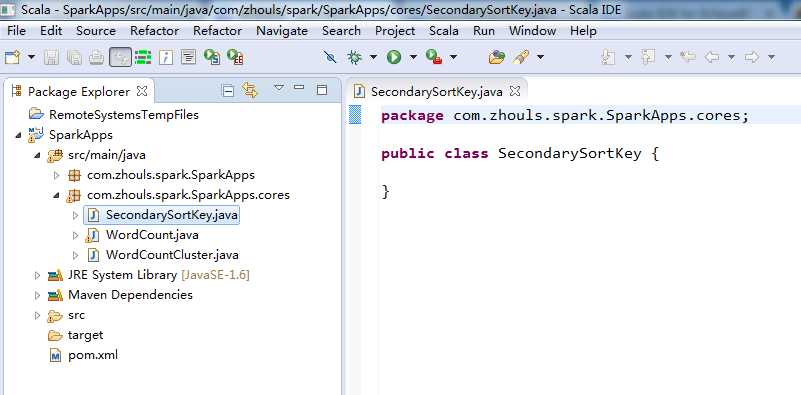
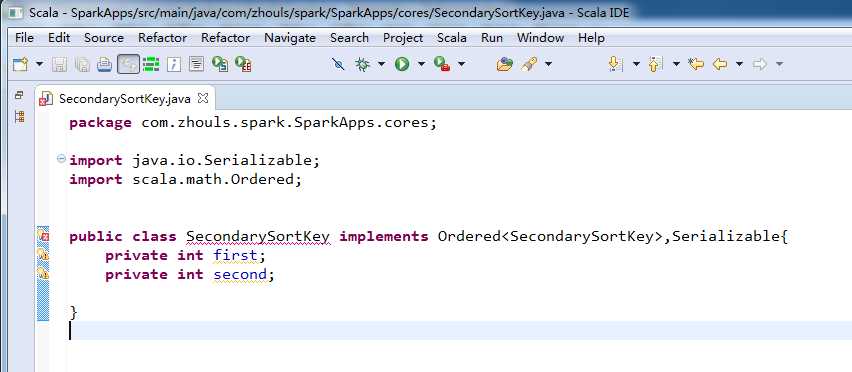
这里,就用,Scala IDE for Eclipse,来写,

SecondarySortKey.java
package com.zhouls.spark.SparkApps.cores;
import java.io.Serializable;
import scala.math.Ordered;
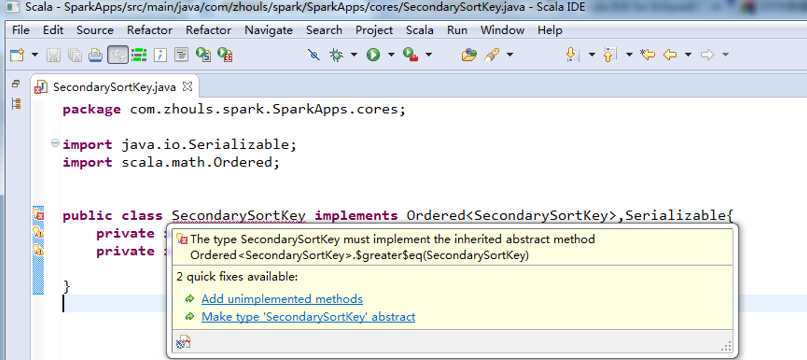
public class SecondarySortKey implements Ordered<SecondarySortKey>,Serializable{
private int first;
private int second;
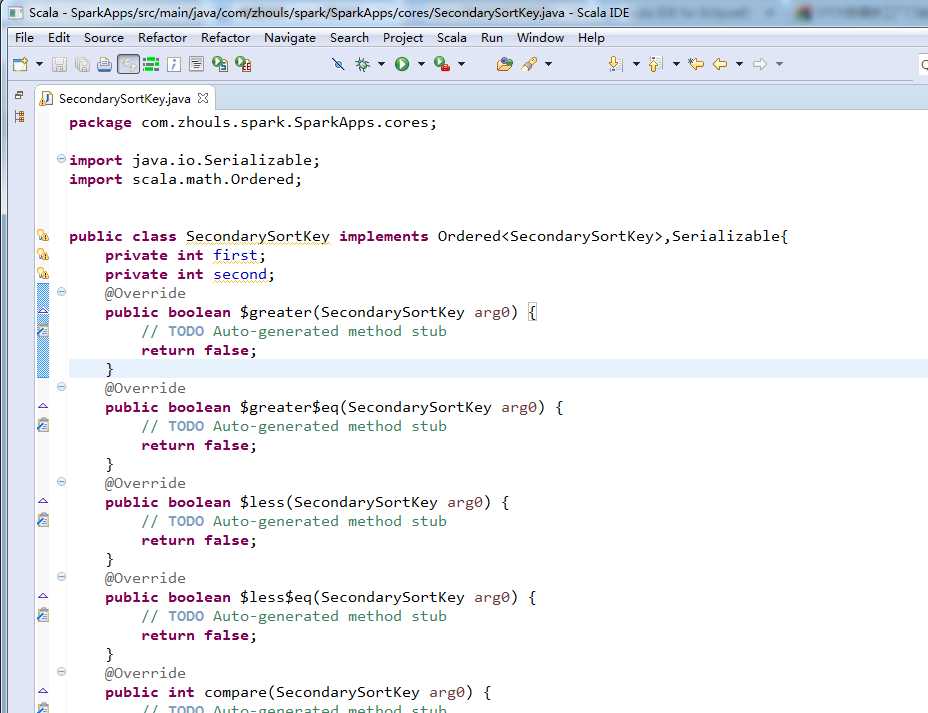
@Override
public boolean $greater(SecondarySortKey arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean $greater$eq(SecondarySortKey arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean $less(SecondarySortKey arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean $less$eq(SecondarySortKey arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
@Override
public int compare(SecondarySortKey arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(SecondarySortKey arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
}
然后,修改成我们自己想要的。
最终的SecondarySortKey.java如下:
package com.zhouls.spark.SparkApps.cores;
import java.io.Serializable;
import scala.math.Ordered;
public class SecondarySortKey implements Ordered<SecondarySortKey>,Serializable{
private int first;
private int second;
//二次排序的公开构造器
public SecondarySortKey(int first,int second){
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
public boolean $greater(SecondarySortKey other) {
if(this.first>other.getFirst()){
return true;
}else if(this.first==other.getFirst()&&this.second>other.getSecond()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean $greater$eq(SecondarySortKey other) {
if(this.$greater(other)){
return true;
}else if(this.first==other.getFirst()&&this.second==other.getSecond()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean $less(SecondarySortKey other) {
if(this.first<other.getFirst()){
return true;
}else if(this.first==other.getFirst()&&this.second<other.getSecond()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean $less$eq(SecondarySortKey other) {
if(this.$less(other)){
return true;
}else if(this.first==other.getFirst()&&this.second==other.getSecond()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int compare(SecondarySortKey other) {
if(this.first-other.getFirst() !=0){
return this.first-other.getFirst();
}else{
return this.second-other.getSecond();
}
}
public int compareTo(SecondarySortKey other) {
if(this.first-other.getFirst() !=0){
return this.first-other.getFirst();
}else{
return this.second-other.getSecond();
}
}
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + first;
result = prime * result + second;
return result;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
SecondarySortKey other = (SecondarySortKey) obj;
if (first != other.first)
return false;
if (second != other.second)
return false;
return true;
}
public int getFirst() {
return first;
}
public void setFirst(int first) {
this.first = first;
}
public int getSecond() {
return second;
}
public void setSecond(int second) {
this.second = second;
}
}
继续。。。
参考 :
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4a7854d90102ws97.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zlslch/p/5921572.html