标签:
树的路径剖分算法
一.算法简介
树链剖分,计算机术语,指一种对树进行划分的算法,它先通过轻重边剖分将树分为多条链,保证每个点属于且只属于一条链,然后再通过数据结构(树状数组、SBT、SPLAY、线段树等)来维护每一条链。
首先引入一道例题:spoj375 QTREE
You are given a tree (an acyclic undirected connected graph) with N nodes, and edges numbered 1, 2, 3...N-1.
We will ask you to perfrom some instructions of the following form:
The first line of input contains an integer t, the number of test cases (t <= 20). t test cases follow.
For each test case:
There is one blank line between successive tests.
For each "QUERY" operation, write one integer representing its result.
Input: 1 3 1 2 1 2 3 2 QUERY 1 2 CHANGE 1 3 QUERY 1 2 DONE Output: 1 3
题目大意,给定一个节点数为N的树,支持以下两种操作
1).查询两个节点间路径上权值最大的边
2).修改某条边的权值。
对于模拟而言,本题数据较大会超时。本文介绍一种神奇的方法——树的路径剖分算法。
我们定义:
Size(U): 以该点为根的子树的节点数
Start(U):该点所在链的第一个节点
Pre(U):节点U的父亲节点
DFN(U):在DFS中该节点被搜索的次序
hv(U):节点U的重儿子
重儿子:Size较大的儿子
重边:父节点与重儿子的连边
重链:重边组成的一条链
对于每个节点,都要将他划分到一条链中,为了保证算法的高效,必须使这条链尽可能长。
一般使用启发式剖分,将Size较大的连在一条链,这条链是重链。
最终按照DFS序加入一个数组中,用线段树等数据结构维护查询即可。
性质 1: 如果 (U,V) 为轻边,则 Size(V) <= Size(U)/2
性质 2: 从根到某一点的路径上轻边的个数不大于 O(log N)
性质 3: 不超过O(logN)条重路径。
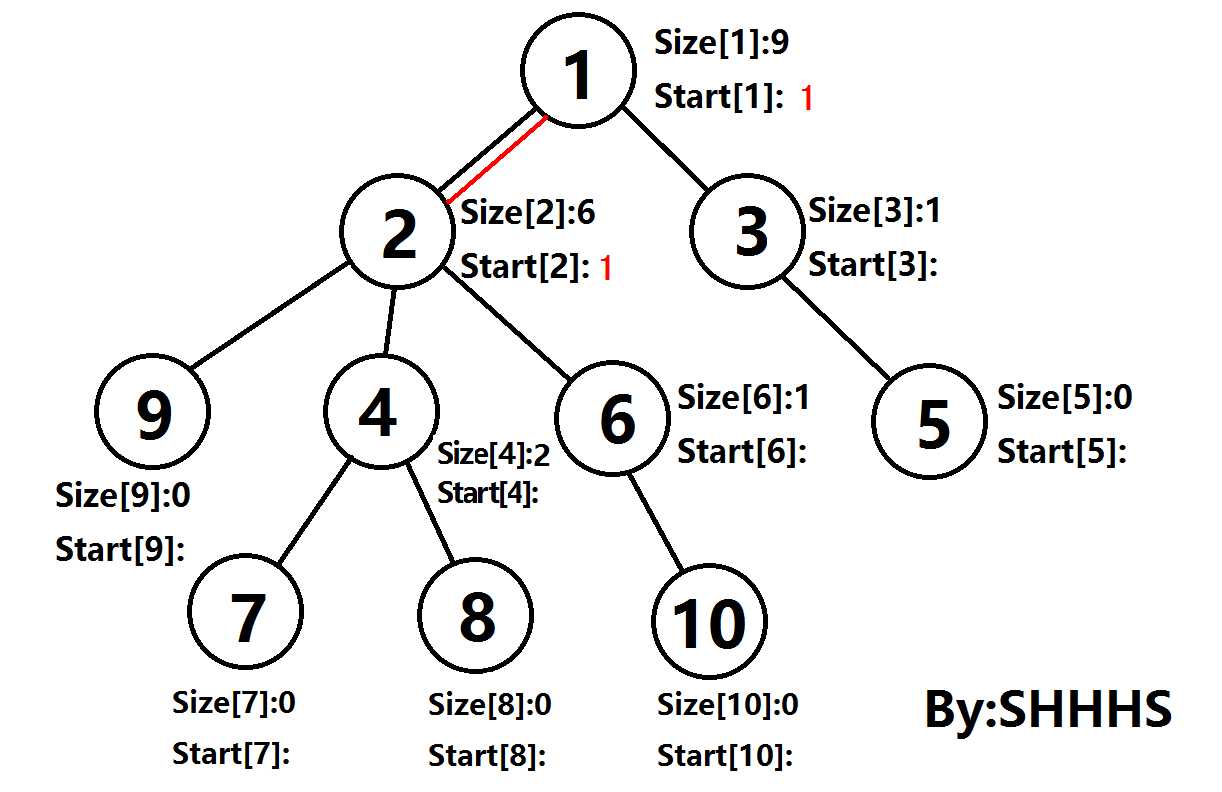
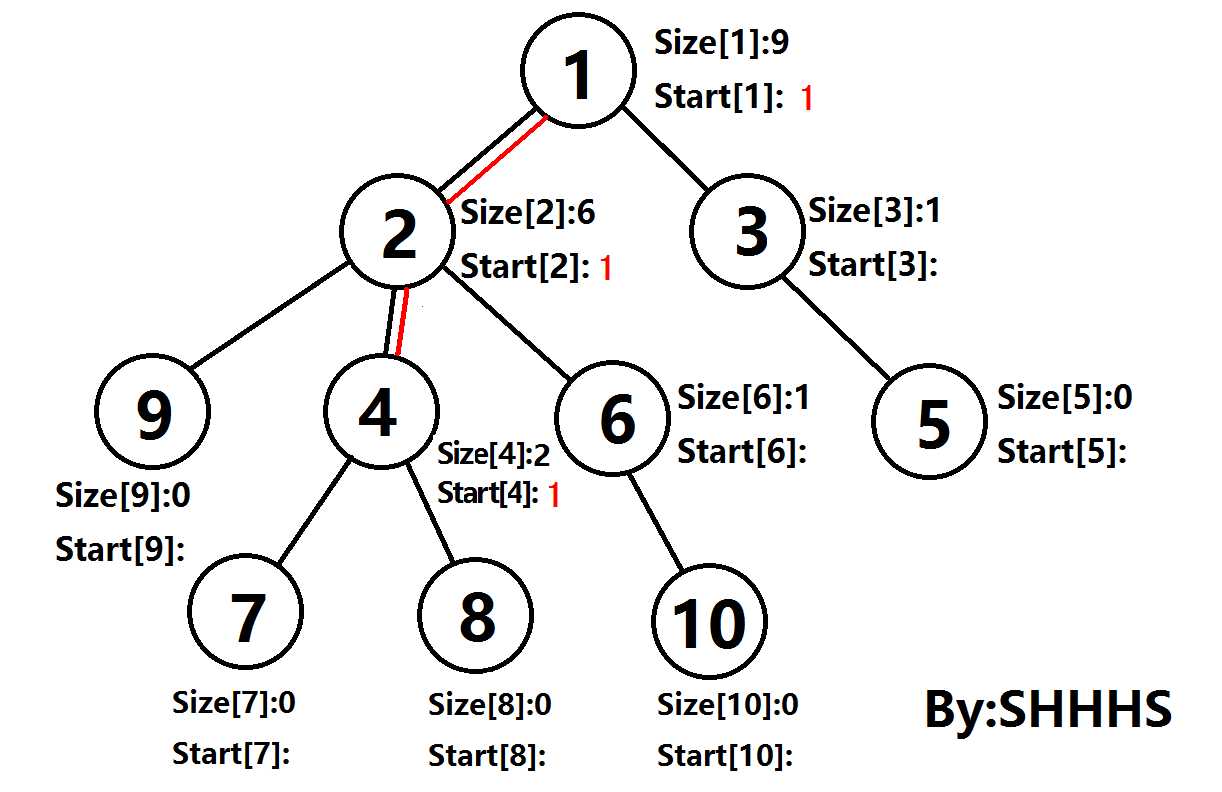
通过以上操作,我们将一棵树转化为若干条链。
以上的操作可以通过两遍DFS实现:
DFS_1:求出每个节点Size[],Pre[]
DFS_2:从根节点开始,对每个节点的重儿子优先DFS。通过这个操作,可以将在最大的子树中找到一条链。
对于其他节点而言,都以该点为根节点DFS,最终可以计算得到每条链的链头Start(U), DFN(U) .
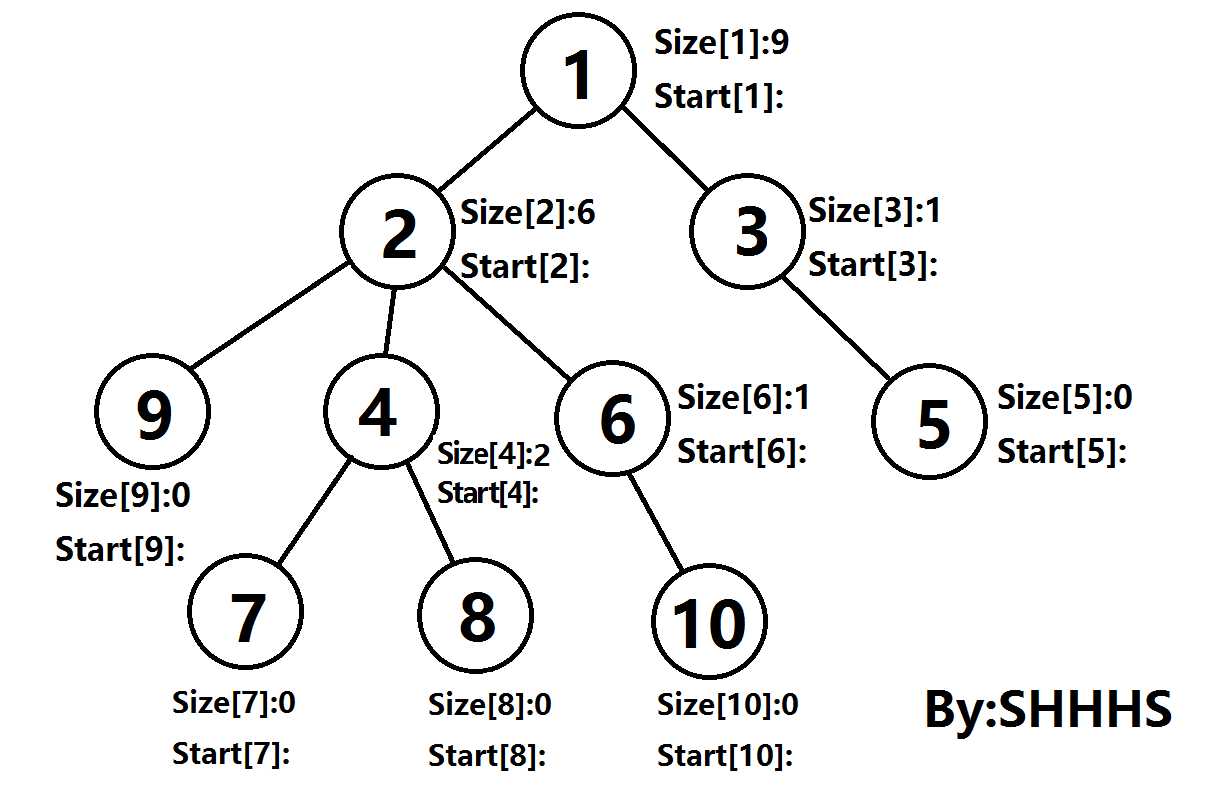
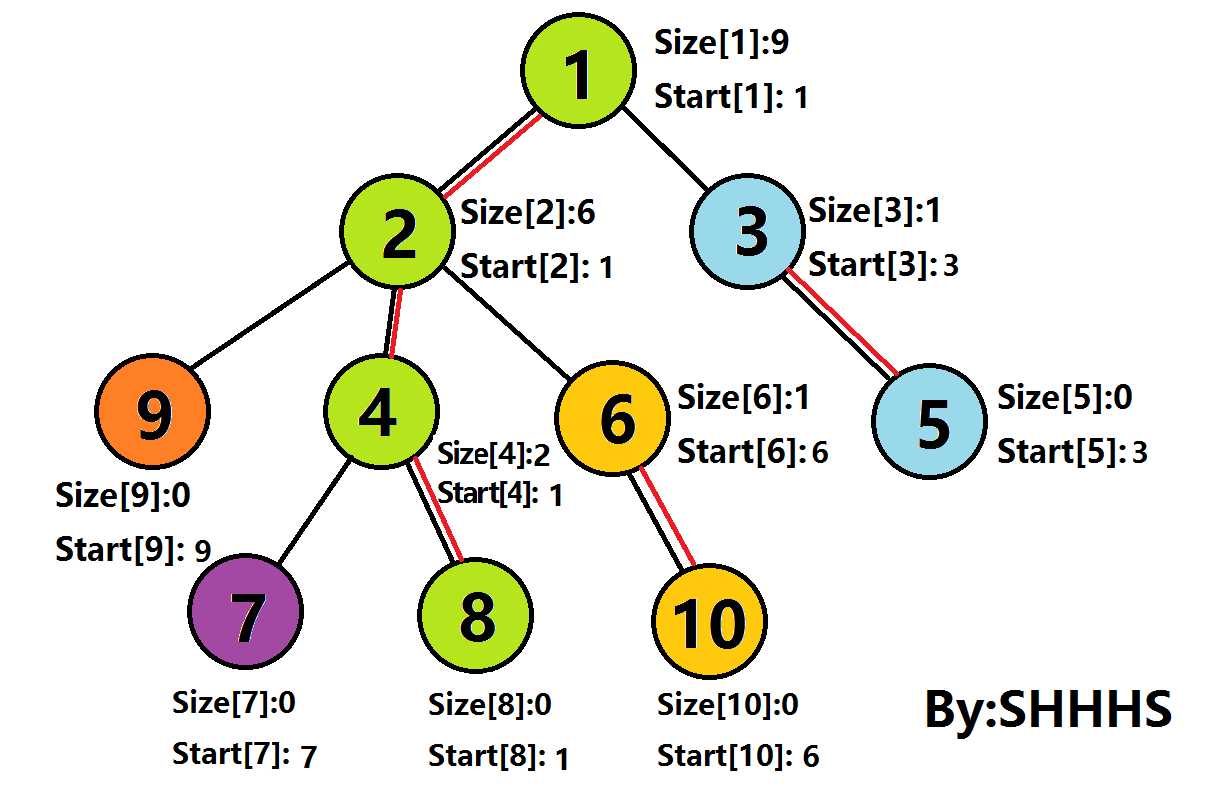
二.算法图示
在下图中
Size[U]:表示节点U的子树节点个数
Start[U]:树链的链头
节点旁的红色数字是DFS序
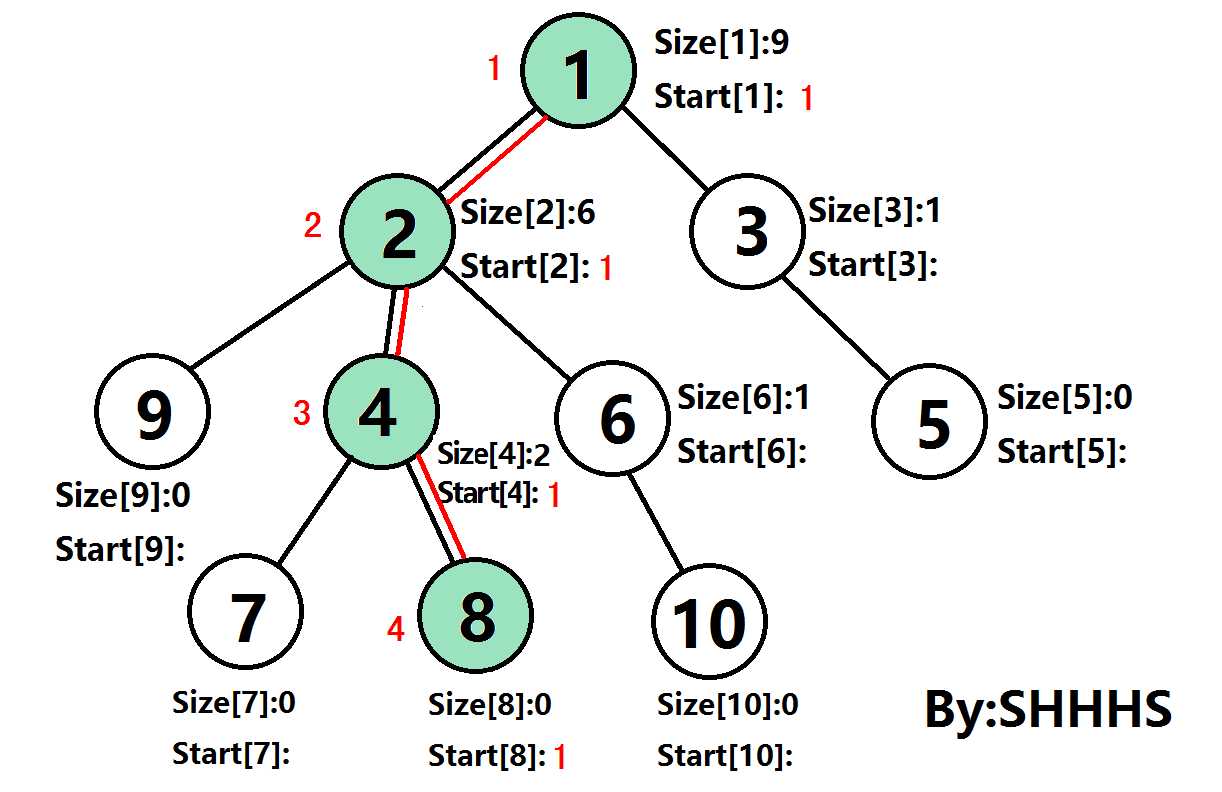
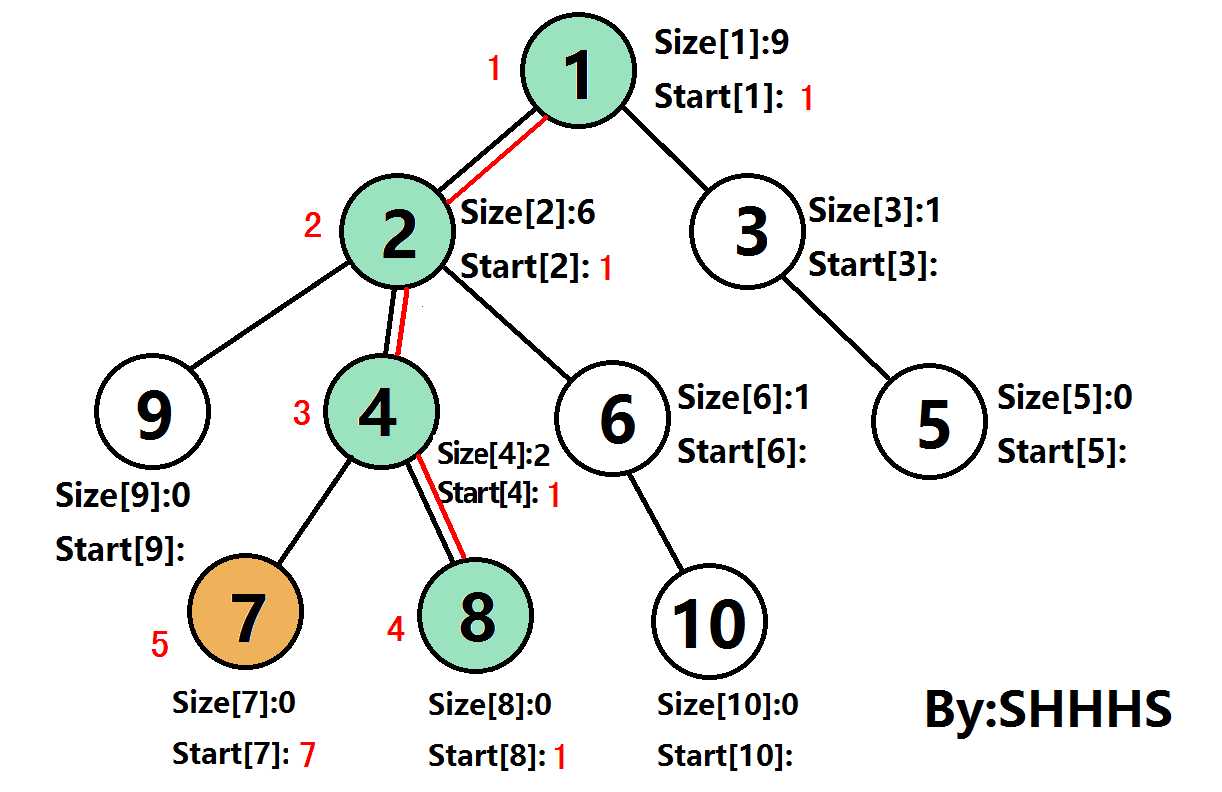
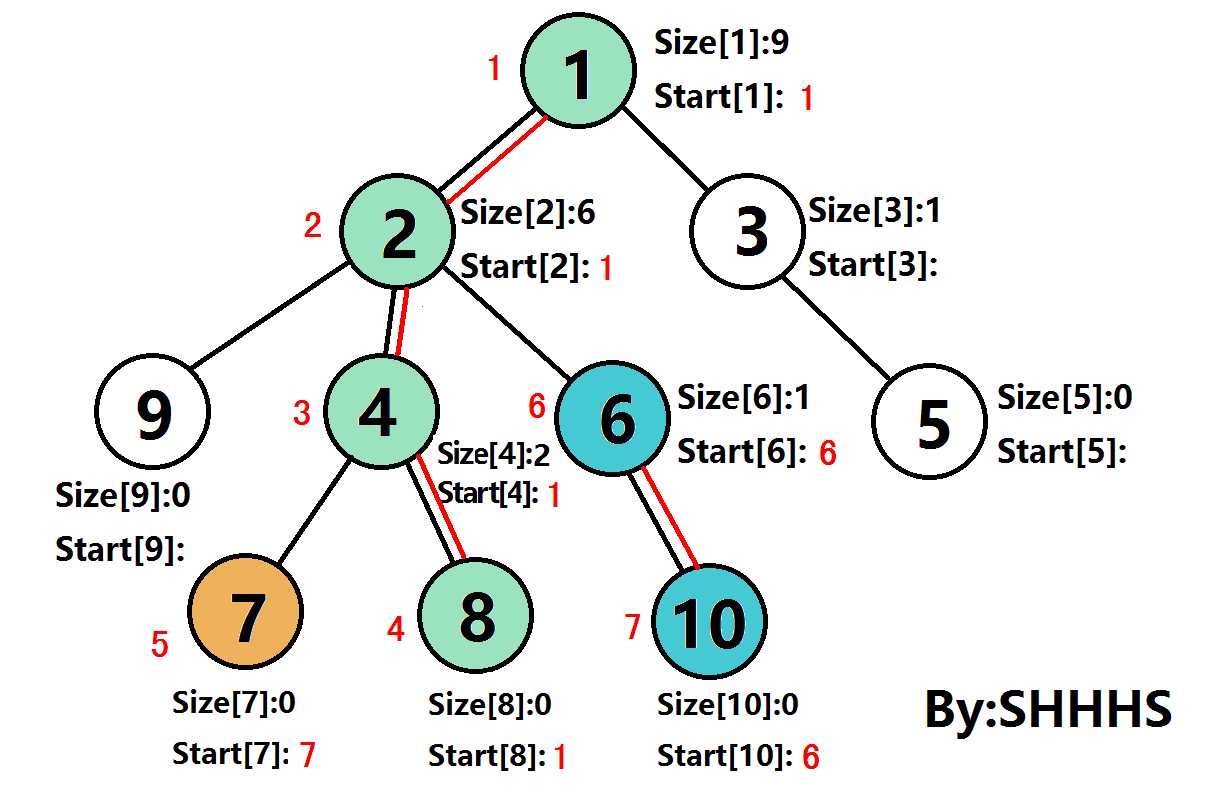
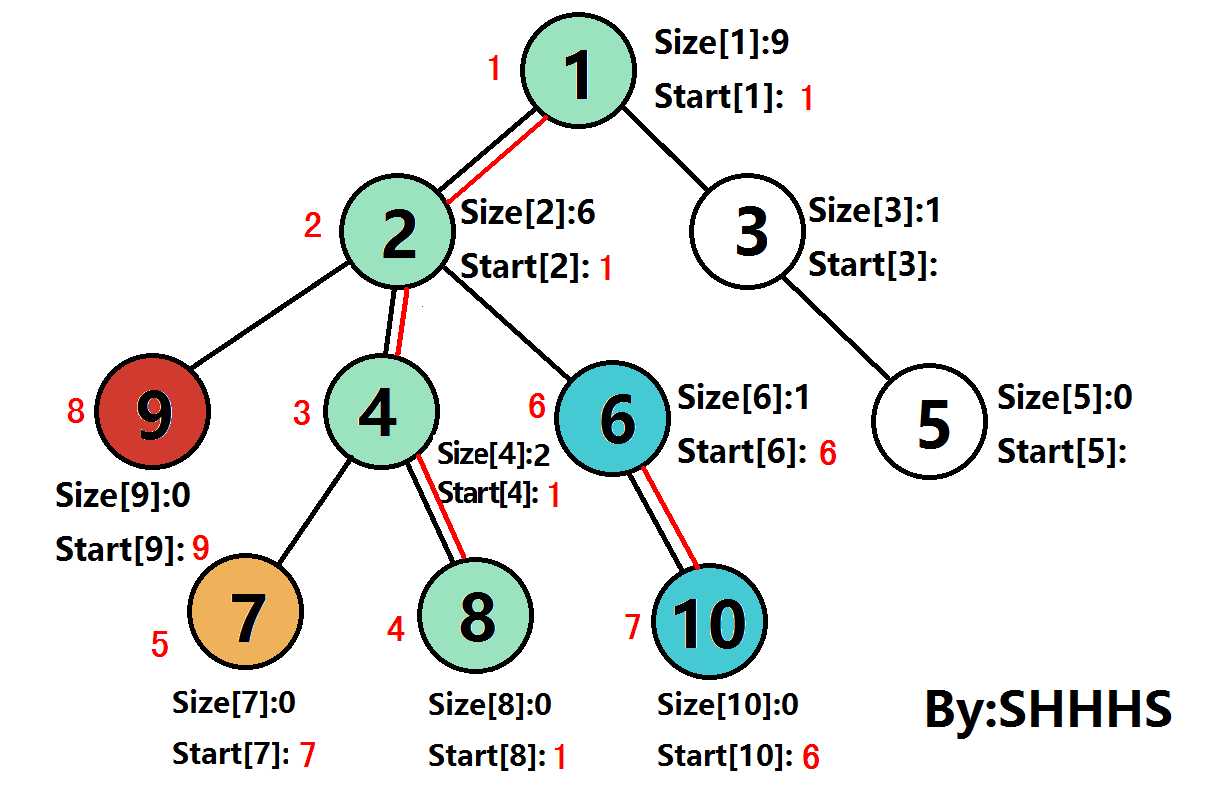
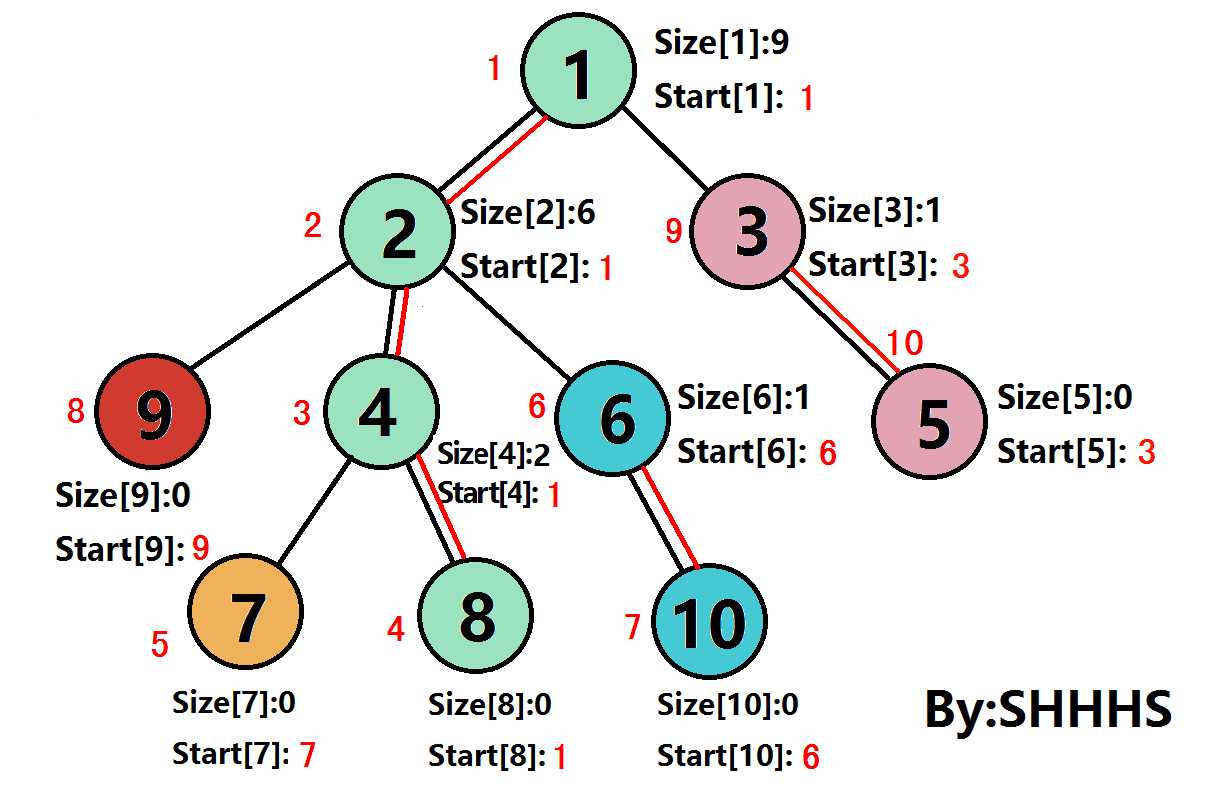
通过上述操作,可以将一颗树剖分成若干条链,再按照DFS序加入一个数组。此时,这棵树已经被转化为一个线性的区间问题,可以使用线段树,Splay Tree 等高效的数据结构解决这个问题。
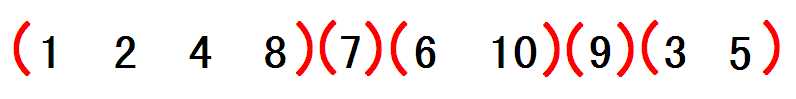
[ATTENTION]:树链剖分的目的是将高效的数据结构扩展到树上。
三.算法模板&注释:
核心代码如下:
QUERY ( x , y ) // 伪代码 while start[ x ] != start[ y ] if DFN[ start[ x ] ] > DFN[ start[ x ] ] then Query_min ( DFN[ start[ x ] ] , DFN[ x ] ) , x = pre[ x ] else Query_min ( DFN[ start[ y ] ] , DFN[ y ] ) , y = pre[ y ] Query_min ( DFN[ x ] , DFN[ y ] )
1 inline void Push_up ( const int i ) {tr[ i ].mintr = gmax(tr[ i<<1|1 ].mintr , tr[ i<<1 ].mintr );} 2 3 int INPUT ( ) {//读入优化 4 int x=0,f=1;char ch = getchar ( ); 5 while ( ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘){if(ch==‘-‘)f=-1;ch=getchar() ;} 6 while ( ch >=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘ ) {x = x*10+ch-‘0‘;ch = getchar( ) ;} 7 return x*f; 8 } 9 10 void Build_Tree ( int x , int y , int i ) {//建树 11 tr[ i ] . l = x ; tr[ i ] . r = y ; 12 if ( x==y && x==Root ) {tr[ i ].mintr = INF ;return;} 13 if ( x==y ){tr[ i ] . mintr = E_val[ rank[ x ] ] ;return ;} 14 else { 15 int mid = ( tr[ i ].l + tr[ i ].r ) >> 1 ; 16 Build_Tree ( x , mid , i<<1 ) ; 17 Build_Tree ( mid+1 , y , i<<1|1 ) ; 18 Push_up ( i ) ; 19 } 20 } 21 void Add_Edge ( const int _x , const int _y , const int _val ) {//建图 22 e[ ++cnt ].to = _y ; 23 e[ cnt ].val = _val ; 24 e[ cnt ].next = head[ _x ] ; 25 head[ _x ] = cnt ; 26 } 27 28 int Init_DFS ( const int x , const int father ) {//启发式树链剖分 29 int cnt_ = 1 , max_ = 0 ; 30 for ( int i=head[ x ] ; i ; i=e[ i ].next ) { 31 int temp = e[ i ].to ; 32 if ( temp==father ) continue ; 33 int _ = Init_DFS ( temp , x ) ; 34 if ( _ > max_ ) {max_ = _ ; hv[ x ] = temp ;} //hv该节点的重儿子 35 cnt_ +=_; 36 } 37 return cnt_ ;//返回节点个数 38 } 39 40 void DFS ( const int x , const int father ) { 41 if ( !start[ x ] ) start[ x ] = start[ father ] ; 42 DFN[ x ] = ++dfs_num ;//节点的DFS序 43 rank[ dfs_num ] = x ; //节点在DFN中的位置 44 if ( hv[ x ] ) DFS ( hv[ x ] , x ) ;//优先DFS重儿子 45 for ( int i=head[ x ] ; i ; i =e[ i ].next ) { 46 E_val[ e[ i ].to ] = e[ i ] .val ; 47 if ( e[ i ].to != hv[ x ] && e[i].to != father ) { 48 int temp = e[ i ].to ; 49 start[ temp ] = temp ;//链头 50 pre [ temp ] = x ;// 父节点 51 DFS ( temp , x ) ; 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 long long Query_Tree ( int q , int w , int i ) {//查询树 57 if ( q <= tr[i].l && w >= tr[i].r ) return tr[i].mintr; 58 else{ 59 long long mid = (tr[i].l + tr[i].r) >> 1; 60 if( q > mid ) { 61 return Query_Tree ( q , w , i << 1 | 1); 62 } 63 else if (w <= mid ) { 64 return Query_Tree ( q , w , i << 1); 65 } 66 else 67 { 68 return gmax(Query_Tree ( q , w , i << 1) , Query_Tree ( q , w , i << 1 | 1 )); 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 73 void Min_Path ( int x , int y ) {//找路径上权值最大的边 74 Ans = INF ; 75 int px = x , py = y ; 76 while ( start[ px ] != start[ py ] ) { 77 if ( DFN[ start[ px ] ] > DFN[ start[ py ] ] ) { 78 Ans = gmax ( Ans , Query_Tree ( DFN[start[ px ]] , DFN[px] , 1 ) ) ; 79 px = pre[ start[ px ] ] ; 80 } 81 else { 82 Ans = gmax ( Ans , Query_Tree ( DFN[start[ py ]] , DFN[py] , 1 ) ) ; 83 py = pre[ start[ py ] ] ; 84 } 85 86 } 87 if(px==py)return ; 88 Ans = gmax ( Ans , Query_Tree ( DFN[px] + 1, DFN[py] , 1 )); 89 } 90 91 92 void DEBUG_ ( int n ) { 93 for ( int i=1 ; i<=n ; ++i ) { 94 printf ("%d:%d %d %d\n",i,DFN[ i ] ,E_val[ i ],rank[ i ] , E_val[ rank[ i ] ]) ; 95 } 96 } 97 98 void Update_Tree ( int p , int val , int i ) { 99 if ( tr[ i ].l == tr[ i ].r && tr[ i ].l == p ) { 100 tr[ i ].mintr = val ; 101 return ; 102 } 103 else { 104 int mid = ( tr[ i ].l + tr [ i ].r ) >> 1 ; 105 if ( p>mid ) { 106 Update_Tree ( p , val , i<<1|1 ) ; 107 } 108 else if ( p<=mid ) { 109 Update_Tree ( p , val , i<<1 ) ; 110 } 111 tr[ i ].mintr = gmax( tr[ i<<1|1 ].mintr , tr[ i<<1 ].mintr ) ; 112 } 113 114 } 115 void Init_all ( ) { 116 dfs_num = 0 ; cnt = 0 ; 117 memset ( ind , 0 , sizeof ( ind ) ) ; 118 memset ( hv , 0 , sizeof ( hv ) ) ; 119 memset ( start , 0 , sizeof ( start ) ) ; 120 memset ( head , 0 , sizeof ( head ) ) ; 121 memset ( pre , 0 , sizeof ( pre ) ) ; 122 memset ( rank , 0 , sizeof ( rank ) ) ; 123 memset ( pre , 0 , sizeof ( pre ) ) ; 124 } 125 int main ( ) { 126 int N , M ; 127 char s[ 50 ] ; 128 int T = INPUT ( ) ; 129 while ( T-- ) { 130 Init_all ( ) ; 131 N = INPUT ( ) ; 132 for ( int i=1 ; i<=N-1 ; ++i ) { 133 int _x , _y ,_val ; 134 _x= INPUT( );_y= INPUT( );_val= INPUT( );//scanf ( "%d%d%d" ,&_x , &_y ,&_val ) ; 135 Node[ i ].x = _x ; Node[ i ].y = _y ; 136 Add_Edge ( _x , _y , _val ) ; 137 ++ ind[ _y ] ;//记录入度 138 } 139 for ( int i=1 ; i<=N ; ++i ) if ( !ind[ i ] ) {Root = i ; break ;}//入度为0即为根节点 140 141 Init_DFS ( Root , Root ) ;//第一遍DFS 142 start[ Root ] = Root ; 143 DFS ( Root , Root ) ;//第二遍DFS 144 145 Build_Tree ( 1 , dfs_num , 1 ) ;//建树 146 //DEBUG_ ( N ) ; 147 148 while ( true ) { 149 scanf ("%s",s) ; 150 if ( s[ 0 ]==‘D‘ ) break ; 151 else if ( s[ 0 ]==‘Q‘){ 152 int u , v ; 153 u =INPUT ( ) ; v = INPUT ( ) ;//scanf ( "%d%d" , &u , &v ) ; 154 Min_Path( u , v ) ; 155 printf ( "%d\n" , Ans ) ; 156 } 157 else if ( s[ 0 ]==‘C‘ ){ 158 int tmp , _val ; 159 tmp =INPUT ( ) ; _val = INPUT ( ) ;//scanf ( "%d%d" , &tmp , &_val ) ; 160 Update_Tree ( DFN[ Node[tmp].y ] , _val , 1 ) ; 161 } 162 } 163 } 164 return 0 ; 165 }
2016-09-30 10:47:46
(完)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shadowland/p/5917635.html